Adoption and Decline of Programming LanguagesWhat Drives Programming Trends
Published on: 2025-11-21
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Adoption and Decline of Programming Languages
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
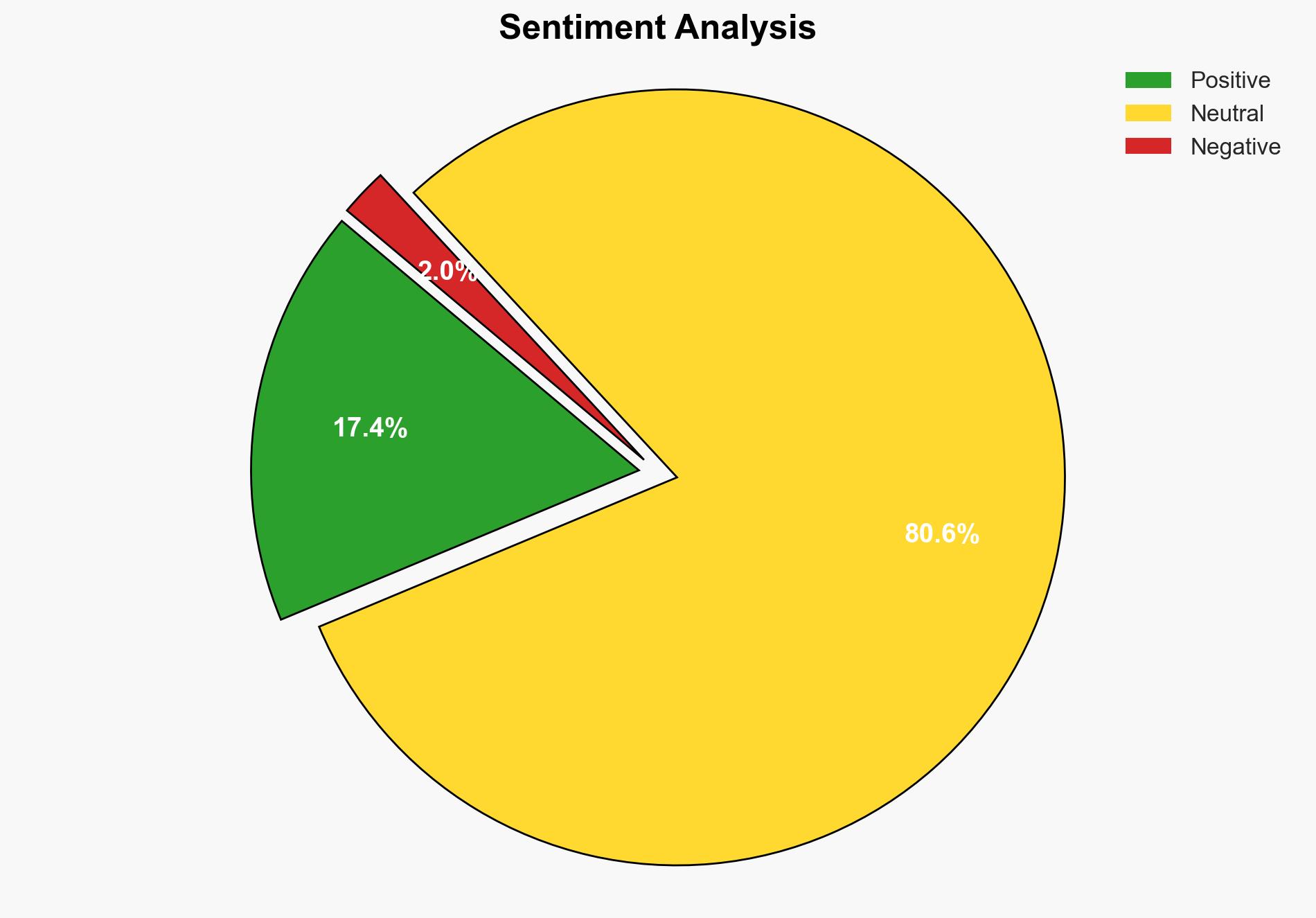
The most supported hypothesis is that the adoption and decline of programming languages are driven primarily by industry demands and community support rather than intrinsic language features. Confidence Level: Moderate. Recommended action includes fostering community ecosystems and aligning language development with emerging industry trends.
