Identifying and Avoiding Holiday Scams: Protect Yourself from Phishing and Fraudulent Links
Published on: 2025-12-08
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Is That Link Legit How to Spot and Avoid Scams in Your Inbox
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
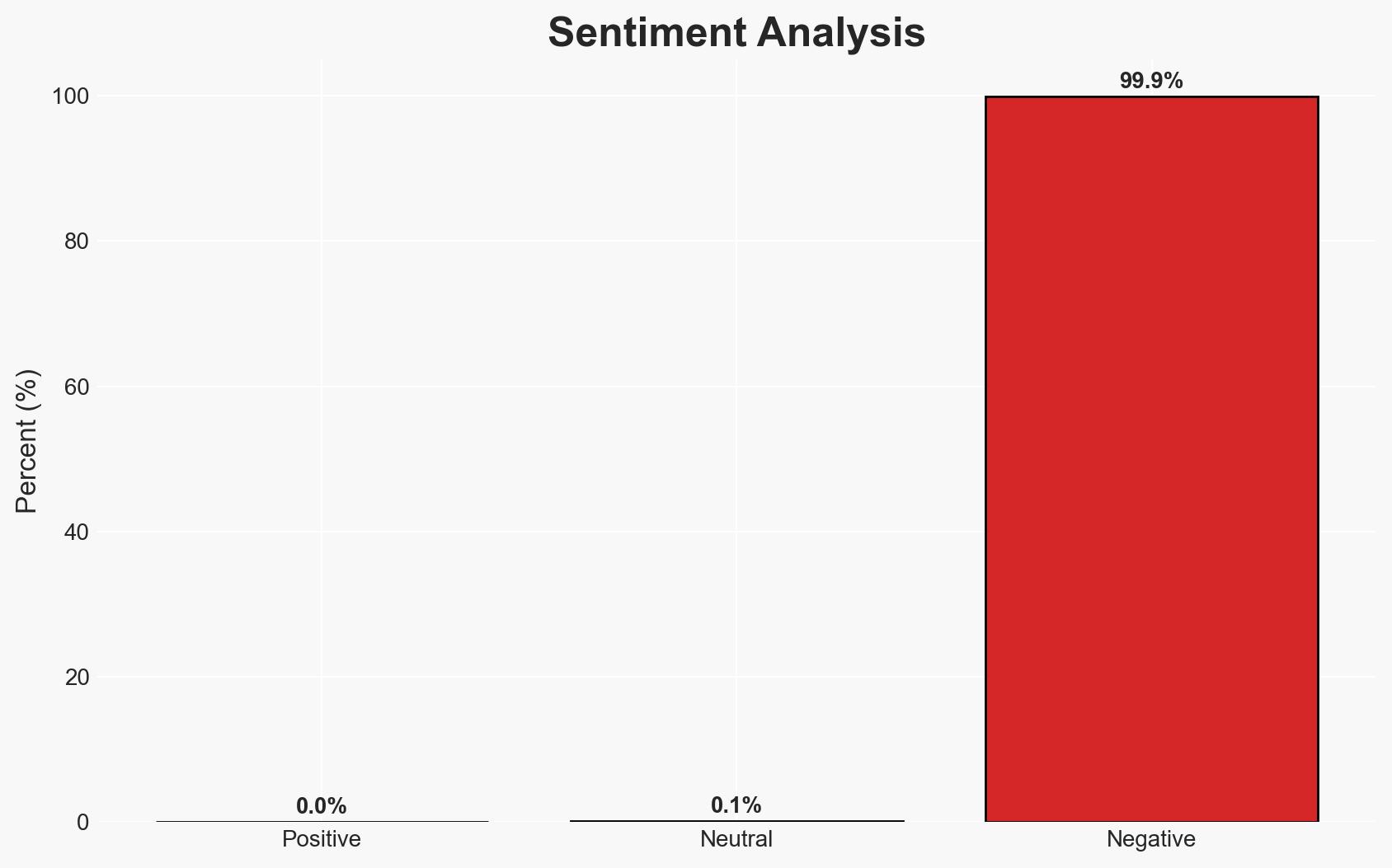
The holiday season sees a significant increase in phishing scams, leveraging sophisticated techniques to deceive users. The primary threat is financial loss and data theft, affecting individuals and businesses. The most likely hypothesis is that cybercriminals will continue to refine their methods, exploiting seasonal vulnerabilities. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to evolving tactics and limited specific data.
