The breaches everyone gets hit by and how to stop them
Published on: 2025-11-25
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report:
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
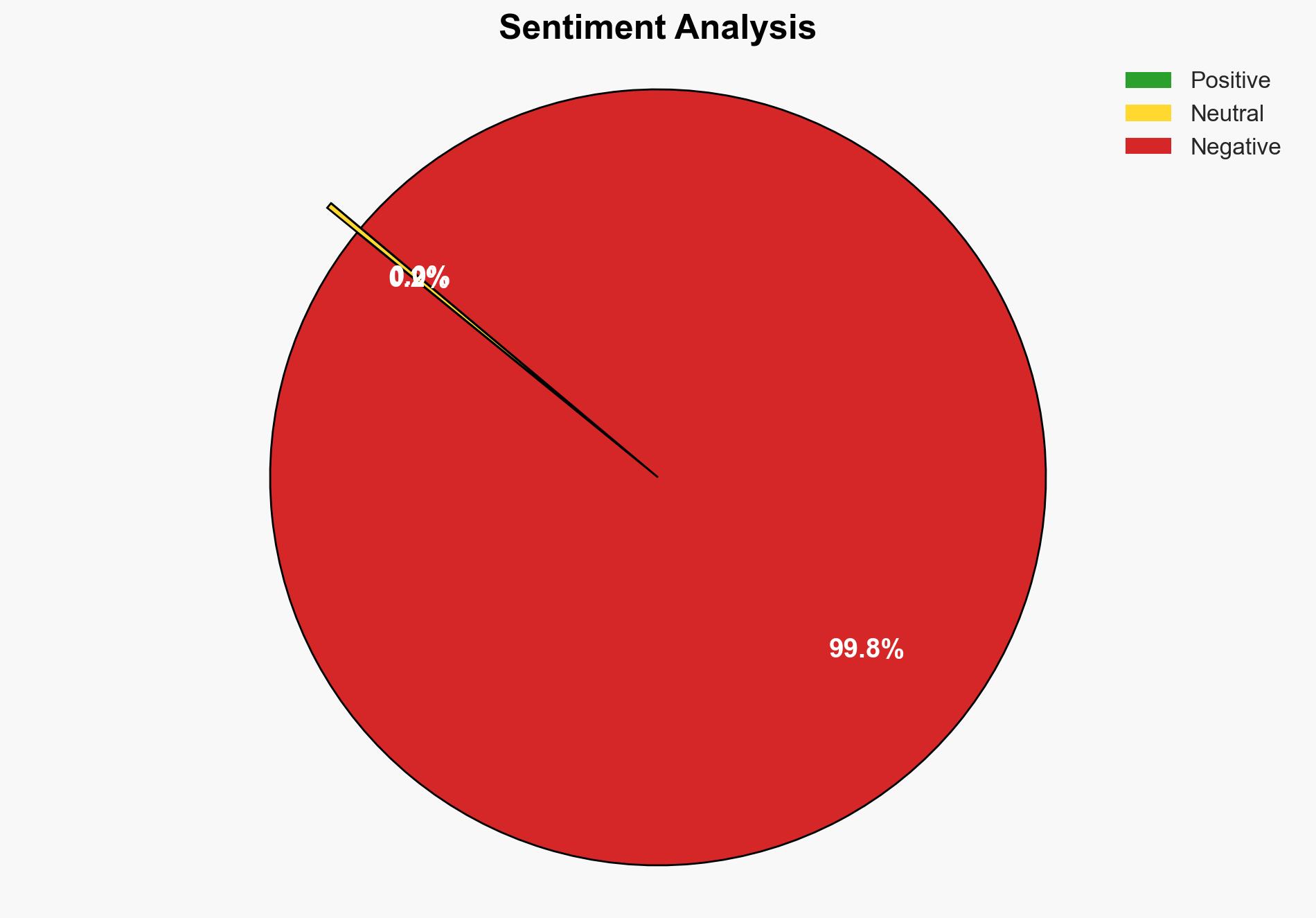
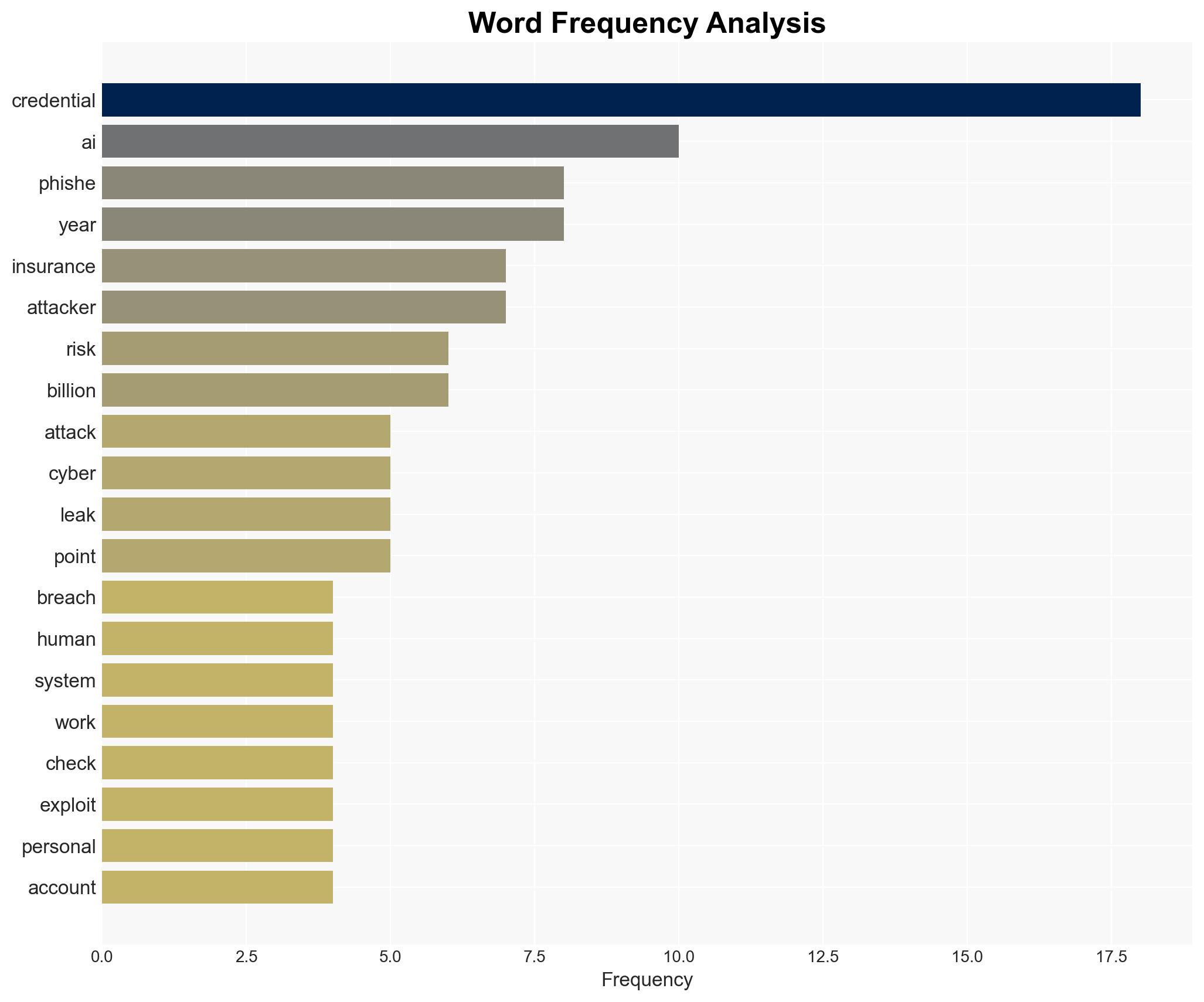
The most supported hypothesis is that credential abuse and phishing remain the predominant methods of cyber breaches due to their low cost, scalability, and effectiveness. A prevention-first strategy focusing on strengthening security fundamentals, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and regular patching, is recommended. Confidence Level: High.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: Credential abuse and phishing are the primary vectors for cyber breaches due to their cost-effectiveness and scalability.
Hypothesis 2: Advanced persistent threats (APTs) and zero-day exploits are the main drivers of significant cyber breaches, overshadowing credential abuse and phishing.
Assessment: Hypothesis 1 is more likely given the evidence of consistent credential leaks and the effectiveness of phishing campaigns. Hypothesis 2, while possible, is less supported by the frequency and scale of such attacks compared to credential-based breaches.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: Credential leaks will continue to rise, and phishing tactics will evolve with AI advancements. Organizations may not prioritize basic security measures over more advanced but less frequent threats.
Red Flags: Over-reliance on cyber insurance as a substitute for robust security measures. Potential deception in the sophistication of phishing campaigns due to AI-generated content.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The persistence of credential abuse and phishing as primary breach vectors poses significant risks, including increased ransomware attacks and data theft. The integration of AI in phishing campaigns could escalate the threat landscape, leading to more sophisticated and widespread attacks. Economically, this could result in higher costs for businesses in terms of both direct losses and increased insurance premiums. Politically, the exploitation of personal and professional identities could lead to misinformation and reputational damage.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Implement and enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) across all systems.
- Regularly update and patch systems to mitigate vulnerability exploitation.
- Enhance employee training to recognize and report phishing attempts.
- Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that includes coordination with cyber insurance providers.
- Best-case scenario: Organizations adopt a prevention-first strategy, significantly reducing breach incidents.
- Worst-case scenario: AI-driven phishing campaigns lead to a surge in successful breaches, overwhelming existing defenses.
- Most-likely scenario: Credential abuse and phishing continue to dominate, with incremental improvements in defense strategies.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Ross Haleliuk (Venture Security Expert)
Check Point (Cybersecurity Company)
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, Credential Abuse, Phishing, AI in Cybersecurity, Ransomware
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us