Coup Wave in West Africa: Unique Triggers Amidst Regional Instability
Published on: 2025-12-03
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: West Africas coup cascade
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
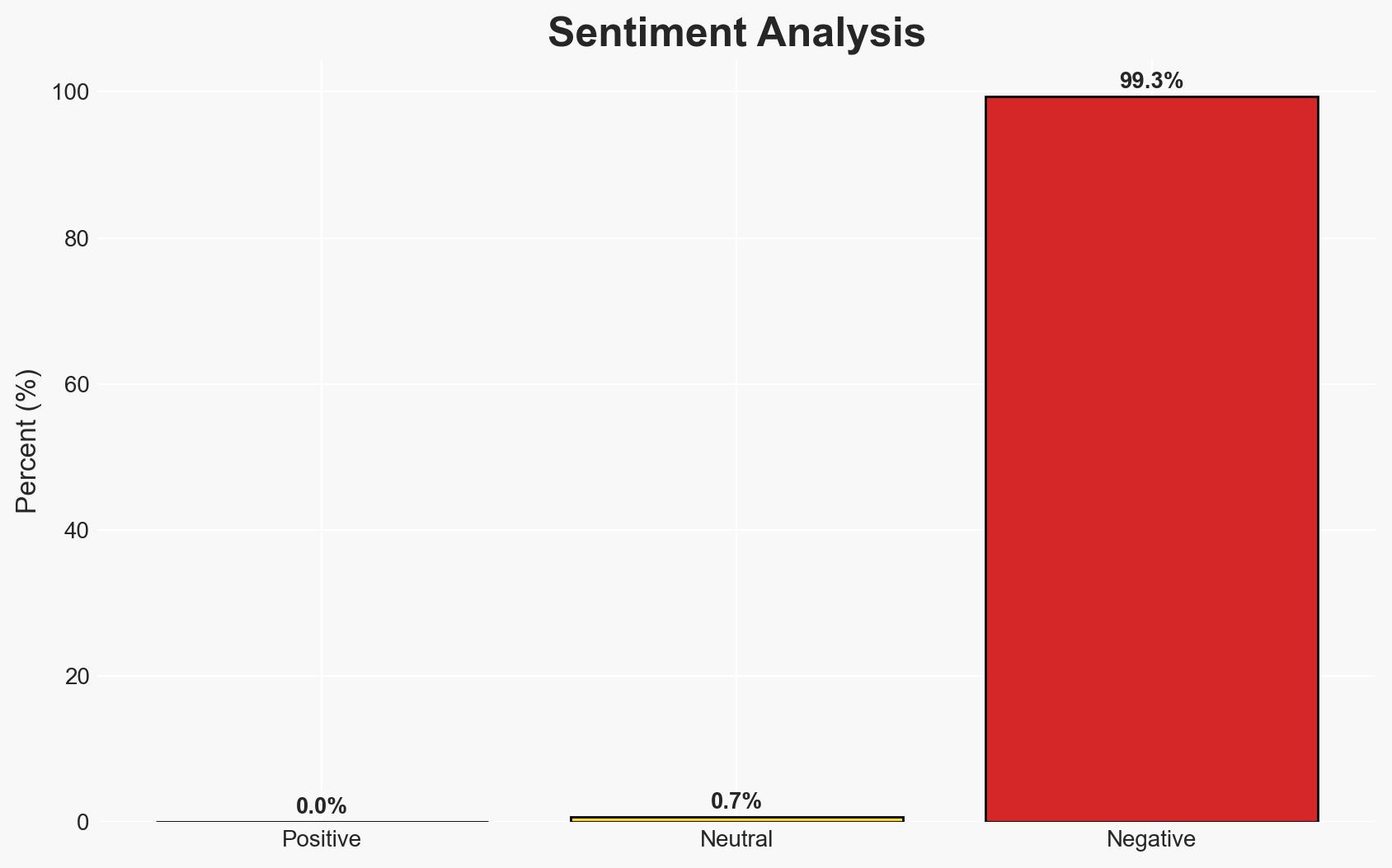
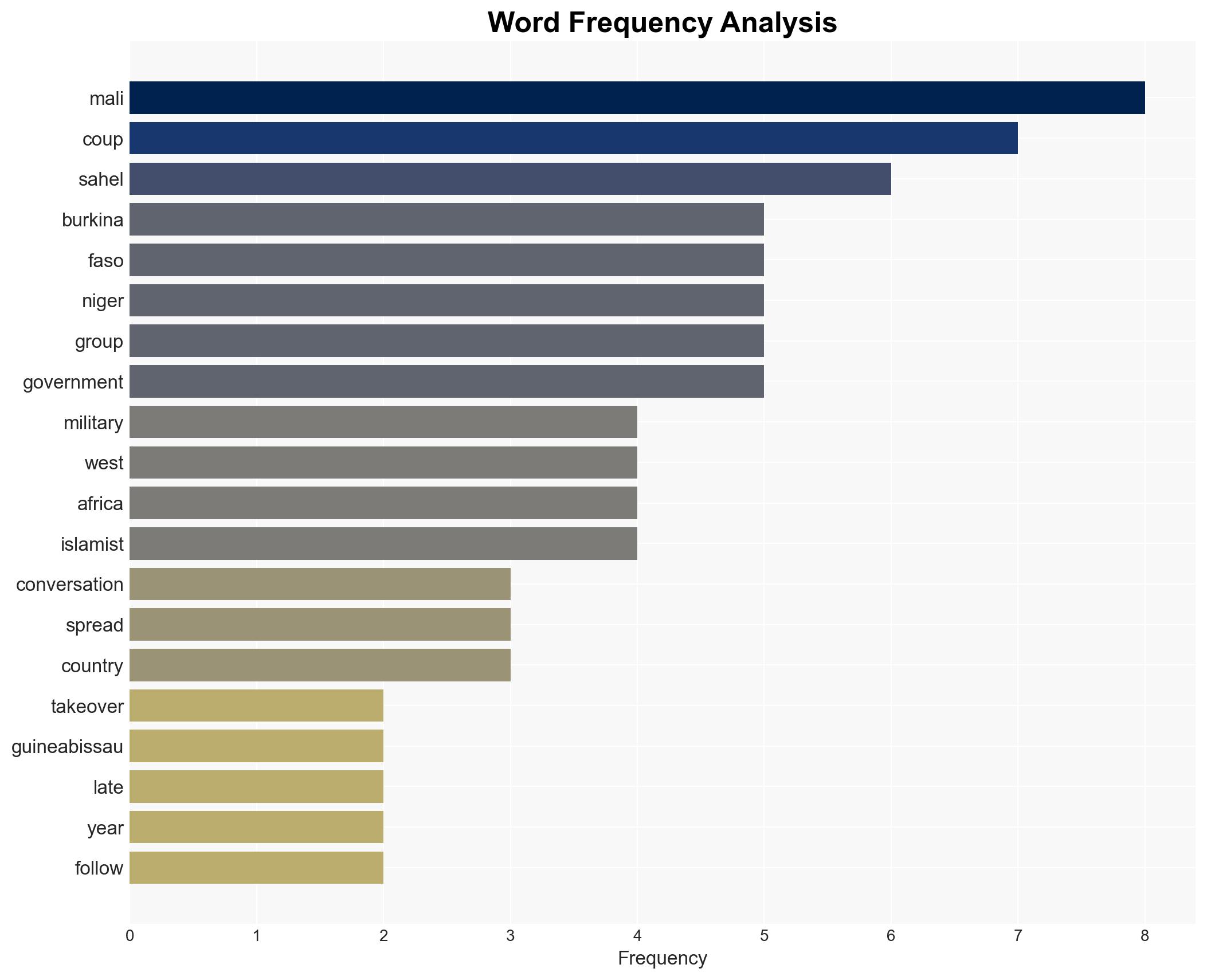
The recent coup in Guinea-Bissau is part of a broader pattern of military takeovers in West Africa, particularly in the Sahel region. This trend is driven by weak governance, regional instability, and shifting geopolitical alliances, notably towards Russia. The situation poses significant risks to regional stability and international interests. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to existing information gaps and potential biases in source reporting.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The coup cascade in West Africa is primarily driven by internal factors such as weak governance, corruption, and local insurgencies. Supporting evidence includes the unique triggers for each coup and the historical context of governance issues. Contradicting evidence includes external influence from foreign powers.
- Hypothesis B: External influences, particularly from Russia and the Wagner Group, are the primary drivers of the coup cascade, leveraging anti-Western sentiment to gain strategic footholds. Supporting evidence includes the presence of Russian mercenaries and anti-French sentiment. Contradicting evidence includes the internal governance issues that predate these influences.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the consistent pattern of governance failures and local insurgencies across the affected countries. However, increased Russian involvement could shift this judgment, especially if further evidence of direct intervention emerges.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Governance failures are the primary drivers of instability; Russian involvement is opportunistic rather than foundational; regional anti-Western sentiment is genuine and not solely externally manipulated.
- Information Gaps: Detailed intelligence on the extent of Russian involvement and local support for military regimes; specific triggers for each coup beyond general governance issues.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in sources emphasizing Russian involvement; risk of manipulation by local actors to justify military takeovers.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ongoing coup cascade could further destabilize the Sahel, exacerbating existing conflicts and humanitarian crises. This may lead to increased foreign intervention and shifts in regional alliances.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased Russian influence and decreased Western presence, altering regional power dynamics.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced operational capabilities for insurgent groups exploiting governance vacuums; increased regional instability.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased disinformation campaigns by foreign actors to influence local populations and international perceptions.
- Economic / Social: Further economic decline and social unrest due to instability and governance failures, potentially leading to increased migration pressures.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Intensify intelligence collection on Russian activities and local military intentions; engage with regional partners to stabilize governance structures.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen regional alliances and support capacity-building initiatives; monitor shifts in public sentiment and foreign influence.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Stabilization through international cooperation and governance reforms. Worst: Escalation of conflicts and increased foreign intervention. Most-Likely: Continued instability with sporadic foreign influence and local insurgencies.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Regional Focus, coup cascade, West Africa, governance, Russian influence, Sahel instability, anti-Western sentiment, insurgency
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Regional Focus Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us