SGS Achieves First EU RED-NB Certification, Enhancing Cybersecurity Standards and Market Competitiveness
Published on: 2025-11-28
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: SGS Highlights Cybersecurity Capabilities With Worlds First EU RED-NB Certification and Cybersecurity Mark
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
SGS’s achievement of the EU RED-NB certification and Cybersecurity Mark positions the company as a leader in cybersecurity standardization and regulatory compliance, potentially enhancing its competitive edge in the global market. This development is likely to influence manufacturers and enterprises seeking to enter or expand within the EU market. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the lack of specific details on the certification process and its immediate impact on market dynamics.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: SGS’s certification will significantly enhance its market position by providing a competitive advantage in cybersecurity compliance. This is supported by the recognition of the certification as a landmark achievement and the growing demand for cybersecurity solutions. However, the specific market impact remains uncertain due to potential competitors achieving similar certifications.
- Hypothesis B: The certification may have limited impact on SGS’s market position due to the presence of other established players with similar capabilities. While SGS’s certification is a notable achievement, the broader market dynamics and existing competition could dilute its competitive advantage.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the unique nature of the certification and SGS’s established reputation in testing and certification. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include the emergence of similar certifications by competitors or changes in EU regulatory requirements.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: SGS’s certification process is rigorous and recognized by key stakeholders; the EU market values such certifications highly; cybersecurity threats will continue to rise, increasing demand for certified solutions.
- Information Gaps: Specific details of the certification criteria and process; market share data post-certification; competitor responses to SGS’s certification.
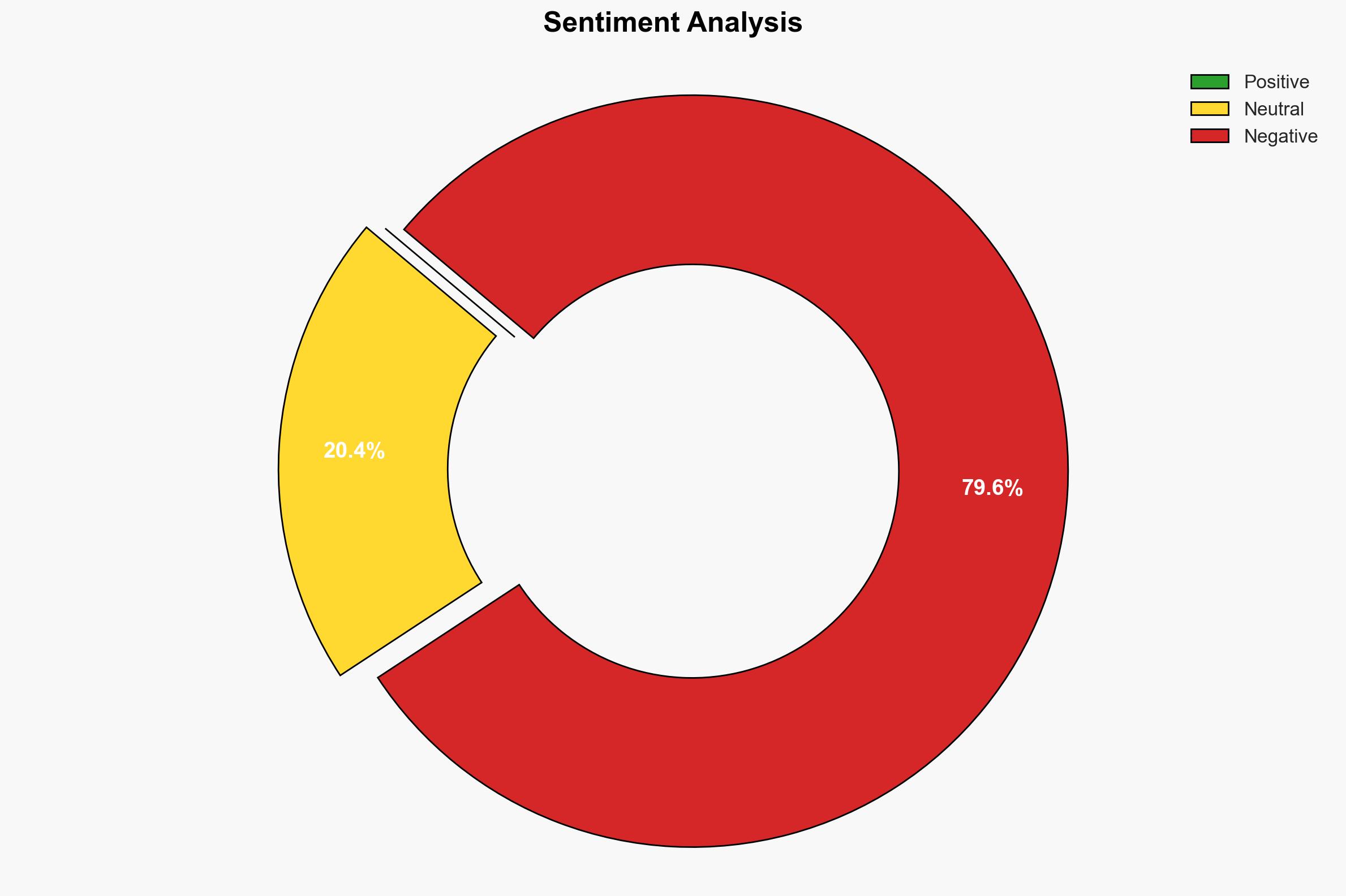
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in source reporting due to promotional nature; lack of independent verification of certification impact; possible overstatement of competitive advantage.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could influence the cybersecurity landscape by setting new standards for compliance and trust. Over time, it may drive other companies to pursue similar certifications, potentially raising the overall cybersecurity baseline.
