Strengthening Password Protocols to Enhance Cybersecurity in Operational Technology Systems
Published on: 2025-12-04
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: How strong password policies secure OT systems against cyber threats
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
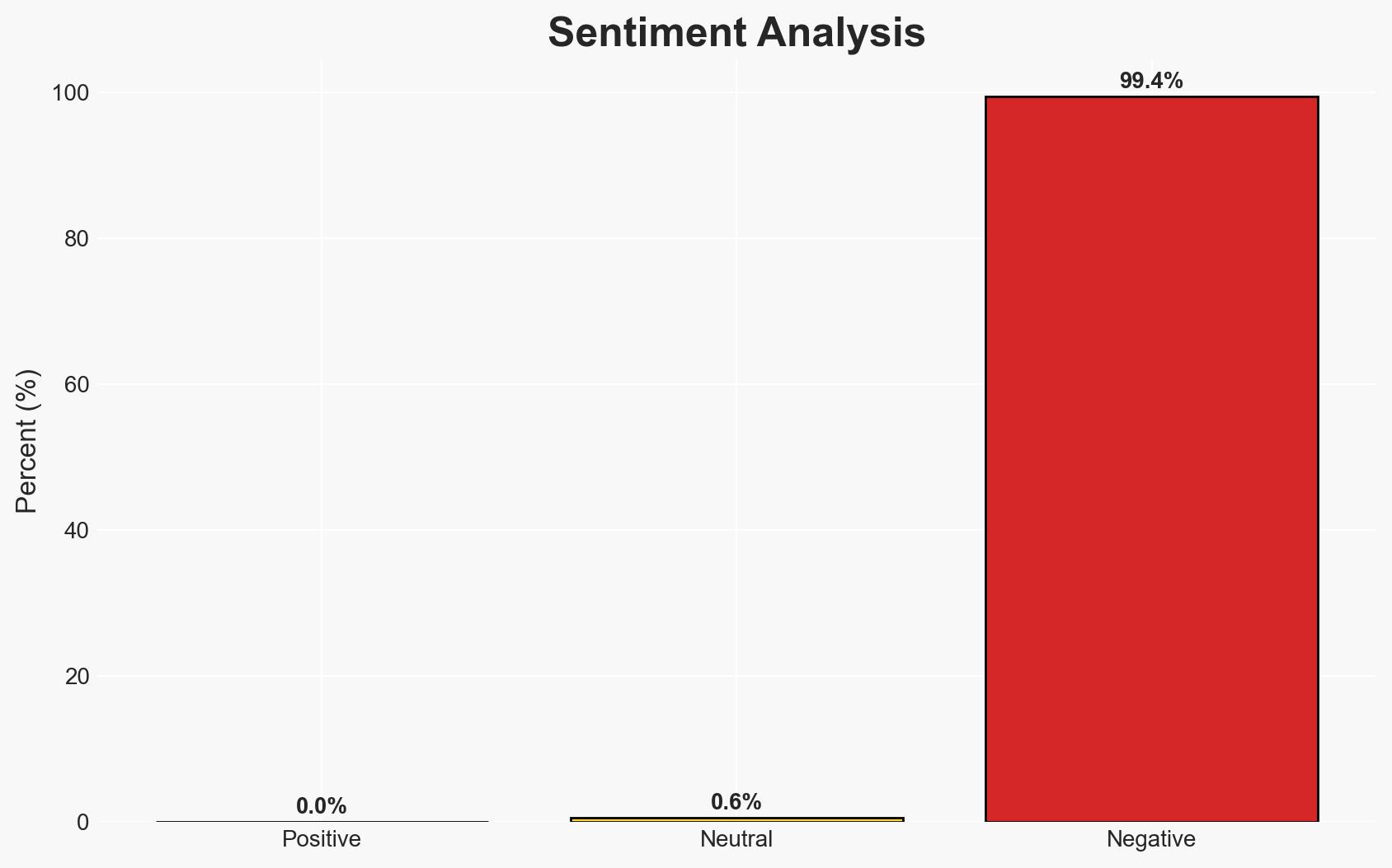
Operational Technology (OT) systems are increasingly vulnerable to cyber threats due to outdated infrastructure and the integration of IT and IoT elements. Implementing strong password policies is critical to mitigating these risks. The most likely hypothesis is that enhanced password security will reduce vulnerabilities, but challenges remain due to legacy systems and shared access practices. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Strengthening password policies in OT environments will significantly reduce cyber vulnerabilities. This is supported by the critical role passwords play in security and the potential to mitigate risks associated with shared accounts and remote access. However, uncertainties include the adaptability of legacy systems to new security protocols.
- Hypothesis B: Enhanced password policies will have limited impact due to the inherent vulnerabilities of outdated OT systems and the complexity introduced by IT/OT convergence. While password policies are important, the systemic issues of legacy infrastructure and shared access may continue to pose significant risks.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported, given the fundamental role of passwords in security frameworks. However, the effectiveness of this approach is contingent on addressing legacy system constraints and ensuring comprehensive implementation. Indicators such as successful integration of password policies in legacy systems could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: OT systems can be updated to support stronger password policies; Multi-factor authentication can be effectively integrated; Users will comply with new security protocols; Remote access can be secured without significant operational disruption.
