HTB AI Range Launches to Evaluate Safety and Performance of Autonomous Cybersecurity Agents
Published on: 2025-12-03
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: HTB AI Range benchmarks the safety and limits of autonomous security agents
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The HTB AI Range represents a significant advancement in testing and benchmarking AI security agents alongside human operators, with moderate confidence that it will enhance enterprise cybersecurity readiness. The initiative is likely to influence how organizations integrate AI into their defense strategies, affecting enterprises, MSSPs, and government entities. However, the effectiveness of AI in complex scenarios remains uncertain.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: HTB AI Range will significantly improve the integration and effectiveness of AI in cybersecurity operations. This is supported by the structured environment for testing AI capabilities and the reported success in simple tasks. However, the limited performance of AI in complex challenges and potential over-reliance on AI without full understanding of its risks are uncertainties.
- Hypothesis B: The HTB AI Range will have limited impact on cybersecurity effectiveness due to AI’s current limitations in handling complex, multi-step challenges. While AI excels in simple tasks, its inability to outperform humans in more complex scenarios suggests a plateau in its current capabilities.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the structured approach of HTB AI Range in fostering AI-human collaboration and the potential for iterative improvements. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include advancements in AI handling complex tasks and broader adoption of AI in cybersecurity strategies.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI capabilities will continue to improve with iterative testing; human oversight will remain integral to AI operations; enterprises will adopt AI solutions based on HTB AI Range findings; AI’s role in cybersecurity will expand.
- Information Gaps: Detailed performance metrics of AI in complex scenarios; specific enterprise adoption rates of AI solutions post-testing; long-term integration strategies of AI in cybersecurity.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential overestimation of AI capabilities due to controlled testing environments; source bias from HTB’s vested interest in promoting their platform; lack of independent verification of AI performance claims.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development of HTB AI Range could redefine cybersecurity strategies, emphasizing hybrid human-AI operations. Over time, this may lead to increased reliance on AI, necessitating robust oversight mechanisms.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential shifts in national cybersecurity policies to incorporate AI-driven defenses, influencing international cybersecurity norms.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced AI capabilities could improve threat detection and response times, but may also introduce new vulnerabilities if not properly managed.
- Cyber / Information Space: AI’s role in cyber operations could expand, necessitating updates to cyber defense frameworks and increased focus on AI ethics and governance.
- Economic / Social: Broader adoption of AI in cybersecurity could drive economic growth in the tech sector, but may also result in workforce displacement and require reskilling initiatives.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor HTB AI Range outcomes for insights on AI-human collaboration; engage with HTB for potential partnerships; assess current AI integration in cybersecurity frameworks.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures to address AI limitations; foster partnerships with AI research entities; invest in AI capability development and workforce training.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: AI significantly enhances cybersecurity, reducing threat response times and improving defense capabilities.
- Worst: Over-reliance on AI leads to new vulnerabilities and ineffective responses to complex threats.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in AI capabilities with continued human oversight, leading to incremental gains in cybersecurity effectiveness.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Haris Pylarinos, CEO of Hack The Box
- Gerasimos Marketos, Chief Product Officer at Hack The Box
- Hack The Box (HTB)
- Enterprises, MSSPs, and government entities (not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet)
7. Thematic Tags
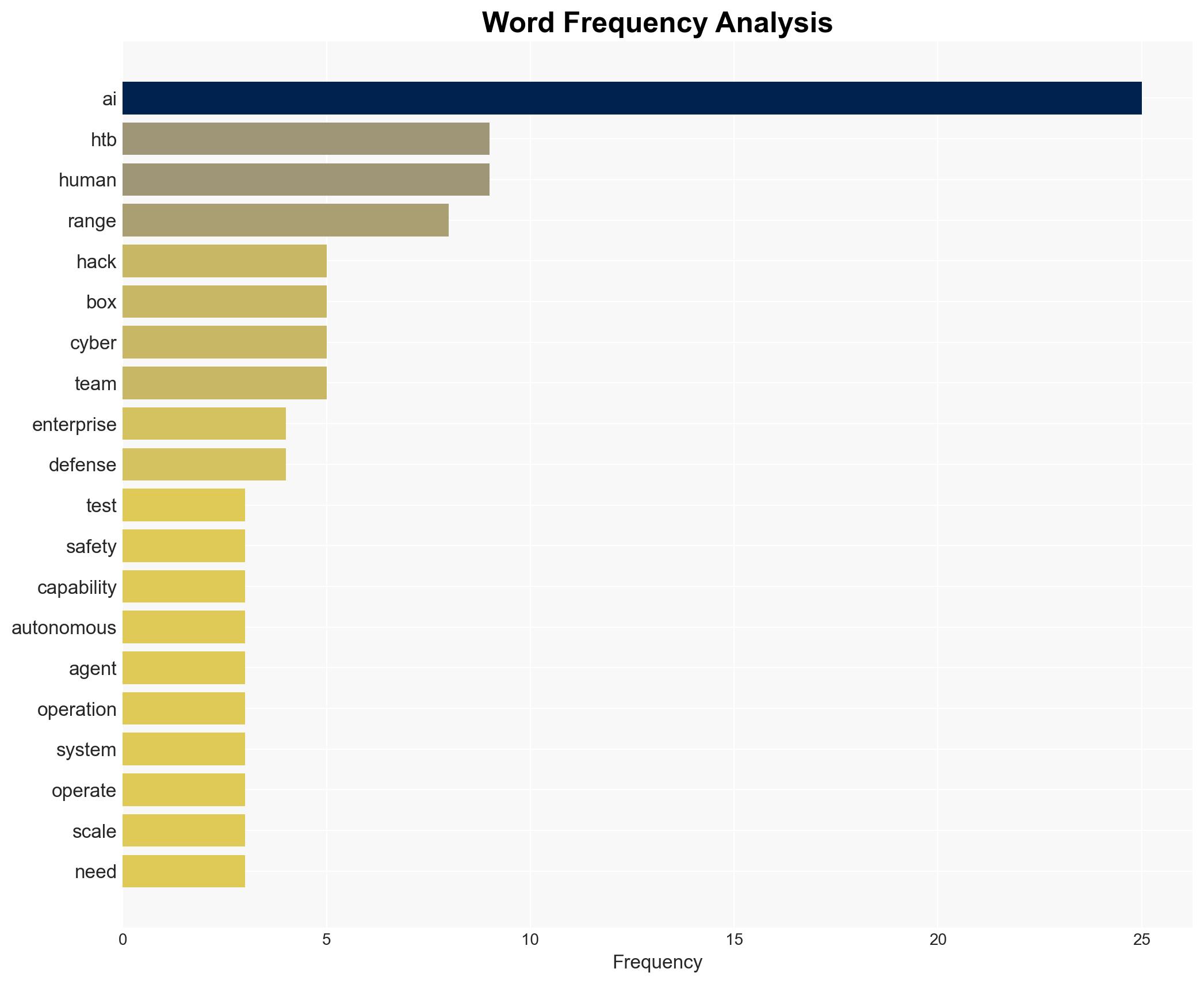
Cybersecurity, AI integration, enterprise defense, human-AI collaboration, cyber training, AI benchmarking
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us