New Malware Detection Enhancements for macOS Strengthen Built-in Security Measures
Published on: 2025-11-28
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Security Bite The malware your Mac can detect and remove
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
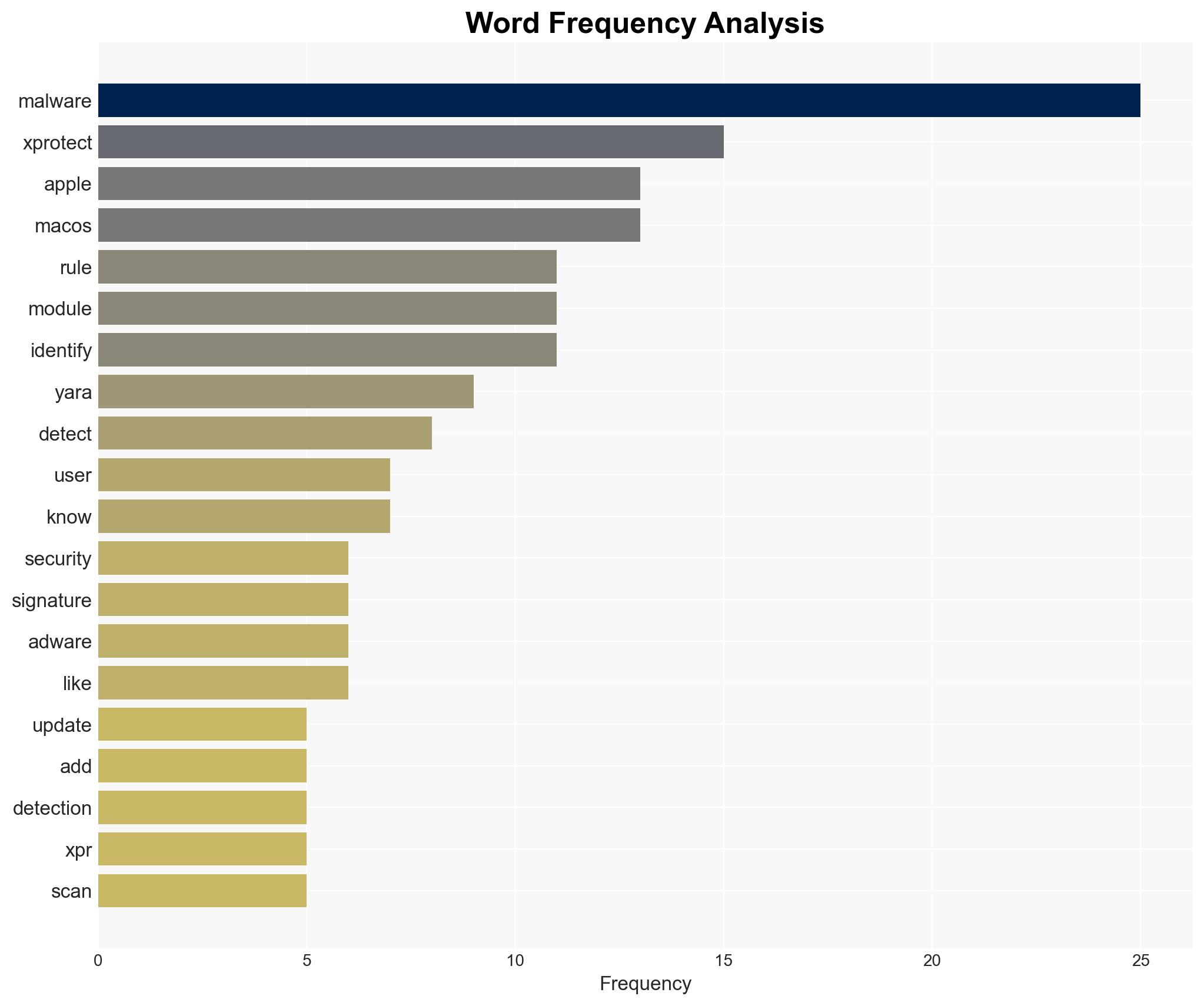
The integration of advanced malware detection tools within Apple’s macOS, such as the XProtect suite, enhances the security posture of Apple devices against emerging threats. The most likely hypothesis is that Apple’s continuous updates to its malware detection capabilities will maintain a robust defense against macOS-targeted malware, affecting users globally. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the proprietary nature of Apple’s internal processes and the evolving threat landscape.
