Bosnia’s War: Three Decades Later, Unraveling the Atrocities of Ethnic Cleansing and Their Impact
Published on: 2025-12-15
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Bosnias war 30 years on How did the atrocities happen
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
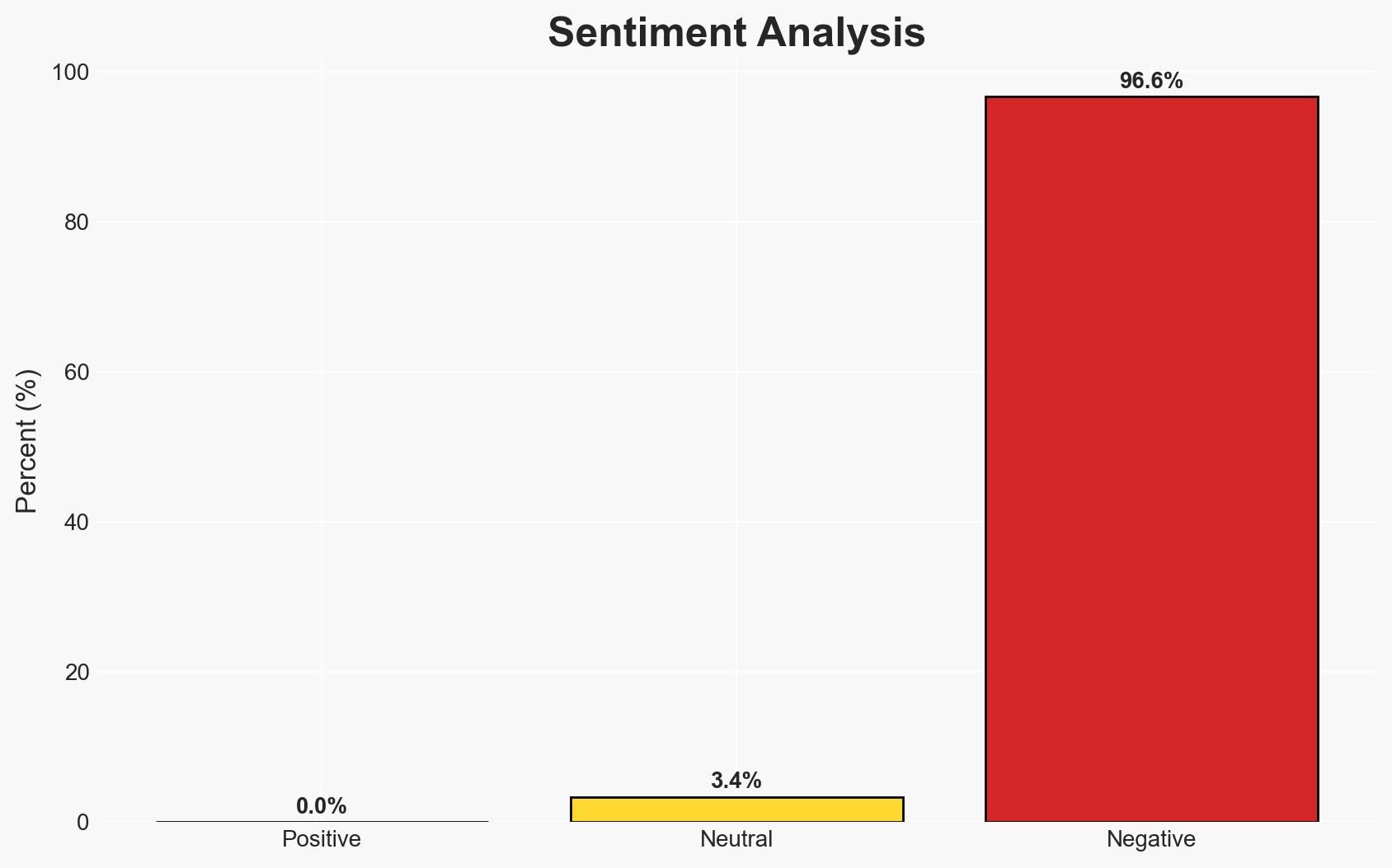
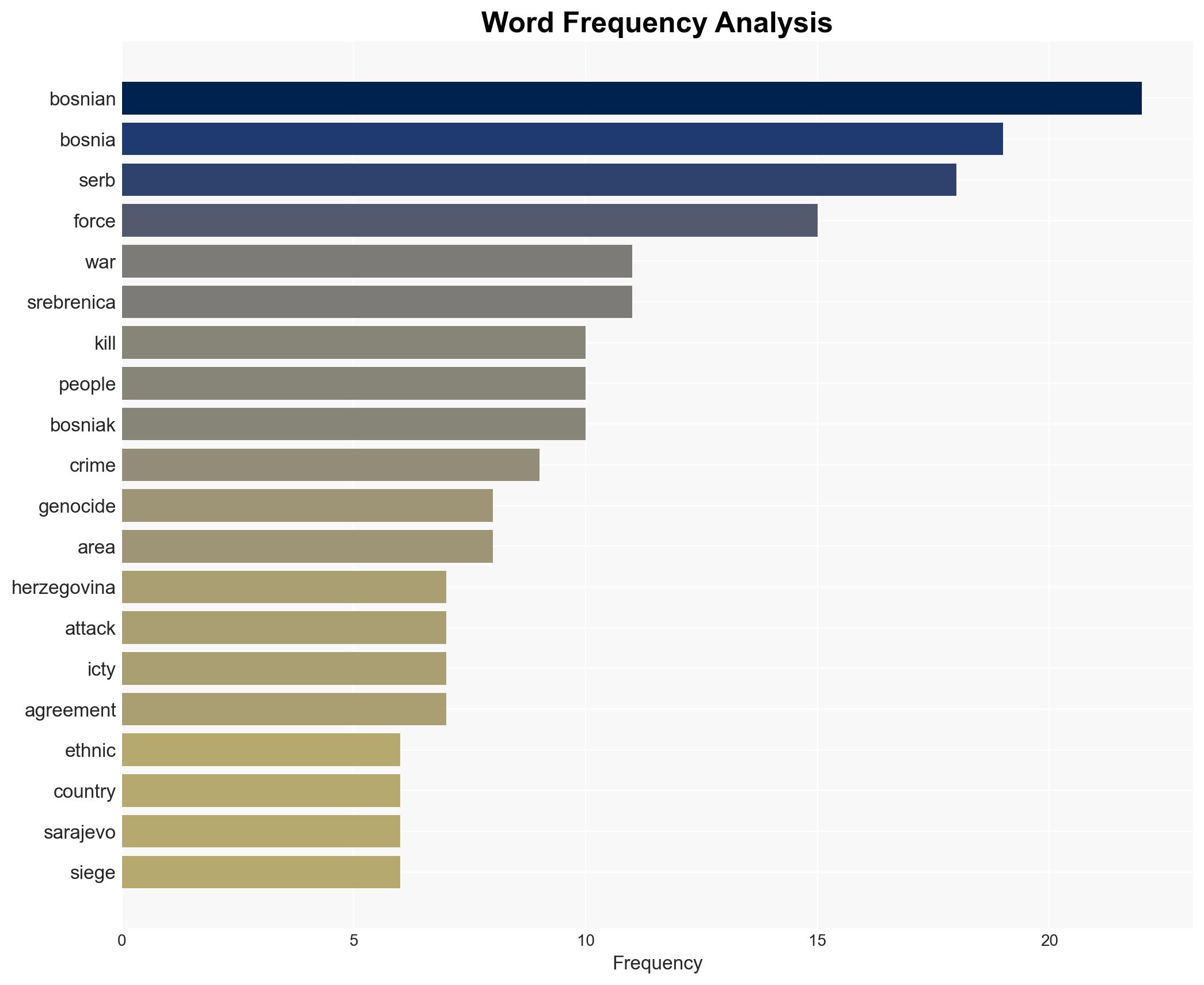
The Bosnian War, marked by ethnic cleansing and genocide, resulted from the disintegration of Yugoslavia and rising nationalism. The conflict left deep scars, with significant civilian casualties and displacement. The most likely hypothesis is that ethnic and nationalist tensions, exacerbated by external influences, were the primary drivers. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The war was primarily driven by ethnic tensions and nationalist ambitions within Bosnia and Herzegovina, exacerbated by the collapse of Yugoslavia. Supporting evidence includes the ethnic cleansing campaigns and the formation of separate Serb and Croat entities. Key uncertainties include the extent of external influence versus internal dynamics.