2. Competing Hypotheses
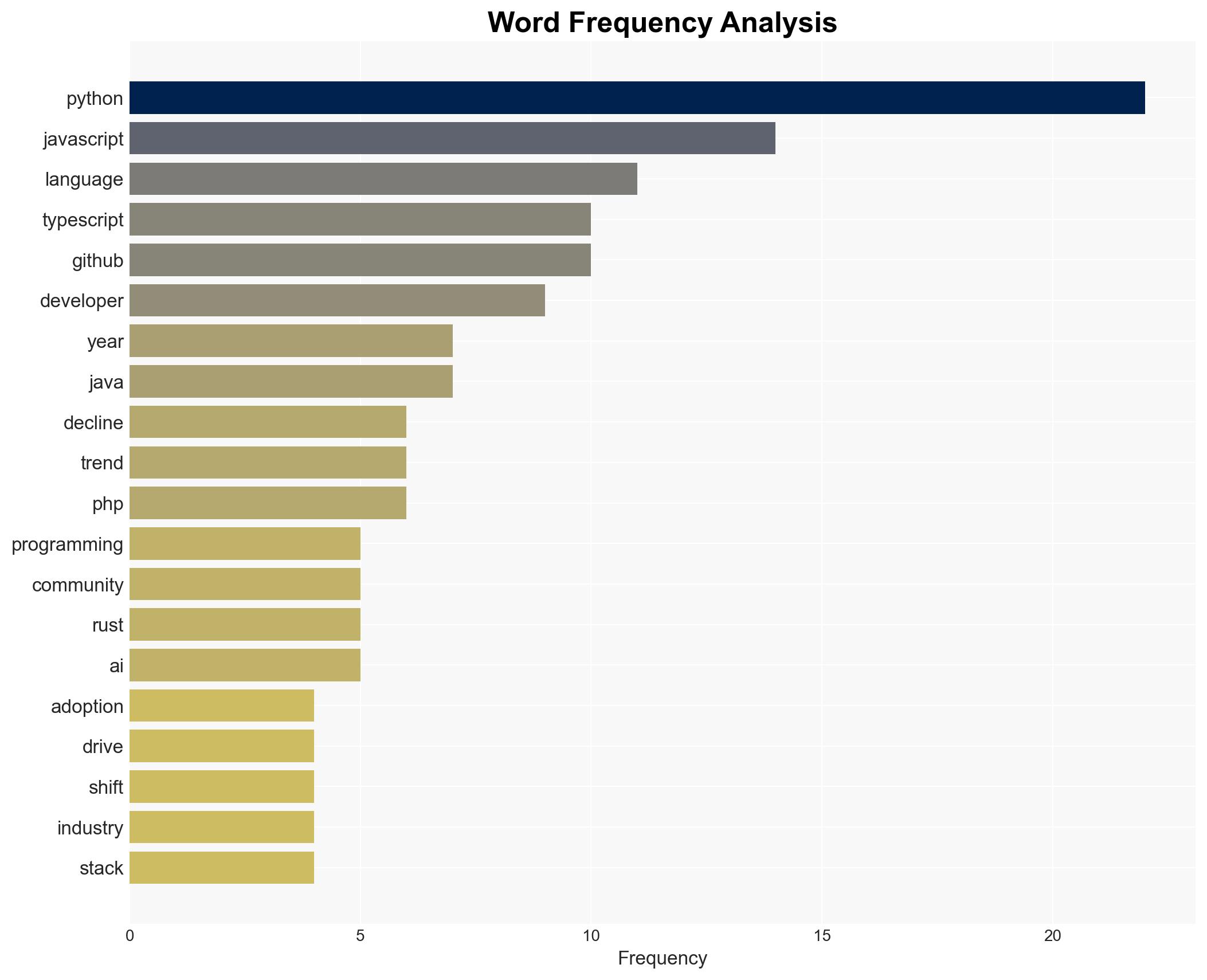
Hypothesis 1: The adoption and decline of programming languages are primarily driven by industry demands and the strength of community ecosystems. This hypothesis is supported by evidence of Python’s popularity in AI and data science due to industry needs, and TypeScript’s rise due to demand for robust typing in web development.
Hypothesis 2: The intrinsic features of programming languages, such as syntax and performance, are the primary drivers of their adoption and decline. While features like Python’s syntax and Rust’s performance are noted, the evidence suggests these are secondary to broader industry trends and community support.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely as it aligns with observed trends in language popularity shifts, which correlate with industry needs and community activity rather than just language features.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that industry needs and community support are accurately reflected in language adoption metrics. There is an assumption that the data from sources like Stack Overflow and GitHub accurately represent global trends.
Red Flags: Potential bias in data collection methodologies from platforms like GitHub and Stack Overflow. Deception indicators include over-reliance on self-reported surveys which may not capture the full spectrum of programming language use.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The shift towards languages like Python and TypeScript indicates a potential risk for businesses heavily invested in declining languages like PHP. This could lead to increased costs for retraining and system upgrades. Additionally, the rise of performance-driven languages like Rust suggests a strategic shift in industries requiring high security and scalability, which could impact competitive dynamics in tech sectors.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Encourage investment in community support and educational resources for emerging languages to ensure alignment with industry trends.
- Monitor industry trends closely to anticipate shifts in language popularity and adjust development strategies accordingly.
- Best-case scenario: Businesses adapt quickly to language trends, leveraging new technologies for competitive advantage.
- Worst-case scenario: Failure to adapt leads to obsolescence and increased operational costs.
- Most-likely scenario: Gradual adaptation with some transitional challenges, but overall alignment with industry trends.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Entities such as GitHub and Stack Overflow are critical in providing data on language trends. No specific individuals are highlighted in the provided text.
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, Programming Trends, Industry Demand, Community Ecosystem
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us