Structural Weaknesses and Governance Failures Pose Greater Threats to Crypto Than Market Volatility
Published on: 2025-11-26
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Crypto’s Biggest Risk Is Not Volatility
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
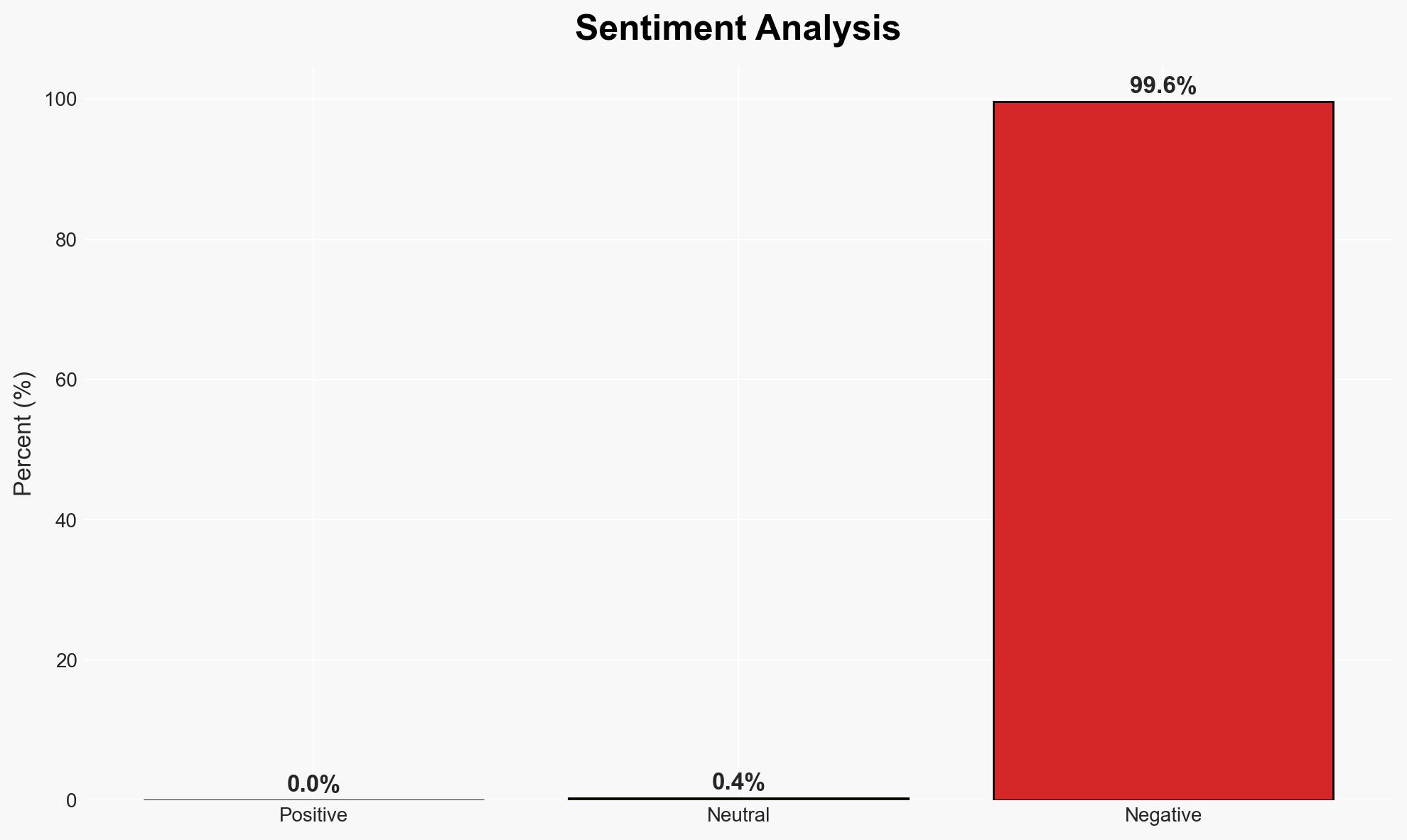
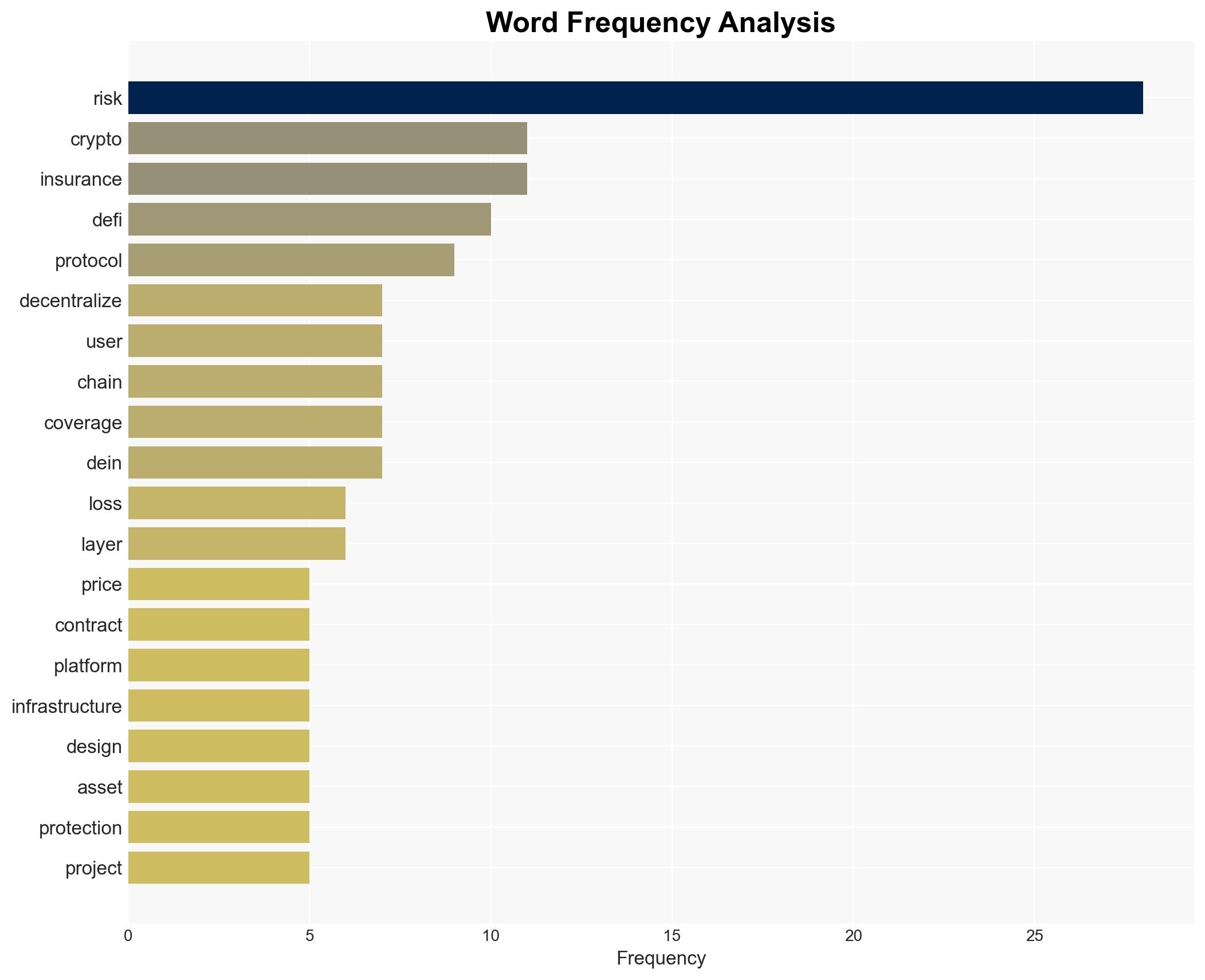
The primary risk in the cryptocurrency sector is not volatility but structural vulnerabilities in decentralized finance (DeFi) systems, including smart contract failures and governance issues. This affects users, developers, and regulators, with moderate confidence in this assessment. The increasing complexity of DeFi protocols poses significant risks that are not fully mitigated by existing security measures.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The main risk in the crypto industry is structural vulnerabilities within DeFi systems, such as smart contract bugs and governance failures. Evidence includes the increase in hacking losses and the complexity of DeFi protocols. However, the rarity of structural failures and the evolving security measures are uncertainties.
- Hypothesis B: Volatility remains the primary risk in the crypto industry, overshadowing structural vulnerabilities. While price swings are a known risk, the lack of traditional financial protections and the nascent state of crypto insurance suggest volatility is more manageable than structural failures.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the documented increase in hacking incidents and the inherent complexity of DeFi systems. Indicators such as improved security protocols or regulatory frameworks could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: DeFi systems will continue to grow in complexity; existing security measures are insufficient; regulatory frameworks will not rapidly adapt.
- Information Gaps: Comprehensive data on the effectiveness of current security measures and the full scope of DeFi protocol vulnerabilities.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in industry reports favoring DeFi growth; manipulation of risk data by stakeholders with vested interests.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of DeFi systems could lead to increased systemic risk if vulnerabilities are not addressed, potentially impacting broader financial stability.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory scrutiny and international cooperation on crypto regulations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of cybercrime exploiting DeFi vulnerabilities.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for misinformation campaigns targeting crypto stability.
- Economic / Social: Possible erosion of trust in digital financial systems, affecting market participation and innovation.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of DeFi protocol vulnerabilities; engage with cybersecurity experts to assess current security measures.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with regulatory bodies to establish clearer guidelines; invest in security research and development.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Enhanced security measures reduce risks; Worst: Major DeFi failure triggers market collapse; Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in security with intermittent failures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us