The new battlefield where capital regulation and technology collide
Published on: 2025-11-25
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report:
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
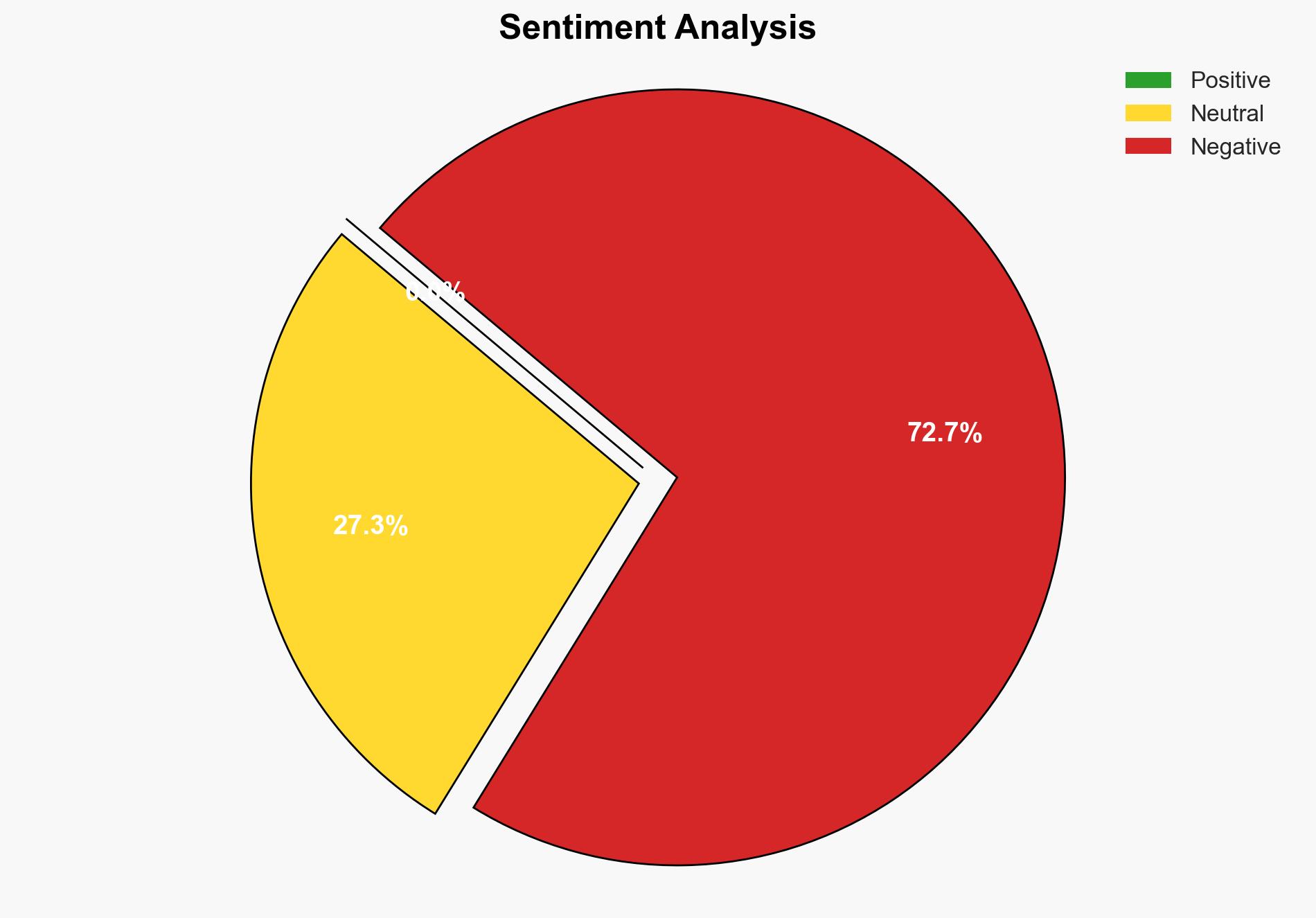
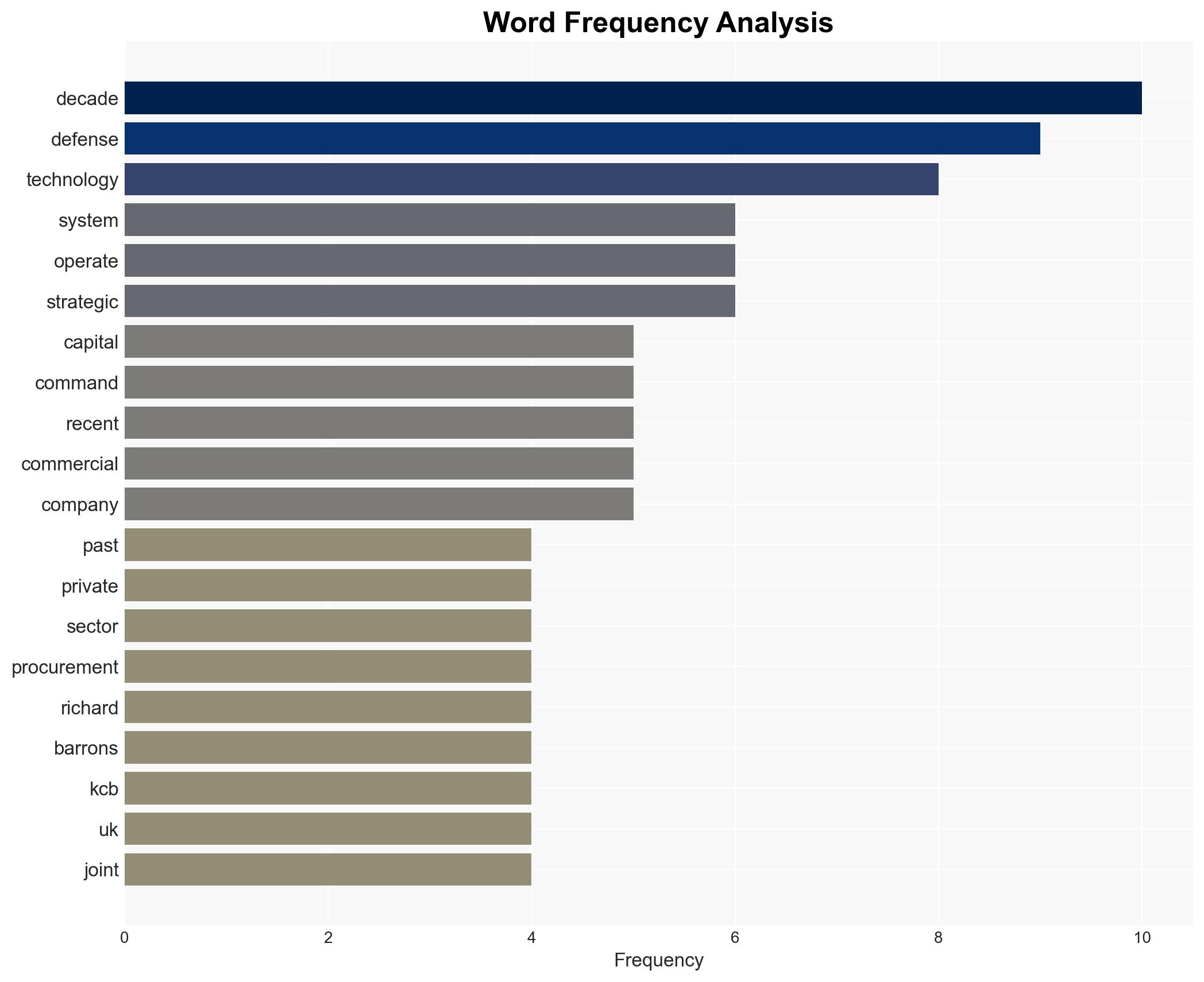
The intersection of capital regulation and technology in the defense sector is reshaping the landscape of military procurement and innovation. The most supported hypothesis suggests that private capital and agile technology firms will increasingly dominate defense innovation, challenging traditional defense contractors. Confidence in this assessment is moderate due to regulatory uncertainties and geopolitical factors. Recommended actions include enhancing regulatory frameworks to facilitate innovation while ensuring national security.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: Private capital and technology firms will outpace traditional defense contractors in innovation and procurement due to their agility and ability to rapidly iterate technologies.
Hypothesis 2: Traditional defense contractors will maintain dominance by adapting to new technologies and leveraging established relationships with governments and military entities.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely given the current trend of increased private capital inflows and the ability of tech firms to quickly adapt to operational feedback. However, the entrenched position and resources of traditional contractors cannot be discounted.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that regulatory environments will adapt to support innovation without compromising national security. Another assumption is that private capital will continue to flow into the defense sector.
Red Flags: Potential regulatory bottlenecks and geopolitical tensions could disrupt capital flows and technology integration. There is also a risk of over-reliance on commercial technologies that may not meet military-grade requirements.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The shift towards private capital and technology firms in defense could lead to a more fragmented industrial base, increasing the risk of cyber vulnerabilities and intellectual property theft. Politically, this could strain relationships between governments and traditional defense contractors. Economically, it may lead to increased competition and innovation but also potential market volatility.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Enhance regulatory frameworks to balance innovation with security, ensuring that new technologies are integrated safely into defense systems.
