Enhancing Drupal Site Security: Efficient Key Management with the Key Module
Published on: 2025-11-26
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: ImageX Keep your Drupal Site Secure Managing All Keys Safely and Easily with the Key Module
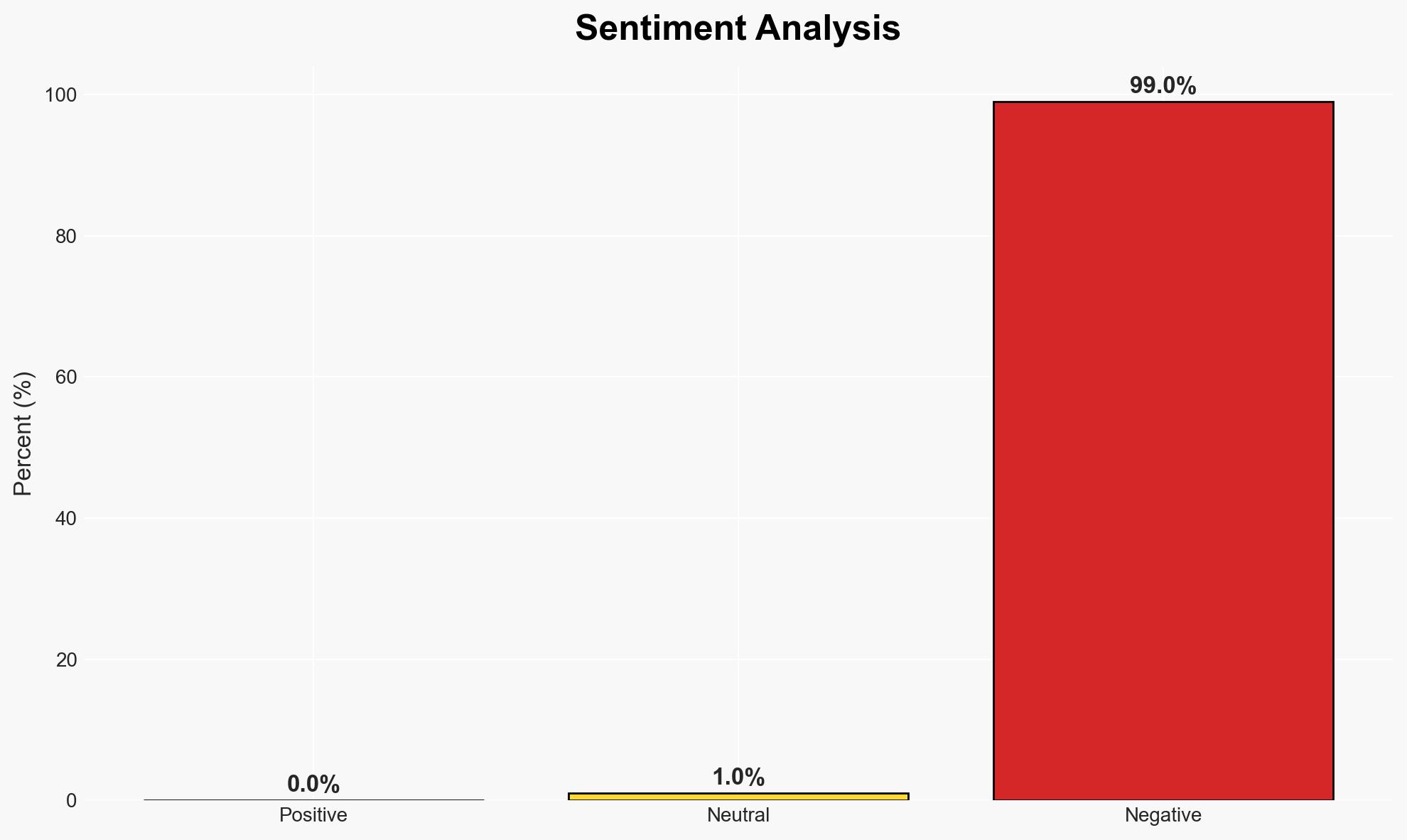
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The Drupal Key Module provides a centralized and secure method for managing website keys, essential for maintaining the security of Drupal sites. This tool is likely to enhance the security posture of organizations using Drupal by preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data. The overall confidence level in this assessment is moderate, given the limited information on potential vulnerabilities or implementation challenges.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The Key Module significantly enhances Drupal site security by providing a centralized and secure management system for keys, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. This is supported by the module’s features and its alignment with security best practices. However, uncertainties remain regarding its integration with existing systems and potential vulnerabilities.
- Hypothesis B: The Key Module may introduce new security risks if not implemented correctly, potentially leading to mismanagement of keys and exposure of sensitive data. This hypothesis is less supported due to the module’s design focus on security, but it highlights the importance of proper implementation and user training.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the module’s comprehensive security features and alignment with best practices. Indicators that could shift this judgment include reports of vulnerabilities or implementation failures.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The Key Module is implemented as designed without significant bugs; users are trained in its use; the module integrates smoothly with existing Drupal sites.
- Information Gaps: Detailed performance data on the module’s integration with various third-party services; user feedback on implementation challenges.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on vendor-provided information; lack of independent security audits could lead to unrecognized vulnerabilities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The adoption of the Key Module could significantly impact the security landscape for Drupal users, enhancing data protection and compliance. However, improper implementation could introduce new vulnerabilities.
- Political / Geopolitical: Minimal direct implications, but increased security could indirectly affect geopolitical dynamics by reducing cyber vulnerabilities.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Improved security posture for Drupal sites could reduce the risk of exploitation by malicious actors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Enhanced data protection and compliance with security standards; potential target for cyber adversaries if vulnerabilities are discovered.
- Economic / Social: Improved trust in digital services could bolster economic activity; however, breaches due to mismanagement could undermine confidence.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a security audit of the Key Module; provide training for users on secure implementation practices.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for ongoing security assessments; enhance user support and documentation.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Widespread adoption of the Key Module enhances security across Drupal sites, reducing data breaches.
- Worst Case: Mismanagement or vulnerabilities lead to significant data breaches, undermining trust in Drupal security.
- Most Likely: Gradual adoption with minor implementation challenges, leading to improved security over time.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us