2. Competing Hypotheses
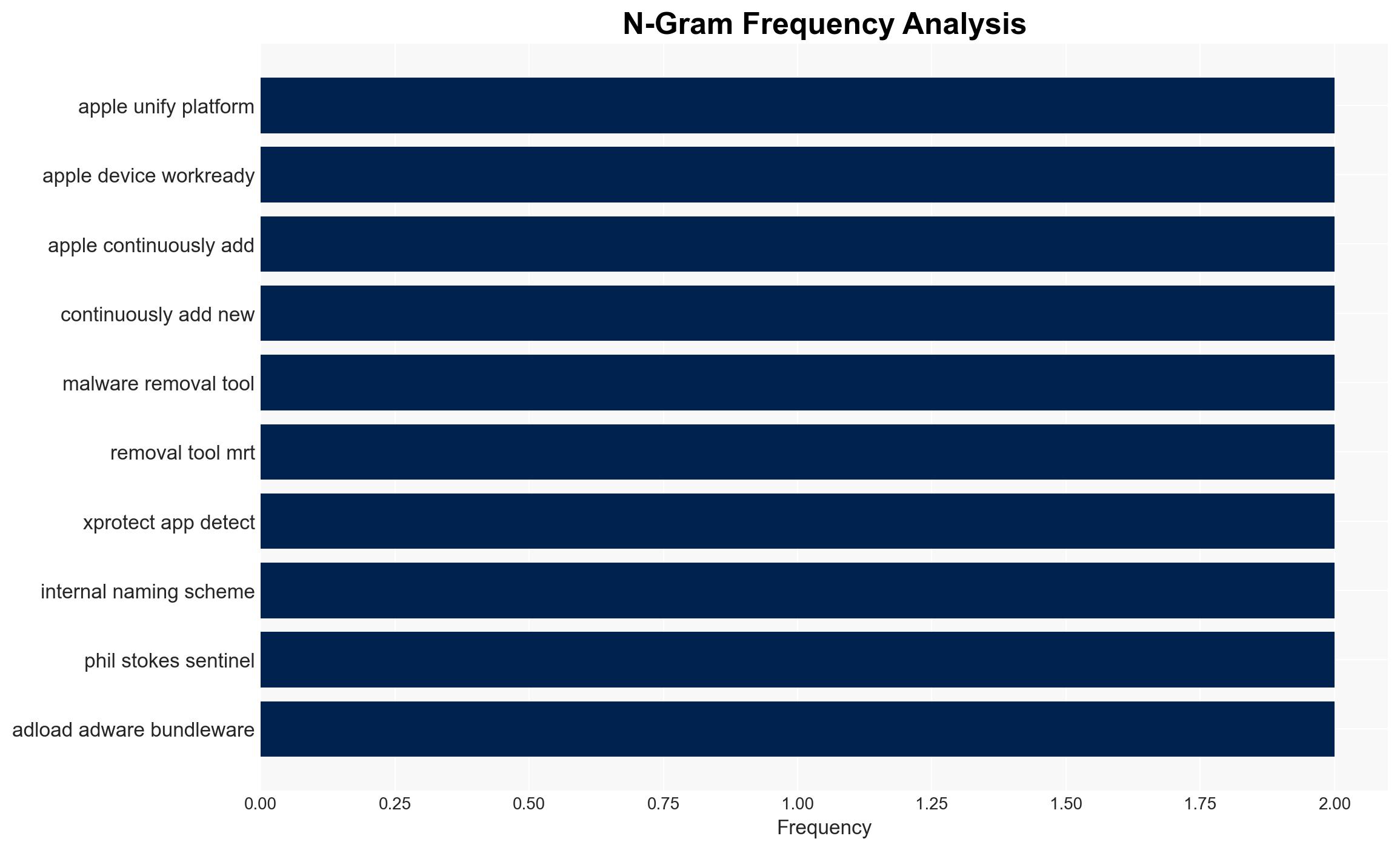
- Hypothesis A: Apple’s XProtect suite and related tools provide comprehensive protection against macOS malware. This is supported by the continuous updates and integration of advanced detection rules, such as YARA signatures. However, uncertainties remain regarding the transparency of Apple’s internal naming schemes and the full scope of malware coverage.
- Hypothesis B: Despite enhancements, Apple’s malware detection tools may not fully protect against sophisticated threats due to potential gaps in detection capabilities and the obfuscation of malware signatures. This is supported by the challenges researchers face in mapping Apple’s internal signatures to known malware names.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the proactive measures Apple has taken to update and expand its malware detection suite. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include the emergence of new, undetected malware strains and independent assessments of Apple’s detection efficacy.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Apple’s updates to its malware detection tools are timely and effective; macOS users apply updates regularly; the threat landscape evolves predictably.
- Information Gaps: Detailed information on Apple’s internal malware naming conventions and the full list of detected threats is lacking.