2. Competing Hypotheses
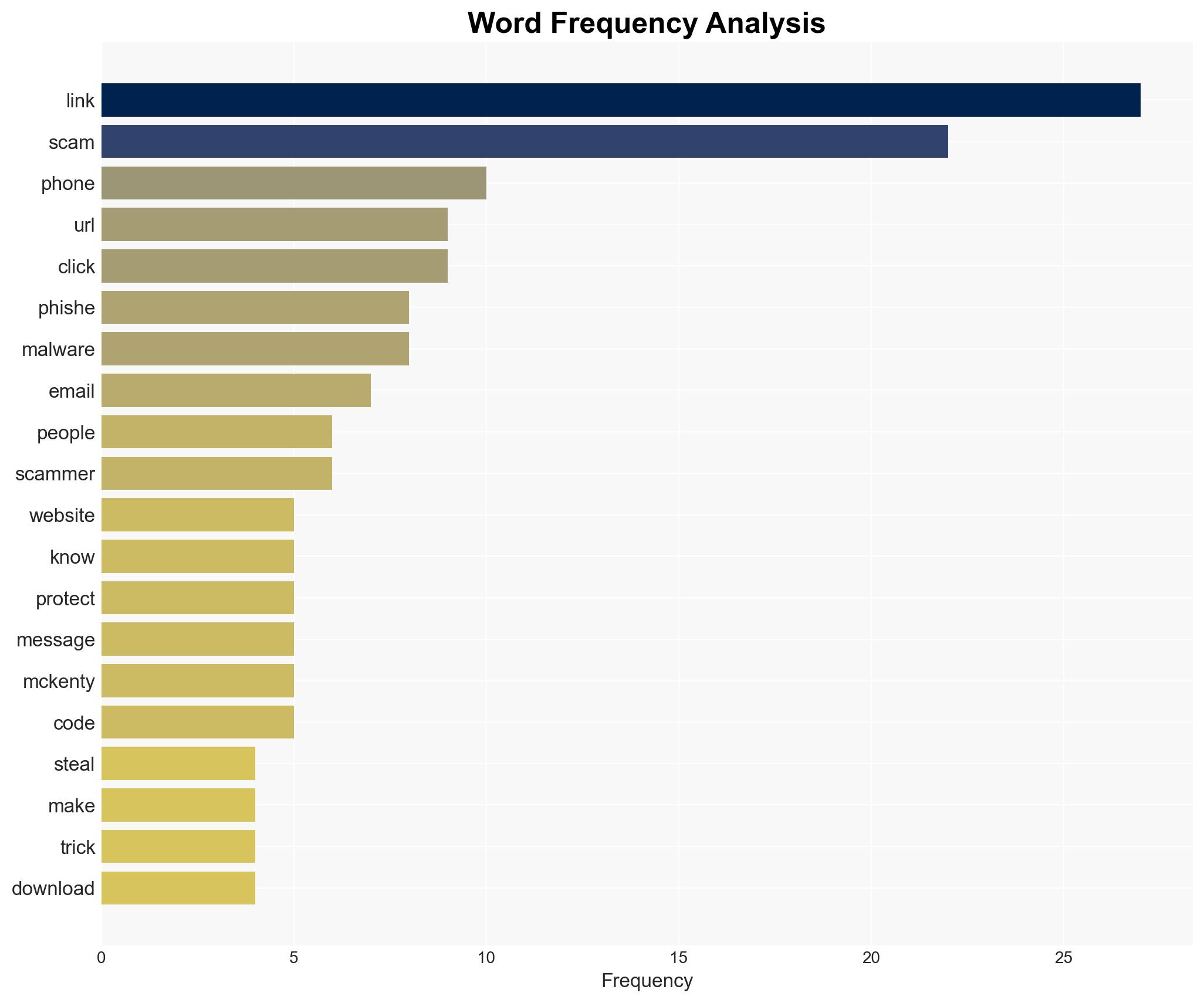
- Hypothesis A: Cybercriminals are primarily targeting individuals with phishing scams during the holiday season, using advanced techniques such as AI to increase success rates. This is supported by the reported increase in scams and the use of sophisticated URL manipulation.
- Hypothesis B: Cybercriminals are equally targeting businesses and individuals, with businesses being a more lucrative target due to higher potential financial gains. While the snippet focuses on individual scams, the mention of business protection suggests broader targeting.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the specific focus on individual-targeted scams in the snippet. Indicators such as increased sophistication in URL manipulation and AI usage could shift this judgment if more evidence of business-targeted attacks emerges.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Cybercriminals will continue to exploit seasonal vulnerabilities; individuals are less equipped to identify sophisticated scams; AI will enhance phishing effectiveness.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the proportion of scams targeting businesses versus individuals; specific AI techniques used in phishing scams.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in focusing on individual scams due to public reporting; deception risk from cybercriminals using legitimate-seeming URLs.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of phishing scams could lead to increased financial losses and data breaches, impacting trust in digital communications and e-commerce.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for international tensions if state actors are suspected of involvement.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased burden on cybersecurity infrastructure and law enforcement resources.
- Cyber / Information Space: Greater need for public awareness campaigns and cybersecurity enhancements.
- Economic / Social: Potential decrease in consumer confidence in online transactions during peak shopping periods.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance public awareness campaigns on identifying phishing scams; increase monitoring of phishing patterns.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms to improve detection and response; invest in AI-driven defense mechanisms.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Reduction in phishing success due to improved awareness; Worst: Significant financial losses and data breaches; Most-Likely: Continued refinement of phishing tactics with moderate success rates.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Joshua McKenty, CEO of Polyguard.ai
- Dave Meister, Cybersecurity Spokesman for Check Point
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, phishing, data theft, AI-driven scams, financial loss, public awareness, holiday season
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us