Data Breach at Marquis Software Solutions Exposes Customer Information of Over 250,000 Individuals
Published on: 2025-12-04
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Marketing and Compliance Software Vendor to Banks Breached
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
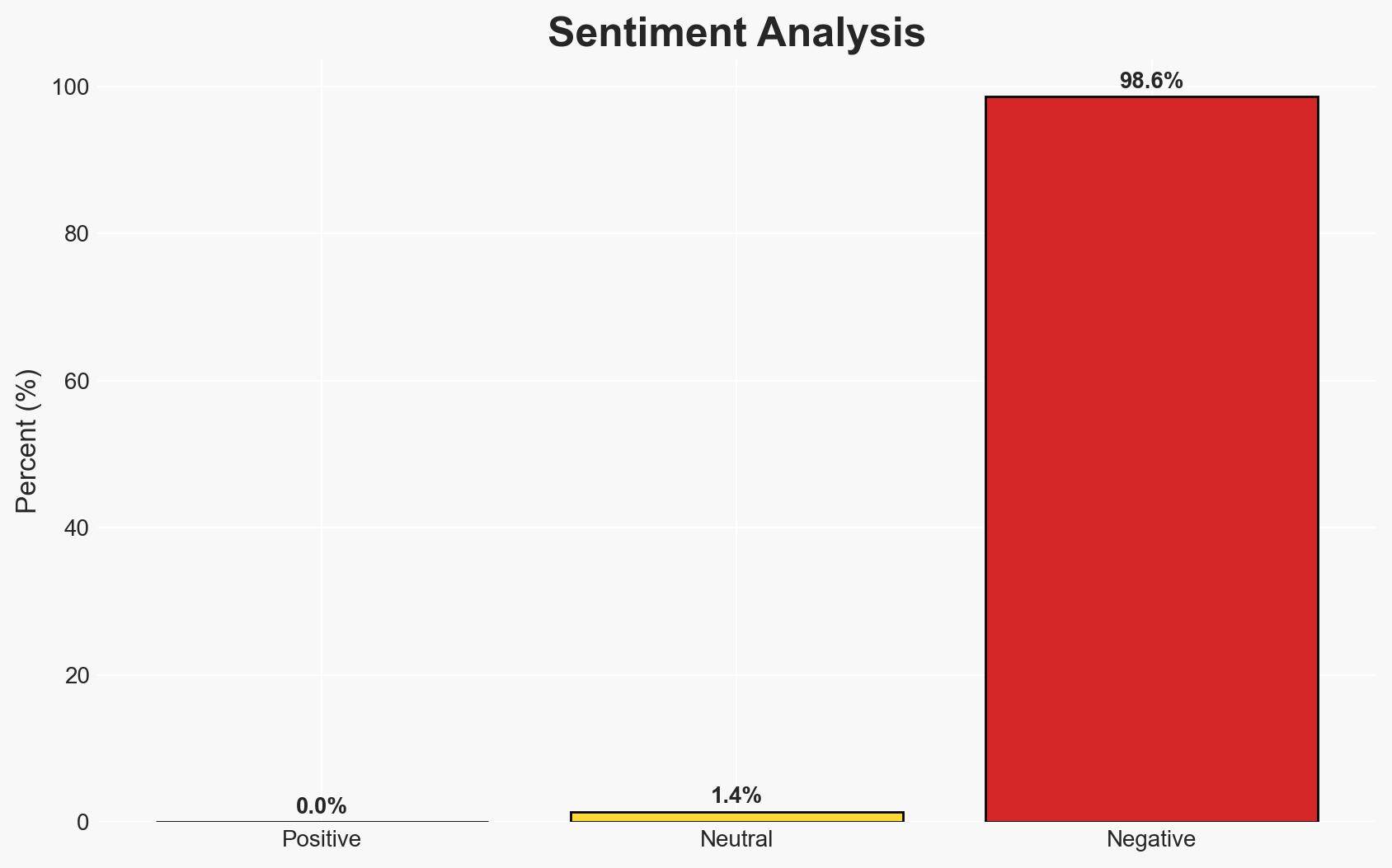
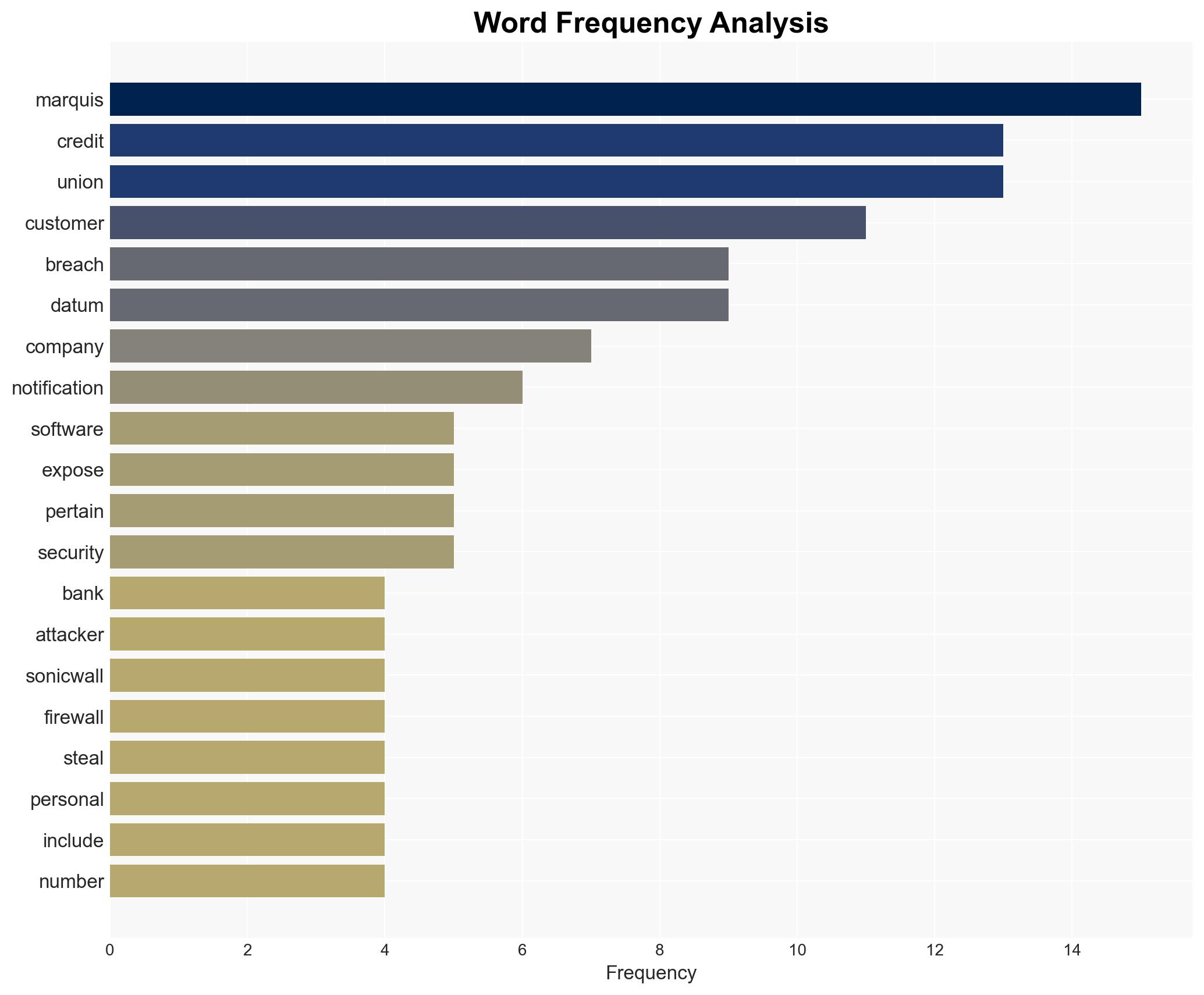
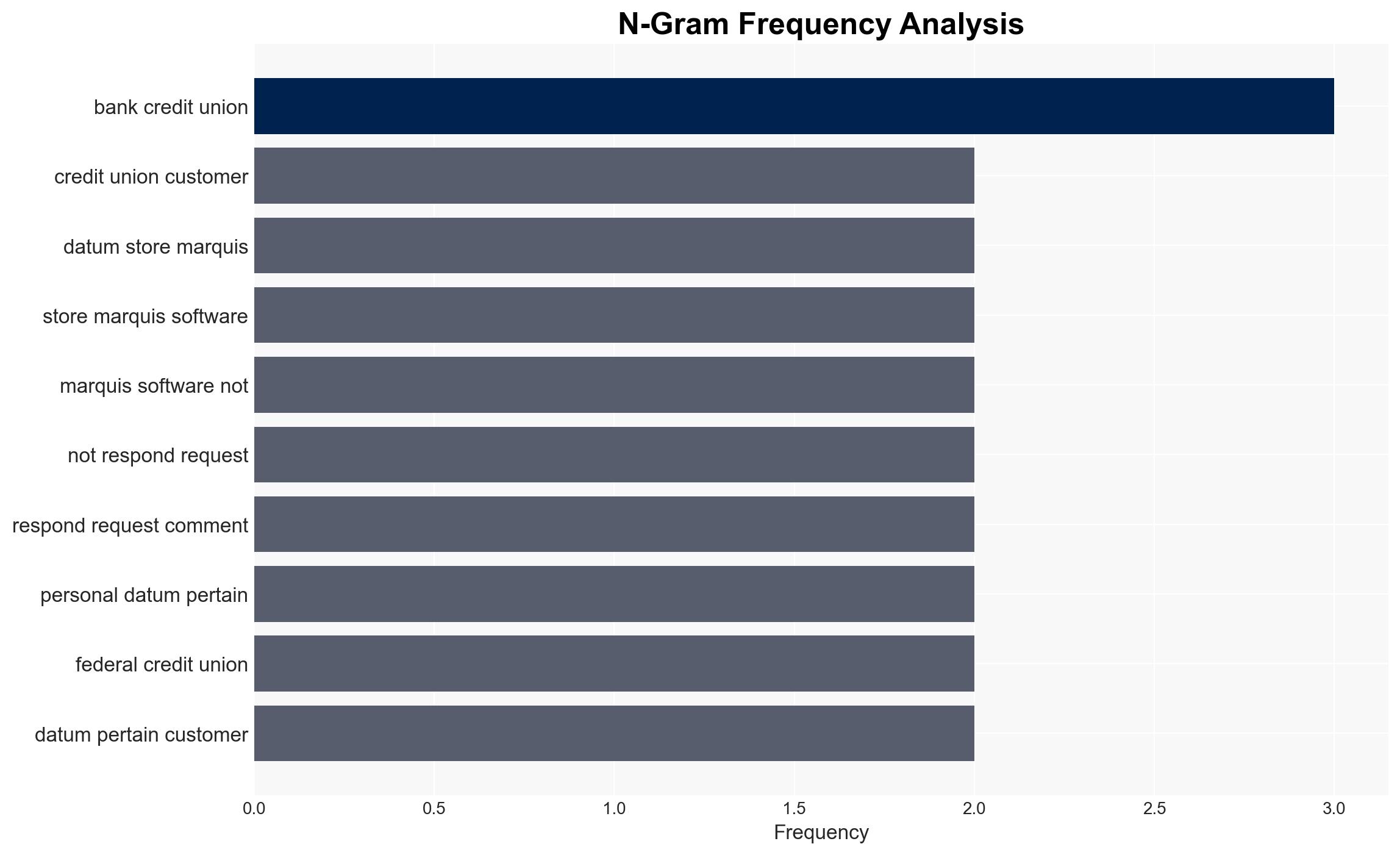
The data breach at Marquis Software Solutions has exposed personal information of over 250,000 individuals, affecting numerous banks and credit unions. The breach was facilitated by a ransomware attack exploiting a SonicWall firewall vulnerability. The incident poses significant risks to the financial sector’s data security. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to incomplete data on the extent of data theft and potential impacts.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The breach was primarily financially motivated, with attackers seeking ransom payments and potentially selling stolen data on illicit markets. This is supported by the fact that a ransom was paid and the attack involved ransomware. However, the lack of clarity on data theft limits full confirmation.
