Mobile sector warns fragmented cybersecurity regulations are escalating operational costs
Published on: 2025-11-26
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Mobile industry warns patchwork cyber regs are driving up costs
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
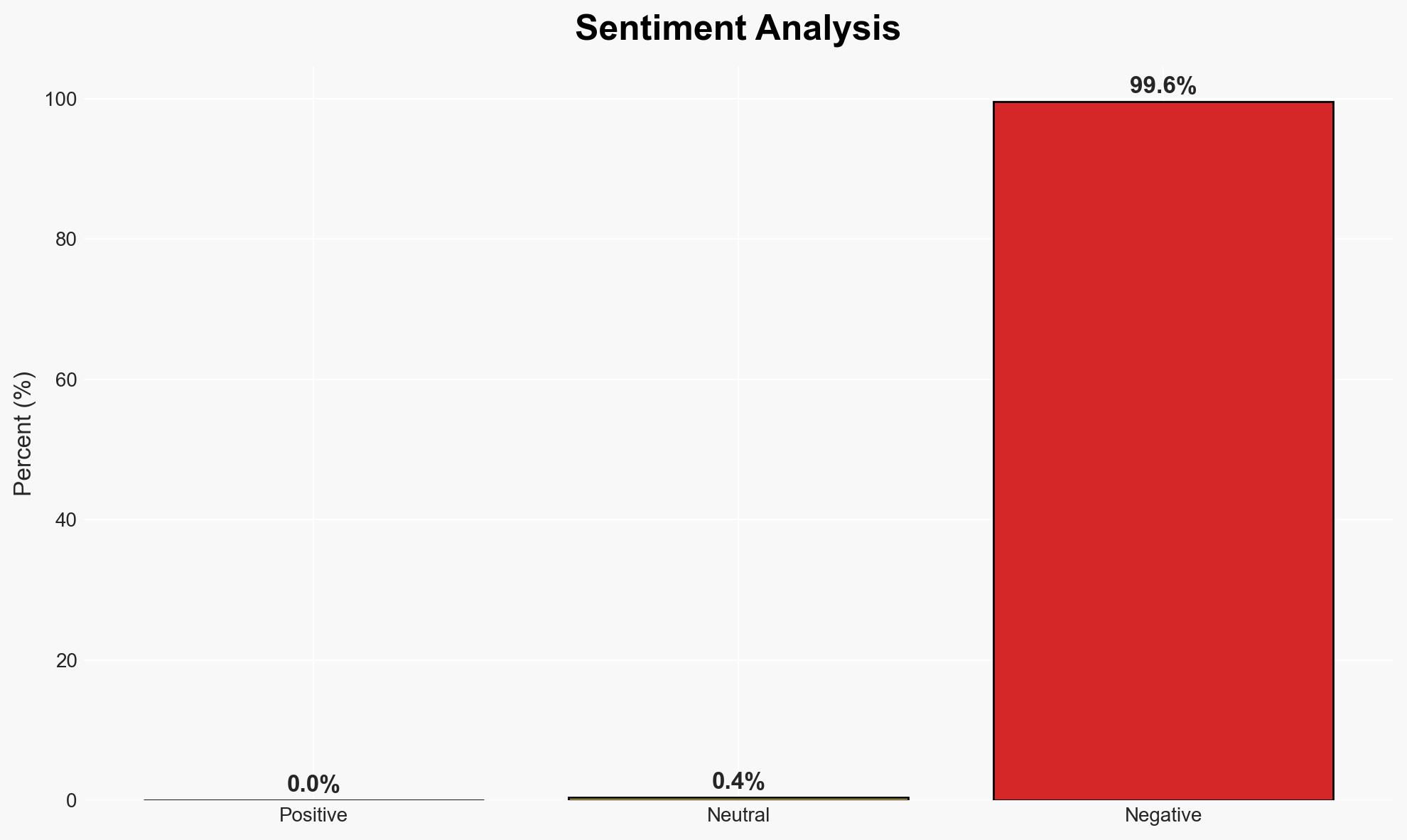
The mobile industry, represented by GSMA, warns that fragmented cybersecurity regulations are increasing operational costs and hindering effective risk mitigation. The most likely hypothesis is that the lack of harmonized regulations leads to inefficiencies and increased compliance burdens on mobile operators. This affects global mobile network operators and potentially impacts cybersecurity resilience. Overall confidence in this judgment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Fragmented cybersecurity regulations are primarily responsible for increased costs and inefficiencies in mobile network operations. Supporting evidence includes GSMA’s report highlighting the burden of compliance and the need for harmonization. Contradicting evidence is limited but could include successful compliance strategies by some operators.
- Hypothesis B: The increase in costs is mainly due to the evolving and sophisticated nature of cyber threats, independent of regulatory fragmentation. Supporting evidence includes the reported rise in global cyber threats. Contradicting evidence includes GSMA’s emphasis on regulatory burdens.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the specific emphasis on regulatory fragmentation by industry representatives. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of effective compliance strategies or a significant rise in cyber threats unrelated to regulatory issues.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The GSMA report accurately reflects industry-wide challenges; regulatory fragmentation is a primary driver of increased costs; harmonization of regulations would lead to cost reductions.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the specific costs attributed to compliance versus those due to threat evolution; comparative analysis of regions with harmonized versus fragmented regulations.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in GSMA’s report due to its role as an industry lobby group; risk of underestimating the independent impact of evolving cyber threats.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development of fragmented cybersecurity regulations could lead to increased operational costs and reduced efficiency in threat mitigation, impacting global cybersecurity resilience.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased lobbying for regulatory harmonization; international tensions if regulations are perceived as trade barriers.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased vulnerability to cyber threats due to diverted resources from threat management to compliance.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber incidents if regulatory compliance overshadows proactive threat mitigation.
- Economic / Social: Higher operational costs could lead to increased service costs for consumers, affecting market dynamics and digital inclusion.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Engage with international regulatory bodies to discuss harmonization; monitor compliance costs and threat mitigation effectiveness.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for sharing best practices in compliance and threat management; invest in adaptive cybersecurity technologies.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Regulatory harmonization leads to reduced costs and improved security (trigger: international agreements).
- Worst: Continued fragmentation increases costs and vulnerabilities (trigger: lack of regulatory dialogue).
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in harmonization with ongoing cost pressures (trigger: partial regulatory cooperation).
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- GSMA (Industry Group)
- Michaela Angonius (GSMA Head of Policy and Regulation)
- Mobile Network Operators (Globally)
7. Thematic Tags
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us