- Encourage partnerships between traditional contractors and tech firms to leverage strengths and mitigate risks.
- Best-case scenario: Seamless integration of new technologies leads to enhanced military capabilities and economic growth.
- Worst-case scenario: Regulatory failures and geopolitical tensions lead to fragmented defense capabilities and increased security risks.
- Most-likely scenario: A gradual shift towards a hybrid model where both traditional and new players coexist, with ongoing regulatory adjustments.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
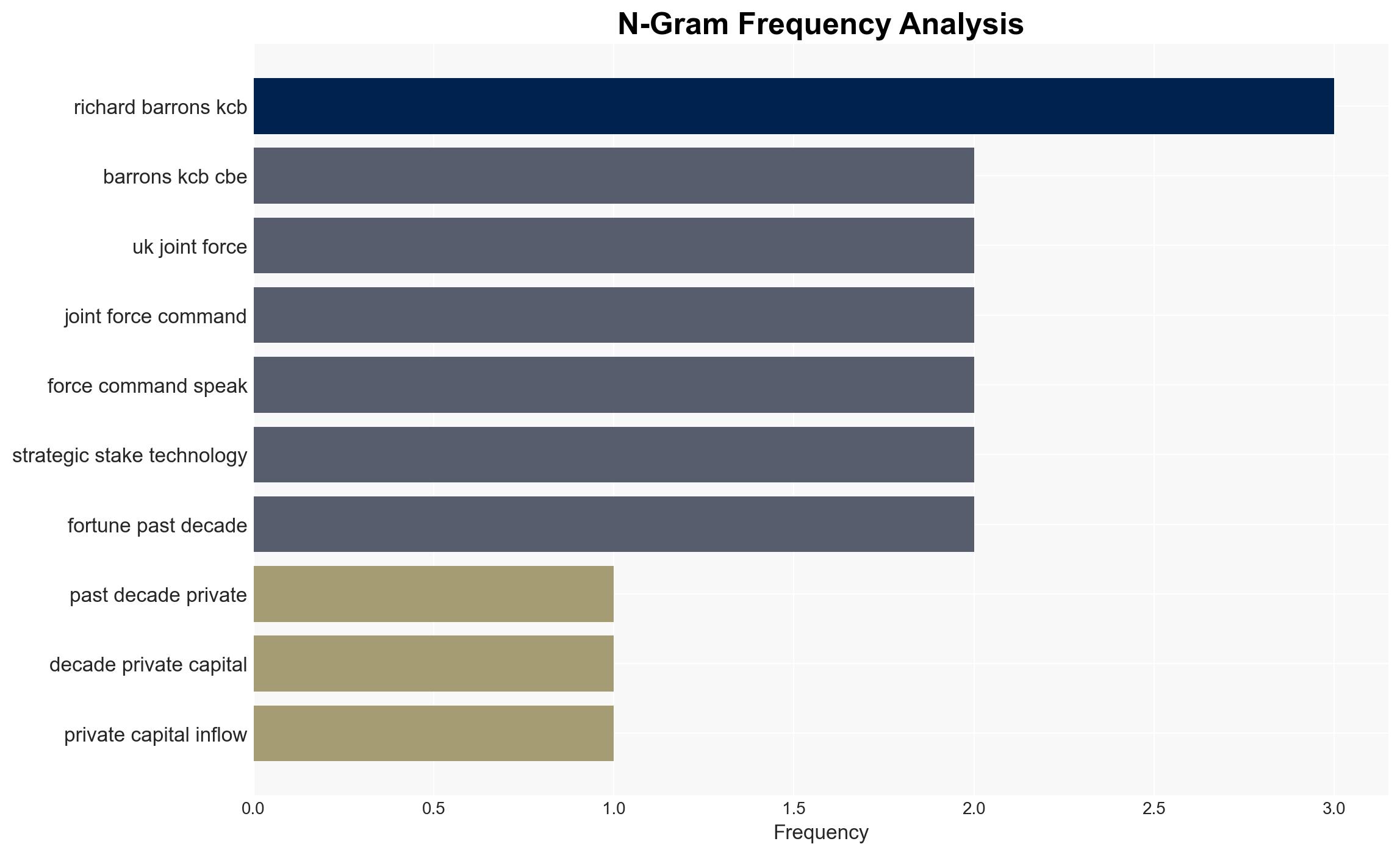
General Sir Richard Barrons, UK Joint Force Command
7. Thematic Tags
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us