- Political / Geopolitical: May influence EU regulatory frameworks and international cybersecurity standards.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced cybersecurity standards could reduce vulnerabilities in critical infrastructure.
- Cyber / Information Space: Could lead to increased demand for cybersecurity solutions and services, impacting digital trust dynamics.
- Economic / Social: May boost economic activity in cybersecurity sectors and influence consumer trust in digital products.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor competitor responses and market reactions; engage with EU regulatory bodies to understand potential changes in compliance requirements.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with key stakeholders to leverage certification; invest in capability development to maintain competitive edge.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: SGS’s certification leads to increased market share and sets industry standards.
- Worst: Competitors quickly achieve similar certifications, neutralizing SGS’s advantage.
- Most-Likely: SGS gains a moderate competitive edge, influencing market dynamics and regulatory standards.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- SGS (world-leading testing, inspection, and certification company)
- Ruijie Networks (enterprise access point product manufacturer)
- Ross Wang (Senior Manager, Business Development, Cybersecurity & Connectivity Product, SGS)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
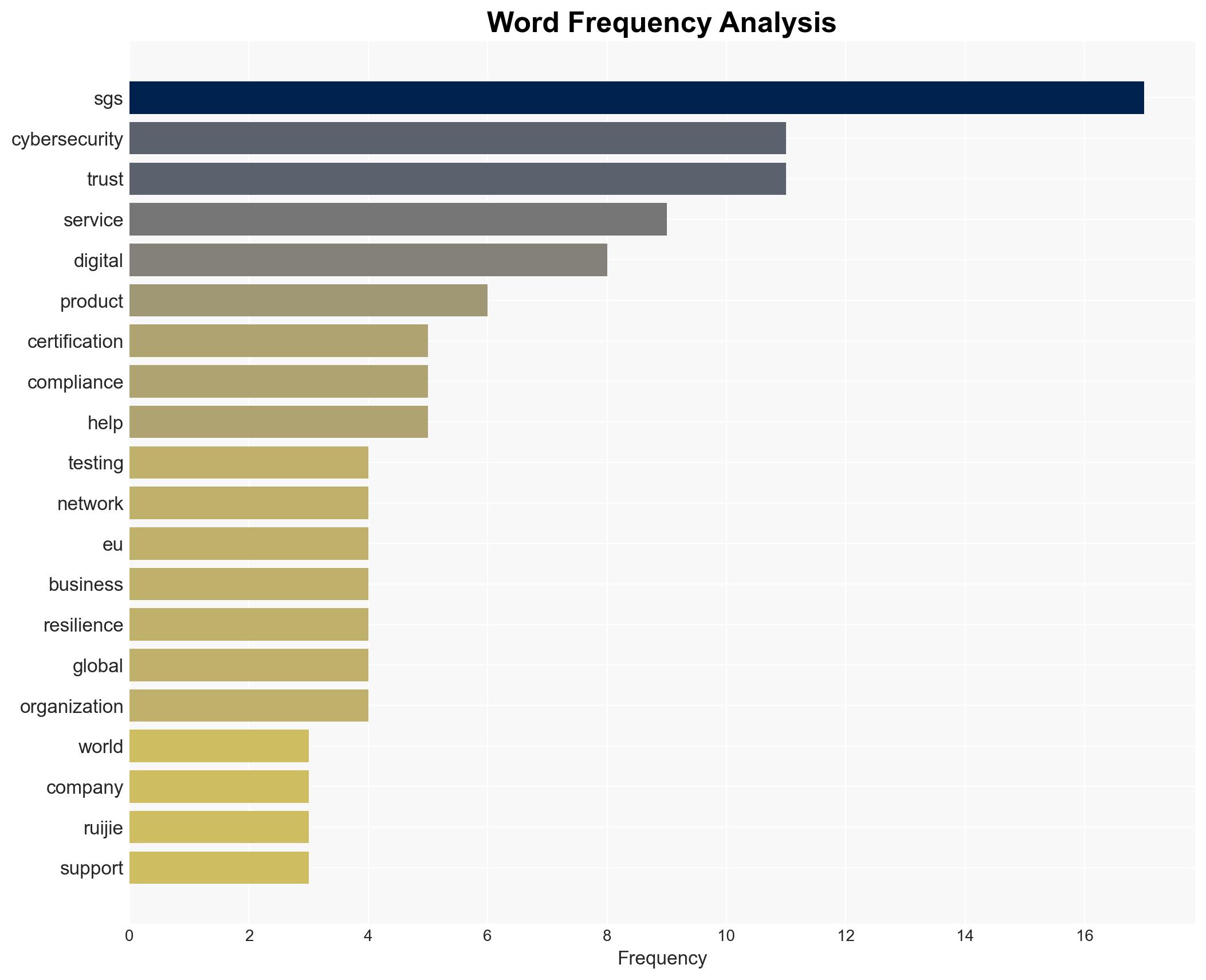
Cybersecurity, EU compliance, certification, digital trust, market dynamics, regulatory standards, competitive advantage
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us