Japan Implements New Regulatory Framework for Crypto Assets Amid Industry Warnings on Compliance Costs
Published on: 2025-11-26
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Japan Approves Regulatory Shift to New Framework Despite Industry Concerns
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The Japanese Financial Services Agency (FSA) has finalized a significant regulatory overhaul affecting the crypto asset sector, aiming to enhance investor protection amidst rising fraud cases. This shift is expected to impose higher compliance costs on industry players, potentially threatening business viability. The most likely hypothesis is that the regulatory changes will lead to increased market consolidation and a reduction in smaller operators. Overall confidence in this judgment is moderate due to existing information gaps and industry pushback.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The regulatory changes will strengthen investor protection and market integrity, leading to a more stable and secure crypto market in Japan. Supporting evidence includes the FSA’s focus on standardized disclosure and oversight similar to traditional securities. However, uncertainties remain regarding the actual enforcement and effectiveness of these measures.
- Hypothesis B: The increased compliance costs will stifle innovation and drive smaller crypto businesses out of the market, leading to reduced competition and innovation. This hypothesis is supported by industry concerns about the viability of businesses under the new regulations. Contradicting evidence includes the potential for self-regulatory improvements suggested by industry groups.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the immediate and tangible impact of compliance costs on business operations, as highlighted by industry leaders. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include successful implementation of self-regulatory measures and adaptation by businesses to the new regulatory environment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The FSA will effectively enforce the new regulations; industry players will not fully adapt to increased compliance costs; investor protection will improve as intended.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the financial impact of compliance costs on different sizes of crypto businesses; clarity on the FSA’s enforcement mechanisms and timelines.
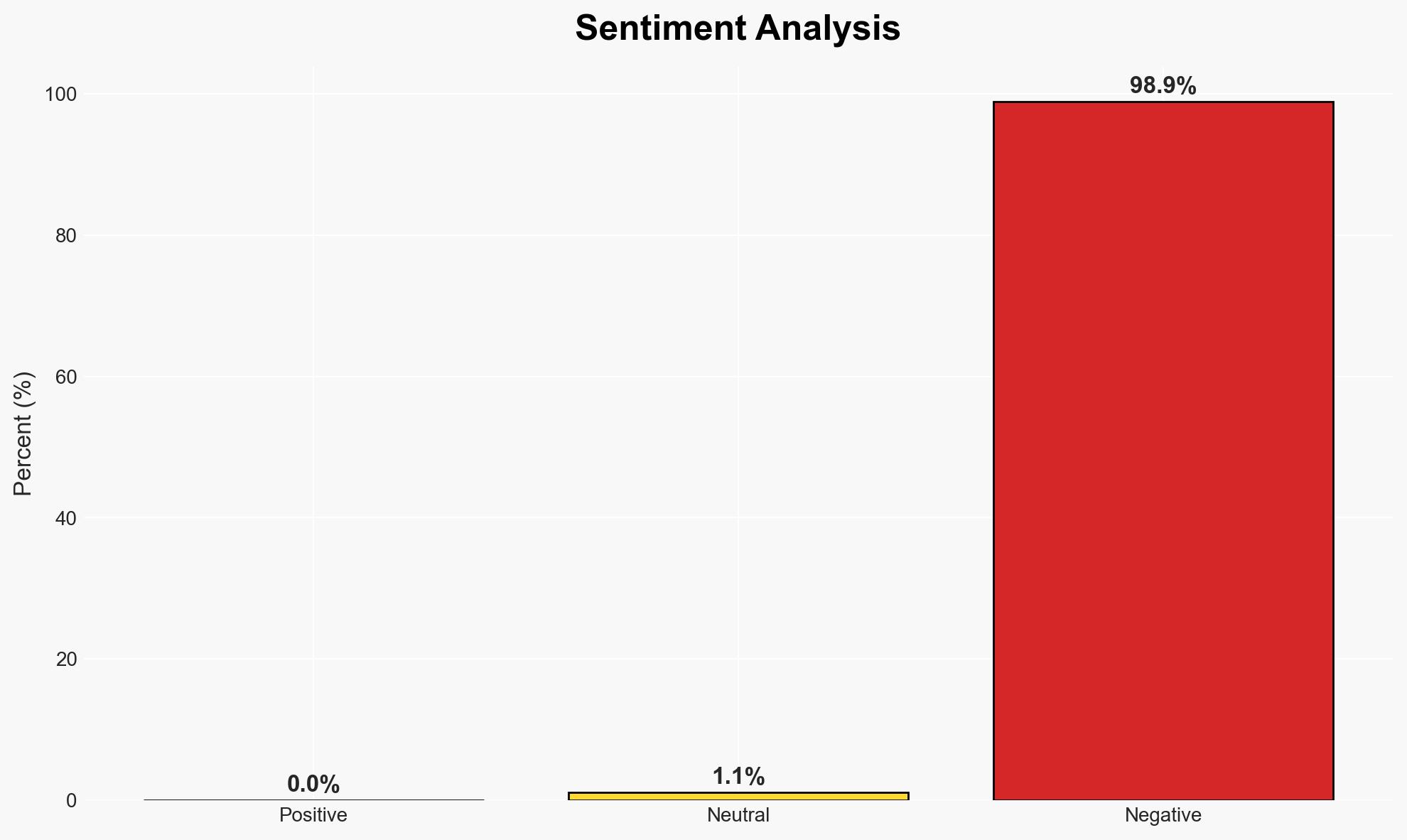
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias from industry sources overstating compliance burdens; risk of regulatory capture or lobbying influencing the FSA’s enforcement rigor.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The regulatory shift could lead to market consolidation and reduced innovation in Japan’s crypto sector. Over time, this may affect Japan’s position as a leader in digital asset innovation.