- Hypothesis B: The breach may have been part of a broader espionage operation targeting financial institutions to gather strategic information. While the breach’s focus on financial data could support this, there is no direct evidence of state-sponsored involvement or strategic data targeting.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the known use of ransomware and ransom payment. Indicators such as further data leaks or connections to known espionage groups could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The breach was limited to Marquis’ environment; attackers primarily sought financial gain; affected institutions will manage customer notifications effectively.
- Information Gaps: Extent of data theft, identity of attackers, and full impact on affected institutions remain unclear.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in relying on breach notifications and company statements; risk of deception in attackers’ motives and methods.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This breach could lead to increased scrutiny of third-party vendors in the financial sector, potentially prompting regulatory changes. It may also encourage other cybercriminals to target similar vulnerabilities.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory pressure on financial software vendors.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment for financial institutions, necessitating improved cybersecurity measures.
- Cyber / Information Space: Likely increase in ransomware attacks targeting financial services; potential misinformation campaigns exploiting the breach.
- Economic / Social: Possible loss of consumer trust in affected institutions, impacting their financial stability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct thorough forensic analysis, enhance monitoring of affected networks, and improve communication with affected customers.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen partnerships with cybersecurity firms, enhance vendor risk management practices, and invest in advanced threat detection capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid containment and mitigation prevent further data misuse, restoring consumer confidence.
- Worst: Additional breaches occur, leading to significant financial and reputational damage.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in cybersecurity posture reduce immediate risks, but long-term vigilance is required.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Marquis Software Solutions
- SonicWall
- Norway Savings Bank
- CoVantage Credit Union
- Community 1st Credit Union
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, ransomware, financial sector, data breach, third-party risk, regulatory compliance, information security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us