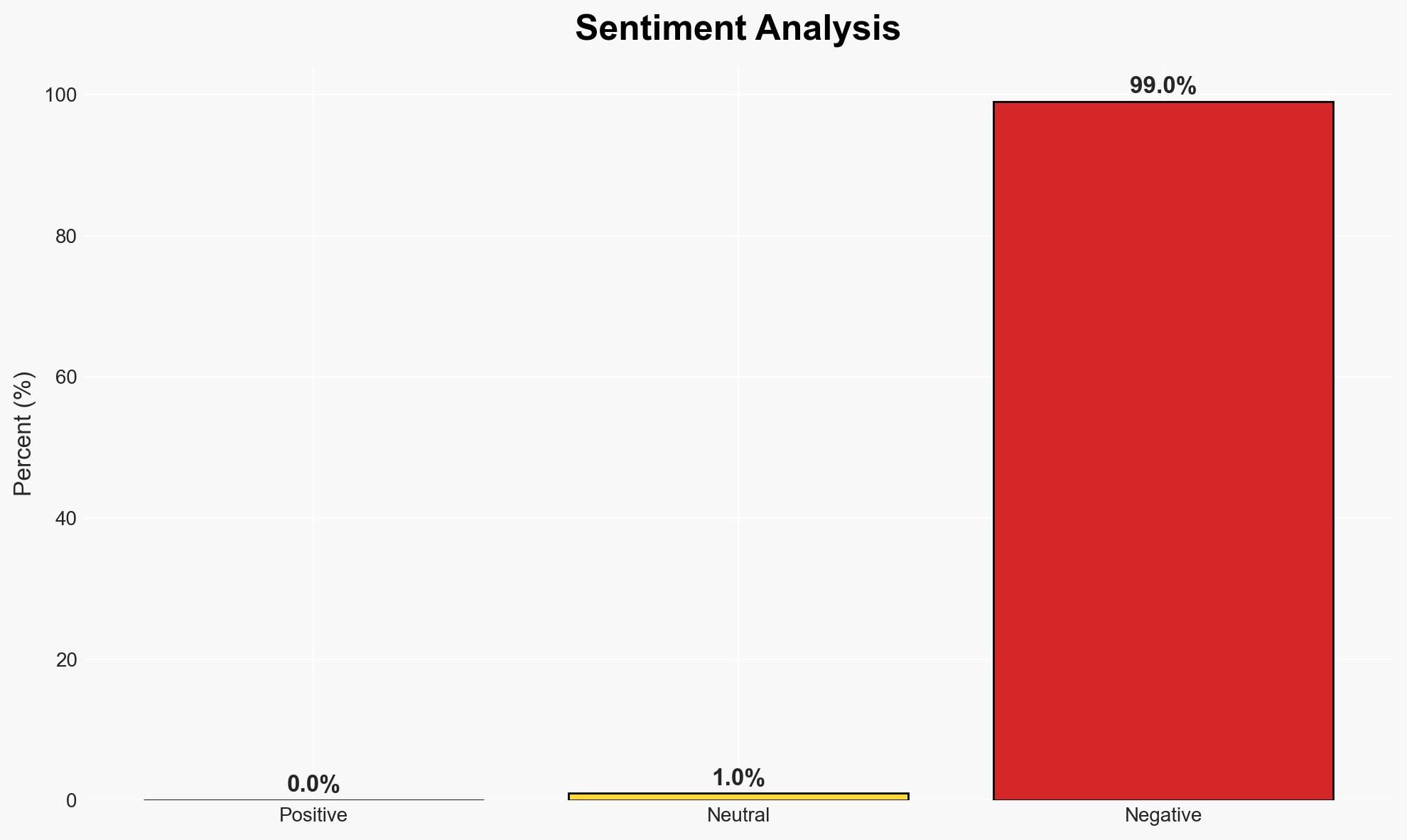
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in relying on Apple’s proprietary data and the risk of underestimating sophisticated threat actors capable of bypassing current detection methods.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of Apple’s malware detection capabilities could influence the broader cybersecurity landscape by setting new standards for device security. However, gaps in detection could lead to increased vulnerability to sophisticated threats.
- Political / Geopolitical: Enhanced security measures may affect international relations with countries where cyber threats originate.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Improved detection tools could reduce the operational capabilities of threat actors targeting macOS.
- Cyber / Information Space: The development may drive other platforms to enhance their security measures, impacting the cyber threat environment.
- Economic / Social: Increased consumer confidence in Apple products could drive economic benefits, but failure to address sophisticated threats could lead to reputational damage.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Encourage users to apply all security updates promptly and monitor for new threat intelligence regarding macOS vulnerabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms to enhance threat detection capabilities and invest in user education on security best practices.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Apple’s tools effectively mitigate most threats, leading to a secure user environment.
- Worst: New malware strains bypass detection, causing widespread security breaches.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in detection maintain a generally secure environment, with occasional breaches.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, macOS security, malware detection, Apple, XProtect, threat intelligence, software updates
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us