Surge in Infostealer Malware Linked to Lax Security and Credential Theft Among Major UK Companies
Published on: 2025-12-15
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: What is driving the rise of infostealer malware
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The rise of infostealer malware is primarily driven by the exploitation of weak security practices and the blending of personal and corporate IT environments. Large corporations, despite their resources, are particularly vulnerable, suggesting even greater risks for smaller enterprises. This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to identified information gaps and potential biases in source data.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Infostealer malware proliferation is primarily due to inadequate security policies and practices within organizations. Supporting evidence includes the high incidence of weak passwords and the blending of personal and corporate IT use. However, the extent of these practices across different sectors remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The rise is driven by external factors, such as increased sophistication of cybercriminal tactics and tools. While the use of hijacked session cookies and targeted phishing campaigns supports this, it does not fully account for the internal vulnerabilities exploited.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the direct link between internal security lapses and the success of infostealer attacks. Indicators such as improved security policies or a decrease in credential leaks could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Organizations have not fully implemented robust security measures; blending of personal and corporate IT use is widespread; cybercriminals prioritize low-effort, high-reward attacks.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on security practices across different industries; specific methods used by cybercriminals to distribute infostealer malware.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in source data focusing on UK companies; risk of underestimating the adaptability of cybercriminals.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The continued rise of infostealer malware could lead to significant disruptions in business operations and increased financial losses. Over time, this may necessitate a reevaluation of cybersecurity strategies and policies across industries.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased international cooperation on cybersecurity standards and practices.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment requiring enhanced monitoring and response capabilities.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on securing digital identities and improving authentication methods.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact due to data breaches and loss of consumer trust; social implications of increased cybercrime awareness.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct security audits to identify vulnerabilities; implement stronger password policies and multi-factor authentication.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop employee training programs on cybersecurity best practices; invest in advanced threat detection technologies.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Significant reduction in infostealer incidents due to improved security measures. Worst: Continued rise in attacks leading to major data breaches. Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in security posture with ongoing challenges.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
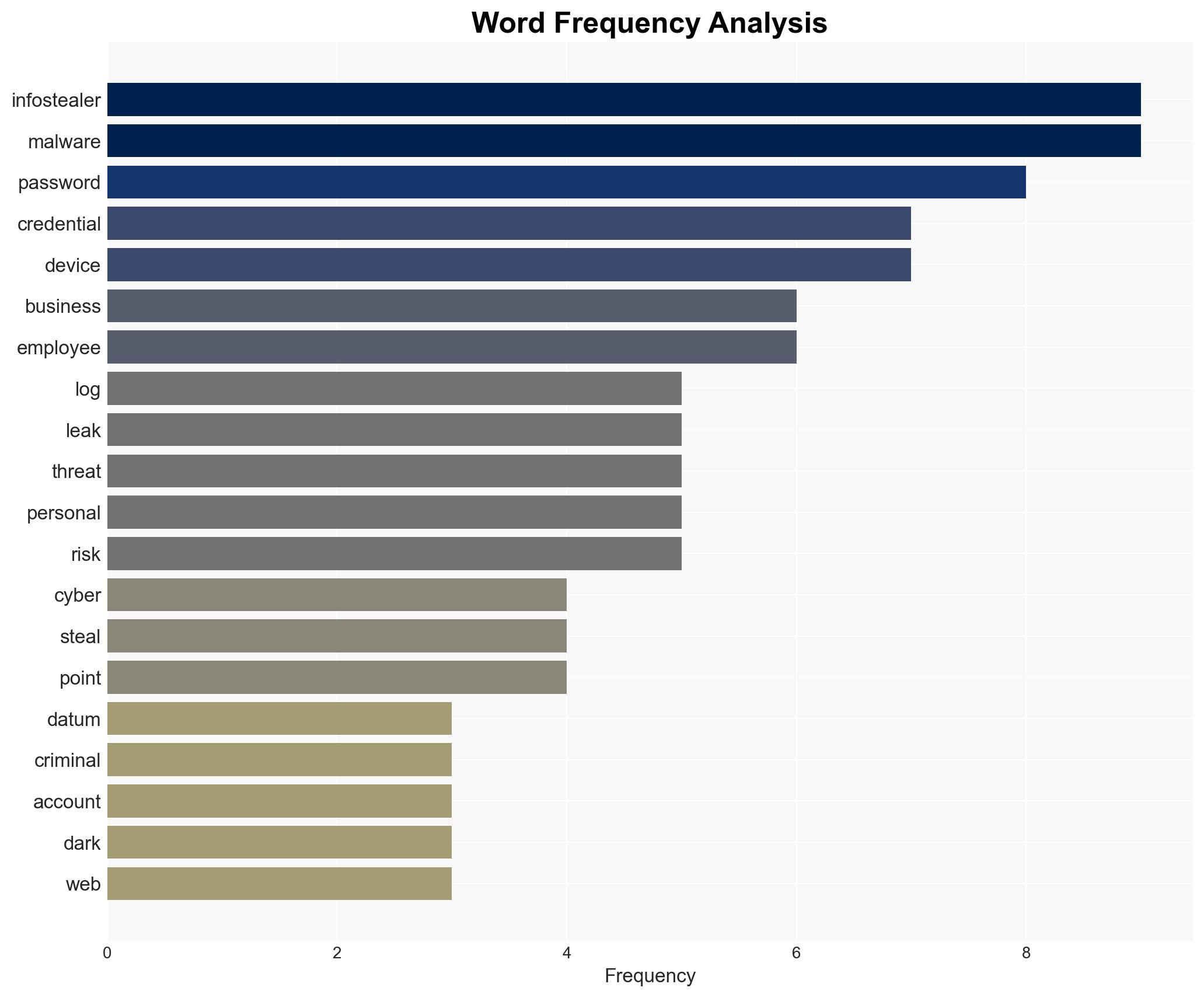
cybersecurity, infostealer malware, corporate IT security, cybercrime, data breach, information security, digital identity
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us