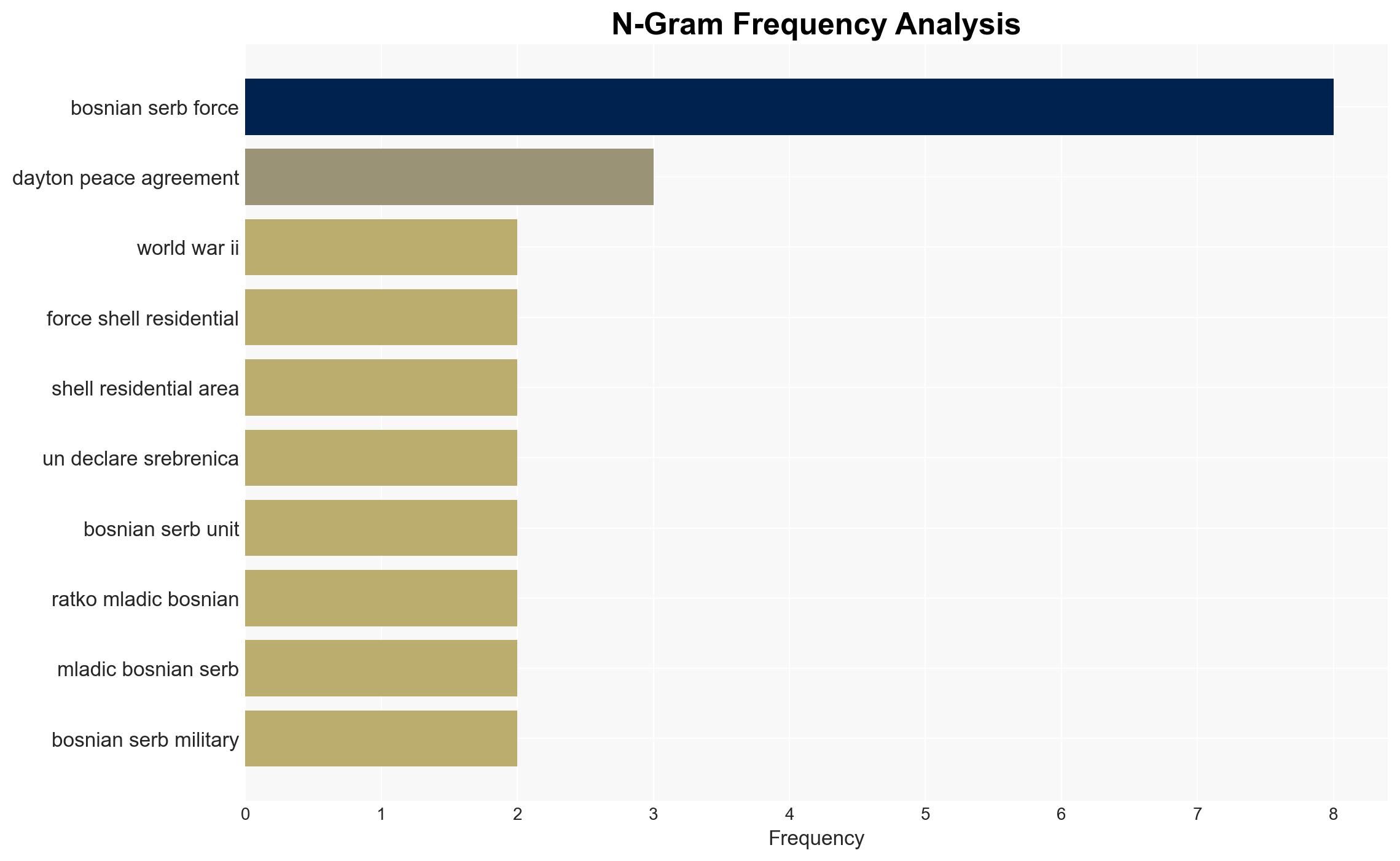
- Hypothesis B: External actors, particularly Serbia under Slobodan Milosevic, were the main instigators, using nationalist rhetoric to justify territorial expansion. Supporting evidence includes Serbia’s support for Bosnian Serb forces and the siege of Sarajevo. Contradicting evidence includes the internal ethnic divisions that predated external interventions.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the documented ethnic divisions and nationalist projects within Bosnia. Indicators that could shift this judgment include new evidence of external orchestration or manipulation.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The ethnic divisions were a primary cause of the conflict; external support was a significant but not sole factor; post-war reconciliation efforts have been insufficient.
- Information Gaps: Detailed accounts of external influence on internal political decisions; comprehensive data on post-war reconciliation success.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in sources emphasizing ethnic narratives; risk of manipulation in historical accounts by involved parties.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The legacy of the Bosnian War continues to affect regional stability, with potential for renewed tensions. The interplay of ethnic divisions and external influences remains a critical factor.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for renewed ethnic tensions or separatist movements; influence of external actors in regional politics.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Risk of radicalization or resurgence of nationalist militias; ongoing security challenges in maintaining peace.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for misinformation campaigns exploiting ethnic divisions; cyber threats targeting reconciliation efforts.
- Economic / Social: Continued economic instability due to unresolved displacement issues; social cohesion challenges in multi-ethnic communities.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of ethnic tensions; engage in dialogue with regional stakeholders to prevent escalation.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for ethnic reconciliation; strengthen partnerships with regional and international organizations.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Successful reconciliation and economic recovery; Worst: Renewed ethnic conflict; Most-Likely: Continued low-level tensions with sporadic incidents.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Slobodan Milosevic (Serbian leader during the war)
- Republika Srpska (Serb Republic entity within Bosnia)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, ethnic conflict, nationalism, Yugoslavia disintegration, genocide, regional stability, reconciliation, displacement
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us