China Leverages AI for Enhanced Censorship and Global Influence on Human Rights Practices
Published on: 2025-12-03
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: China using AI as precision instrument of censorship and repression at home and abroad
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
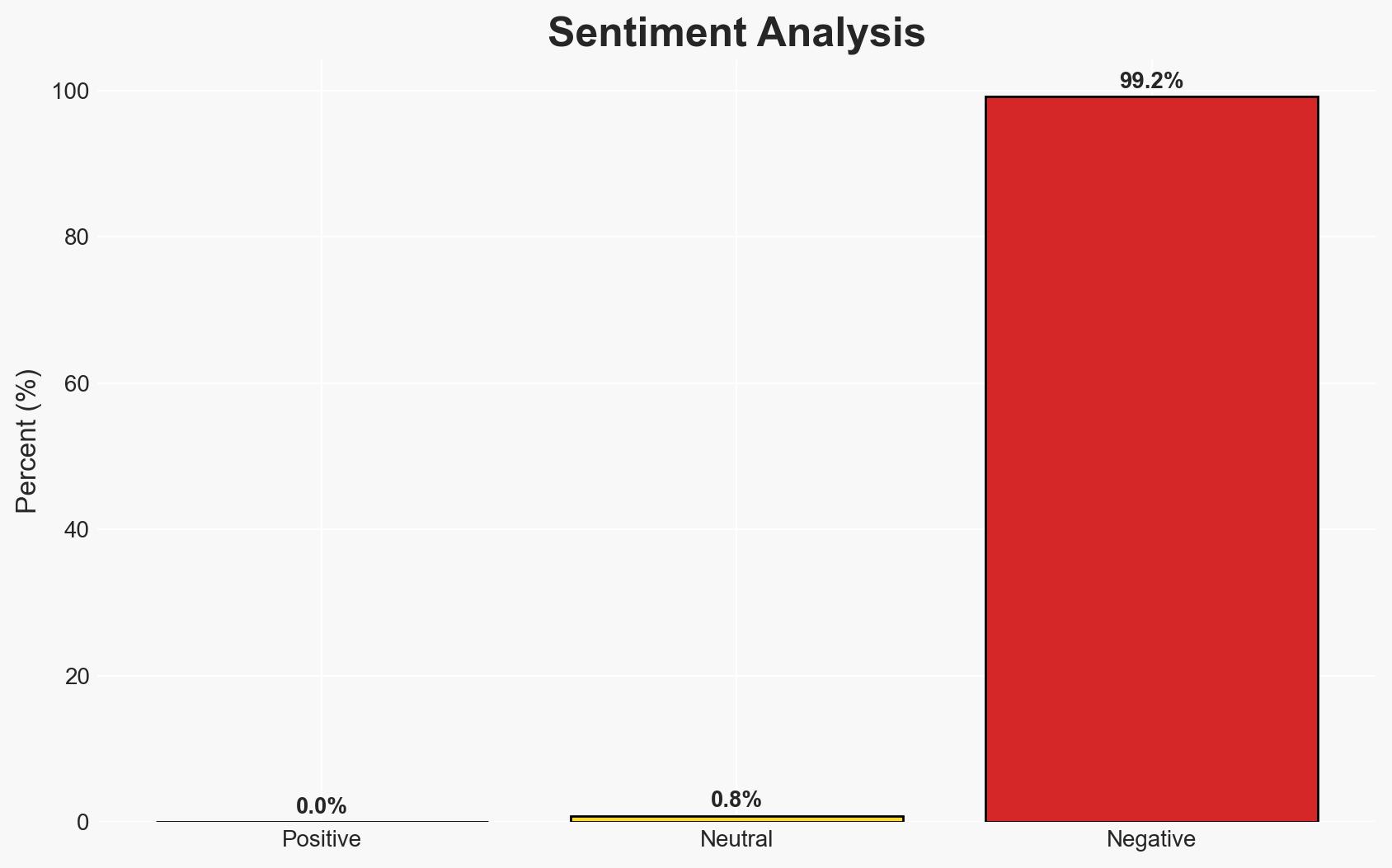
China is leveraging AI technology to enhance its censorship and surveillance capabilities domestically and is exporting these techniques internationally. This development poses a significant challenge to global information integrity and human rights. The most likely hypothesis is that China will continue to refine and expand its AI censorship capabilities, impacting global digital content environments. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: China is using AI primarily to maintain domestic political stability and control over its population. This is supported by evidence of AI systems being used to censor sensitive topics and align with core socialist values. However, the extent of international influence remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: China is strategically exporting AI censorship technologies to extend its influence and control over global information spaces. While there is evidence of AI models being accessed globally, the degree of international adoption and influence is less clear.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the clear domestic applications and alignment with China’s political goals. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include increased adoption of Chinese AI models by foreign governments or entities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: China prioritizes political stability over technological fairness; Chinese AI models are more effective at censorship than their Western counterparts; international adoption of Chinese AI is increasing.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the international adoption rate of Chinese AI models; specific mechanisms of AI censorship beyond refusal to respond.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in the ASPI report towards Western perspectives; risk of underestimating China’s ability to influence global AI standards.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development of AI censorship by China could lead to significant shifts in global information dynamics, potentially affecting freedom of speech and access to information worldwide.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions between China and countries advocating for open information environments.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced domestic surveillance capabilities could suppress dissent but may also drive opposition underground, complicating counter-terrorism efforts.
