Qilin Ransomware Exploits South Korean MSP Breach, Leading to Data Theft from 28 Victims in ‘Korean Leaks’ Ca…
Published on: 2025-11-26
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Qilin Ransomware Turns South Korean MSP Breach Into 28-Victim ‘Korean Leaks’ Data Heist
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
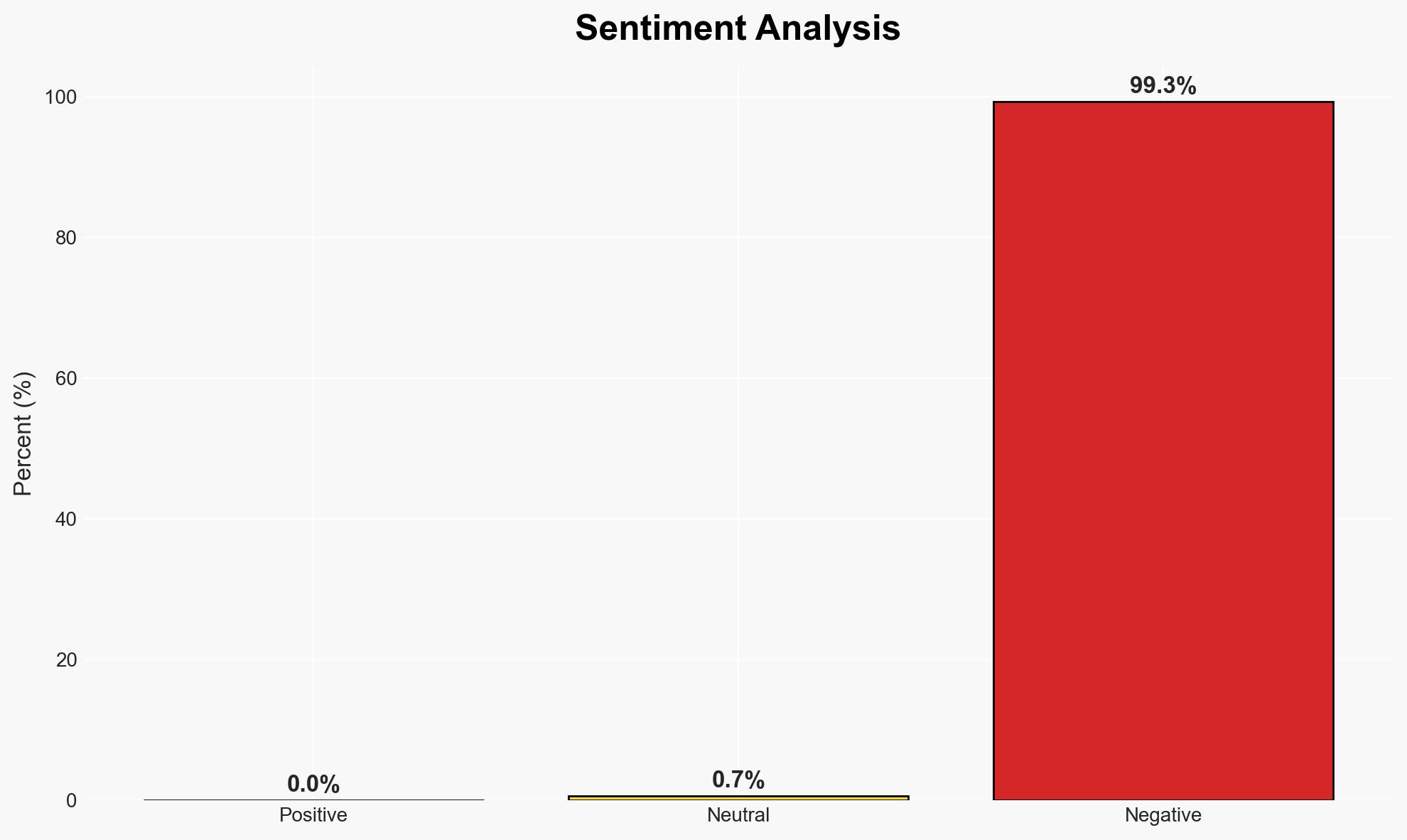
The Qilin ransomware group has executed a significant supply chain attack on South Korea’s financial sector, resulting in a data breach affecting 28 victims. The operation, potentially involving North Korean state-affiliated actors, poses a substantial threat to South Korea’s economic and national security. We assess with moderate confidence that the primary motivation is financially driven, despite political overtones in the messaging.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The Qilin ransomware attack is primarily financially motivated, using political rhetoric as a pressure tactic. This is supported by the group’s history of financially motivated extortion and the use of ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) models. However, the political language and targeting of South Korea’s financial sector introduce uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The attack is politically motivated, potentially involving North Korean state-affiliated actors aiming to destabilize South Korea’s financial system. The use of propaganda and political language supports this, but the financial extortion model and lack of direct attribution to state actors contradict this hypothesis.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the established financial motivations of the Qilin group and the RaaS model. Indicators such as a shift in messaging or direct evidence of state sponsorship could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The Qilin group is primarily financially motivated; the political messaging is a tactic rather than a primary objective; North Korean involvement is speculative without direct evidence.
- Information Gaps: Direct attribution of the attack to North Korean actors; detailed motivations behind the political messaging; comprehensive impact assessment on the South Korean financial sector.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential confirmation bias towards financial motivations; source bias from cybersecurity firms with vested interests; possible deception in the political framing of the attack.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The Qilin ransomware attack could exacerbate tensions in the Korean peninsula and destabilize South Korea’s financial sector. The incident highlights vulnerabilities in supply chain security and the potential for ransomware to be used as a geopolitical tool.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased tensions between North and South Korea; potential international diplomatic fallout if state involvement is confirmed.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment for South Korean critical infrastructure; potential for copycat attacks.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on supply chain vulnerabilities; potential for misinformation campaigns leveraging the breach.
- Economic / Social: Potential destabilization of financial markets; erosion of public trust in financial institutions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of South Korean financial networks; engage in public-private partnerships for threat intelligence sharing; initiate diplomatic channels to address potential state involvement.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for supply chain security; strengthen regional cybersecurity alliances; invest in counter-ransomware capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Attack is contained with minimal economic impact; no state involvement confirmed.
- Worst Case: Confirmed state involvement leads to geopolitical escalation; significant financial market disruption.
- Most-Likely: Financially motivated attack with limited political fallout; increased cybersecurity measures in response.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Qilin Ransomware Group
- Moonstone Sleet (potential North Korean actor)
- South Korean Financial Institutions (victims)
- Bitdefender (cybersecurity firm)
- Microsoft (tracking North Korean actors)
7. Thematic Tags
National Security Threats, This brief is tagged under: national security threats; cybersecurity; counter-terrorism; regional focus. Additional tags include: ransomware; supply chain security; financial sector vulnerability; geopolitical tensions
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us