- Political / Geopolitical: Japan’s regulatory stance may influence other countries’ approaches to crypto regulation, potentially leading to regional harmonization or divergence.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced oversight could reduce the use of crypto assets for illicit activities, but may also push such activities to less regulated jurisdictions.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased regulatory scrutiny may lead to improved cybersecurity practices among compliant businesses, but also heighten risks of cyber attacks on non-compliant or smaller entities.
- Economic / Social: The economic impact on small and medium-sized enterprises in the crypto sector could lead to job losses and reduced economic dynamism.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor industry responses and compliance adaptations; engage with key stakeholders to assess the impact of regulatory changes.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with industry groups to support compliance efforts; invest in capacity-building for regulatory enforcement.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Industry adapts, leading to a more secure and innovative market.
- Worst: High compliance costs drive significant market exit, stifling innovation.
- Most-Likely: Market consolidation occurs with larger players adapting, while smaller ones struggle.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Japanese Financial Services Agency (FSA)
- Japanese Blockchain Association
- CryptoQuant Analyst
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
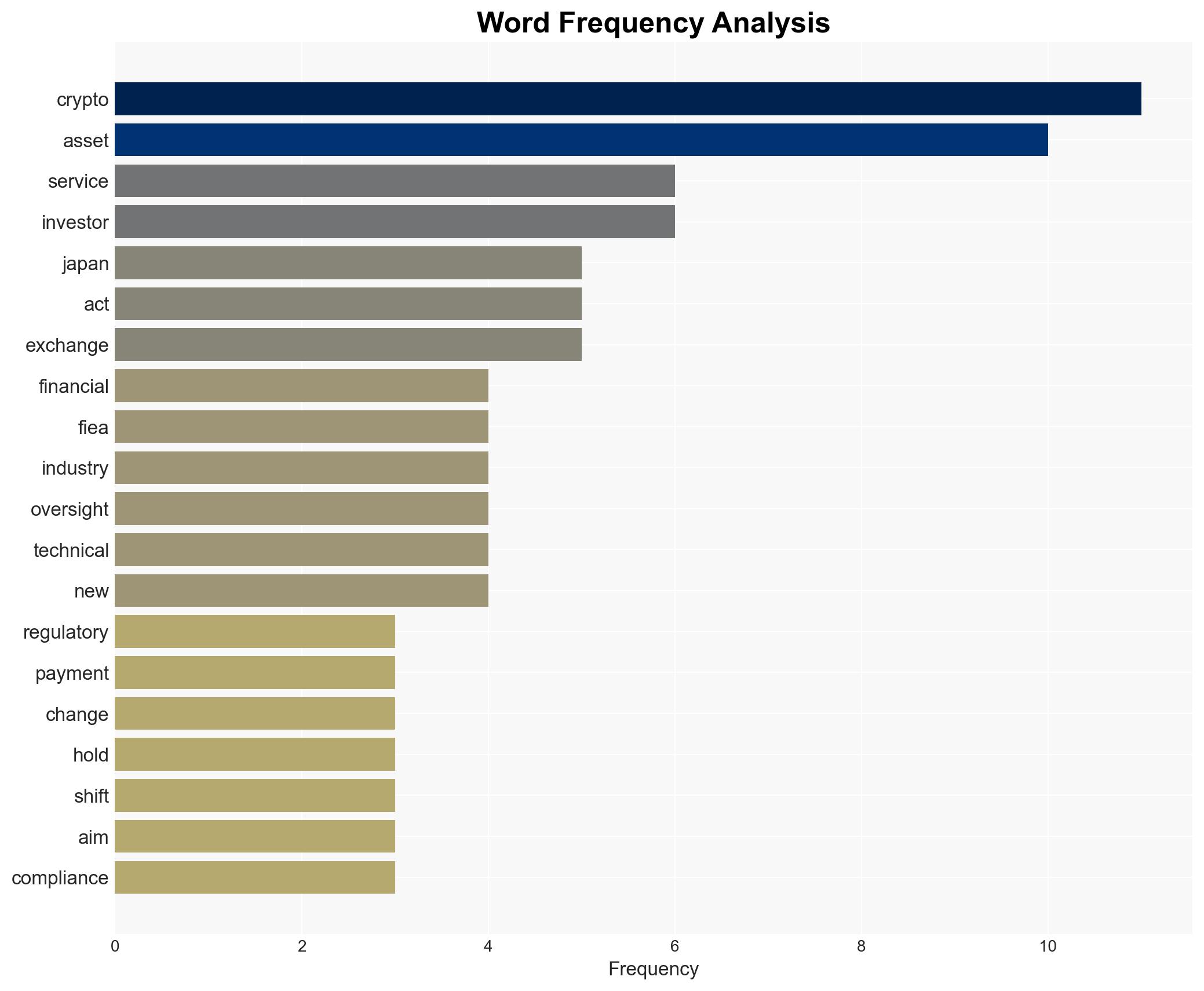
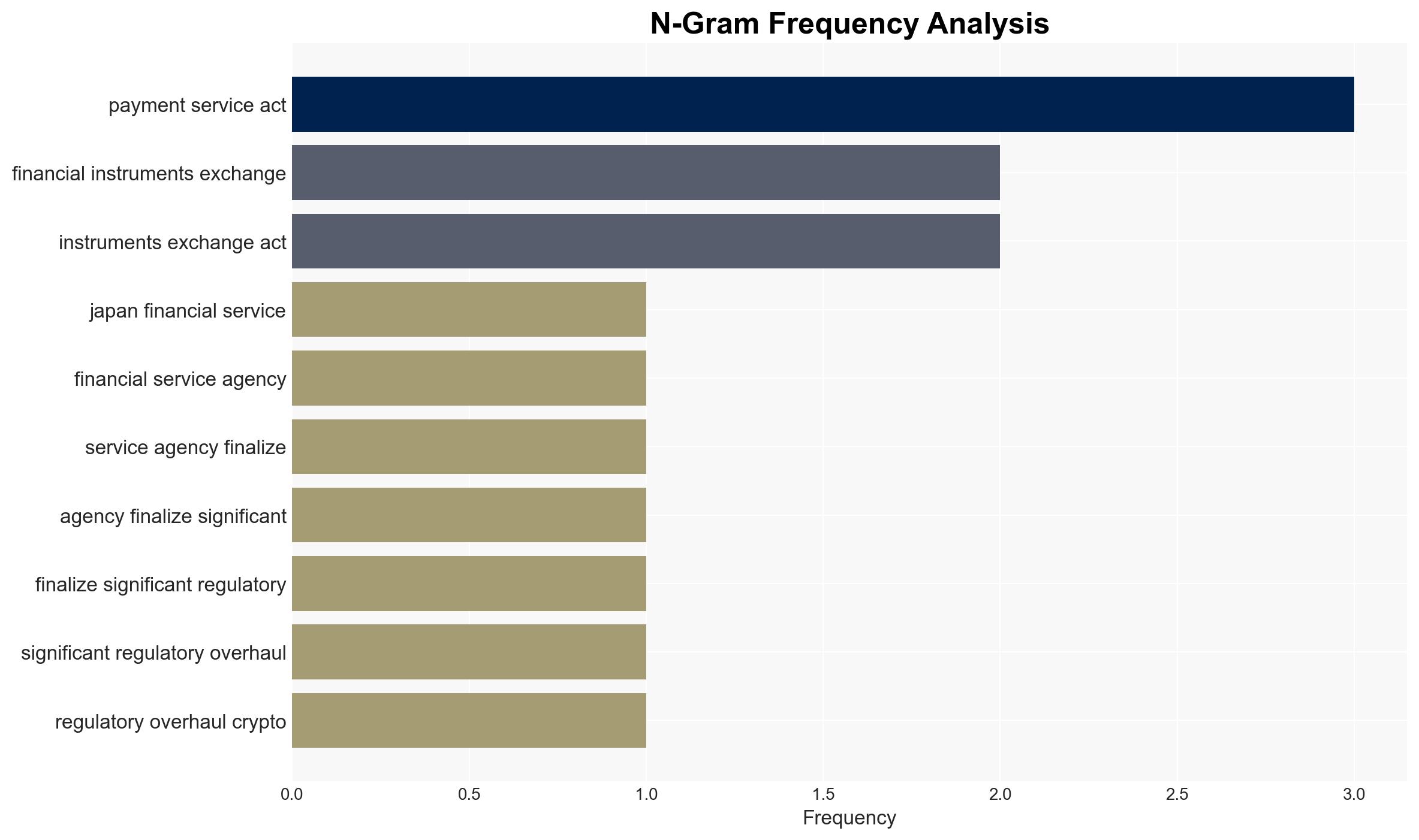
7. Thematic Tags
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us