- Cyber / Information Space: Risk of Chinese AI models influencing global digital content moderation standards, leading to a fragmented information space.
- Economic / Social: Potential impact on international tech markets if Chinese AI solutions become dominant; social unrest in regions adopting strict censorship models.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of Chinese AI technology exports; engage with international partners to assess the impact on global information integrity.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures against AI-driven censorship; strengthen partnerships with tech companies to promote open AI standards.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Global consensus on AI standards that prioritize transparency and fairness.
- Worst: Widespread adoption of Chinese AI models leading to global information control.
- Most-Likely: Gradual increase in Chinese AI influence with regional variations in adoption.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
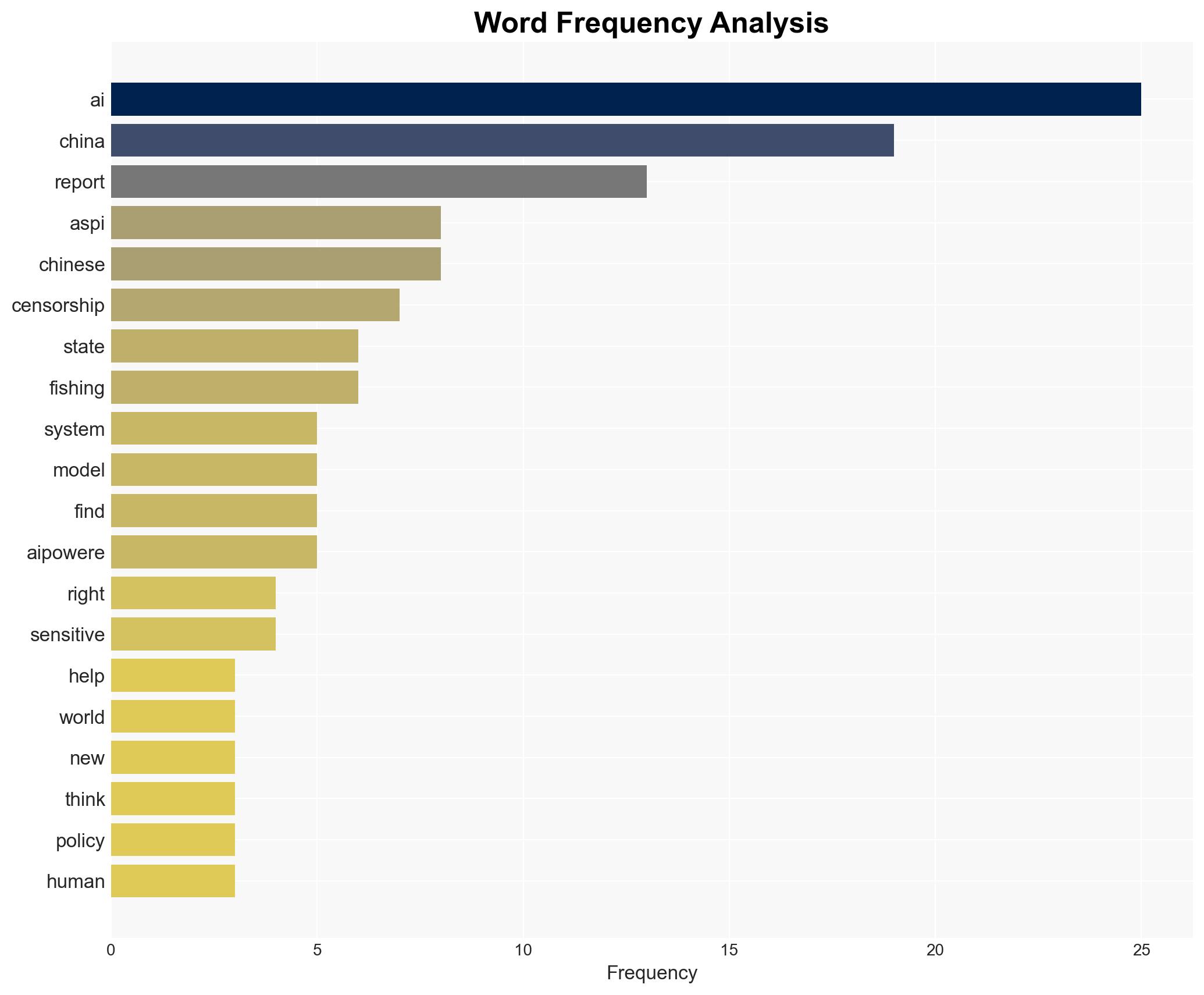
National Security Threats, AI censorship, China, global information control, human rights, digital surveillance, geopolitical influence, technology export
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us