- Information Gaps: Specific data on the current state of OT system updates and the extent of password policy implementation; Detailed understanding of user compliance rates.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on password policies as a singular solution; Vendor bias in promoting specific security tools; Possible underreporting of vulnerabilities due to reputational concerns.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development of stronger password policies in OT systems could lead to improved security postures but may also expose gaps in legacy infrastructure adaptation. This evolution will interact with broader dynamics of cybersecurity and infrastructure resilience.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased focus on national infrastructure protection could lead to policy shifts or international cooperation in cybersecurity.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced security measures could deter cybercriminals but may also push them to exploit other vulnerabilities.
- Cyber / Information Space: A focus on password security could drive innovation in cybersecurity solutions and promote best practices across sectors.
- Economic / Social: Improved security may bolster confidence in critical infrastructure, but the cost of upgrades could impact budgets and resource allocation.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive audit of current password policies and infrastructure vulnerabilities; Initiate training programs for users on new security protocols.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms to enhance OT security; Invest in upgrading legacy systems to support modern security measures.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful integration of password policies leads to a significant reduction in cyber incidents.
- Worst: Failure to address legacy system vulnerabilities results in continued cyber threats.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in security posture with ongoing challenges in adapting legacy systems.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
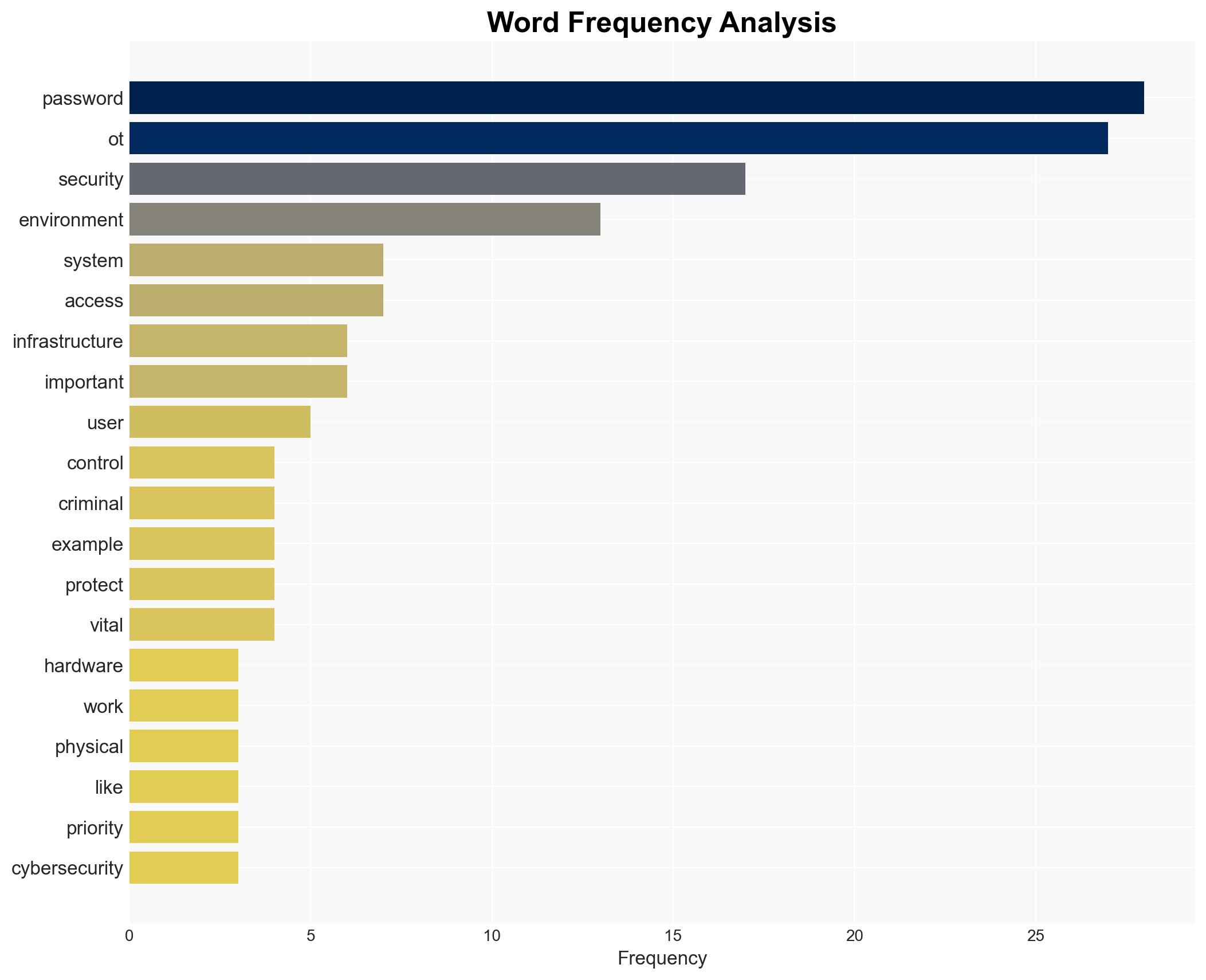
Cybersecurity, operational technology, password policies, infrastructure security, IT/OT convergence, legacy systems, remote access vulnerabilities
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us