5 reasons cyber insurance can be a worthy investment for your small business
Published on: 2025-11-25
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
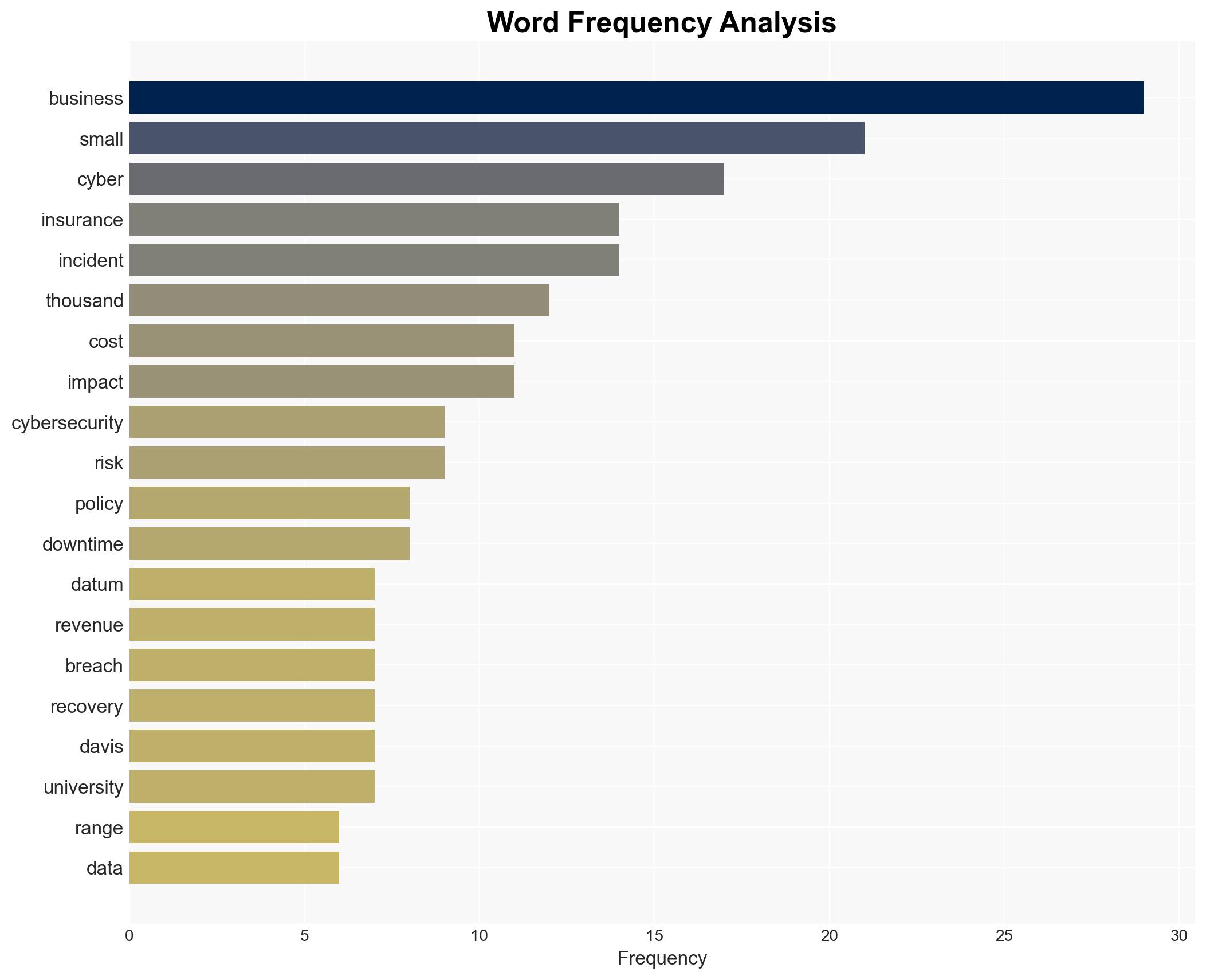
Intelligence Report: Cyber Insurance for Small Businesses
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
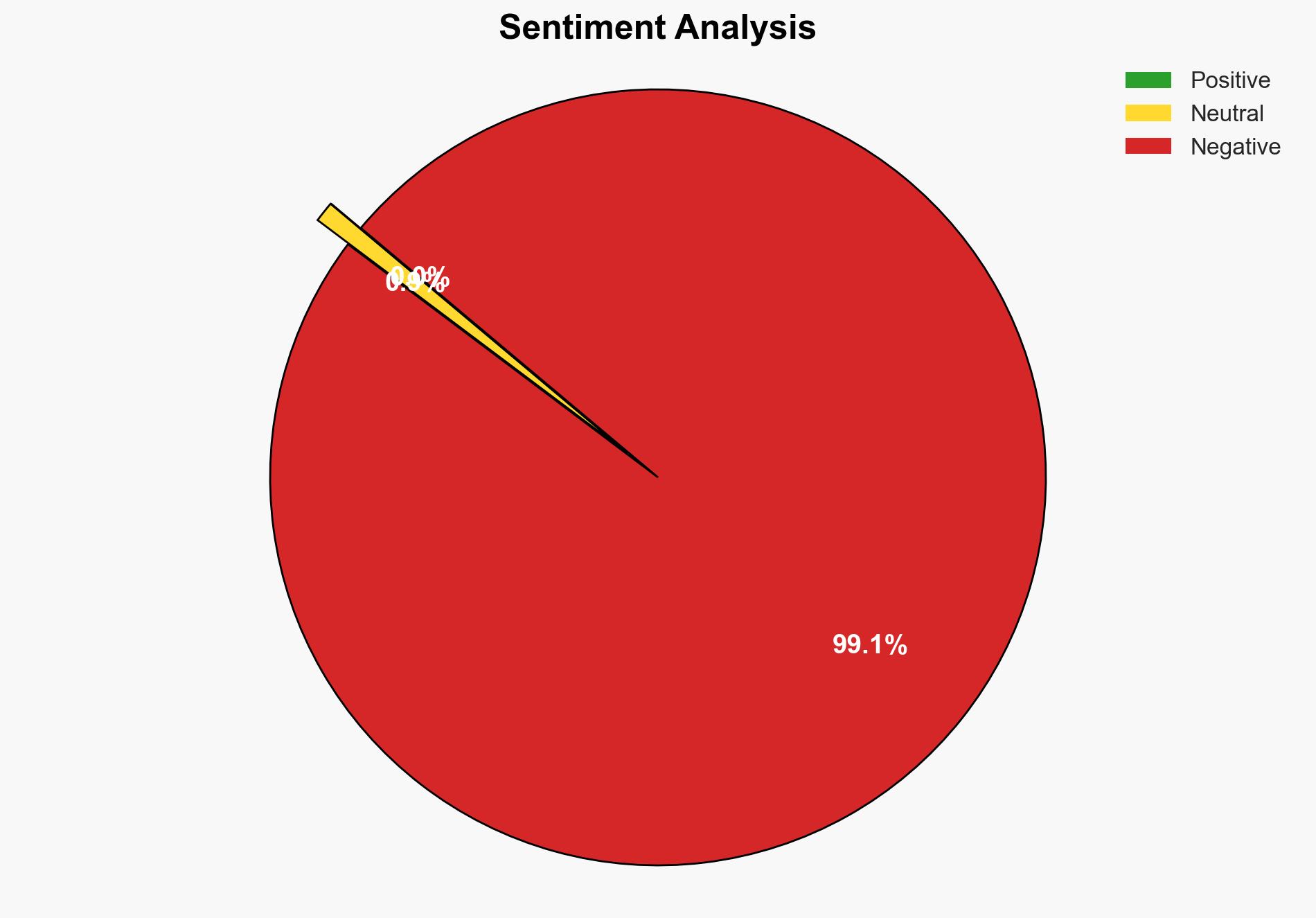
With a moderate confidence level, the most supported hypothesis is that investing in cyber insurance is a strategic move for small businesses due to their vulnerability to cyber threats and the potential financial impact of incidents. Recommended action includes small businesses assessing their cybersecurity posture and considering tailored cyber insurance policies to mitigate risks.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: Cyber insurance is a valuable investment for small businesses, providing financial protection and incentivizing improved cybersecurity practices.
Hypothesis 2: Cyber insurance is not a cost-effective investment for small businesses due to high premiums and deductibles, and the likelihood of incidents may be overstated.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely due to the documented frequency of cyber incidents affecting small businesses and the significant financial impact these incidents can have, as supported by data from the Verizon Data Breach Investigation Report and other sources.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions include the reliability of data on cyber incidents and the effectiveness of cyber insurance in mitigating financial losses. A red flag is the potential bias in sources advocating for cyber insurance, possibly overstating risks to promote insurance sales. Additionally, the assumption that all small businesses face similar risks may not account for industry-specific threats.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The primary implication is that small businesses without cyber insurance may face severe financial strain following a cyber incident. This could lead to business closure, job loss, and broader economic impacts. Strategic risks include the potential for increased cybercrime targeting small businesses perceived as underinsured or vulnerable.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Small businesses should conduct a thorough risk assessment to understand their specific cyber threat landscape.
- Consider investing in cyber insurance as part of a broader cybersecurity strategy, ensuring policies are tailored to their specific needs and risk profile.
- Implement robust cybersecurity measures to reduce premiums and enhance protection.
- Best-case scenario: Small businesses effectively mitigate cyber risks through insurance and improved security practices, reducing financial losses.
- Worst-case scenario: Cyber incidents increase, and businesses without insurance face crippling financial impacts.
- Most-likely scenario: A gradual increase in cyber insurance adoption among small businesses as awareness of cyber risks grows.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
No specific individuals are mentioned. Key entities include small businesses, cyber insurance providers, and cybersecurity firms.
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, Small Business, Cyber Insurance, Risk Management
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us