India indicts two militant groups from Pakistan over deadly Pahalgam attack on tourists
Published on: 2025-12-16
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: India charges Pakistan-based militant groups in Pahalgam attack
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
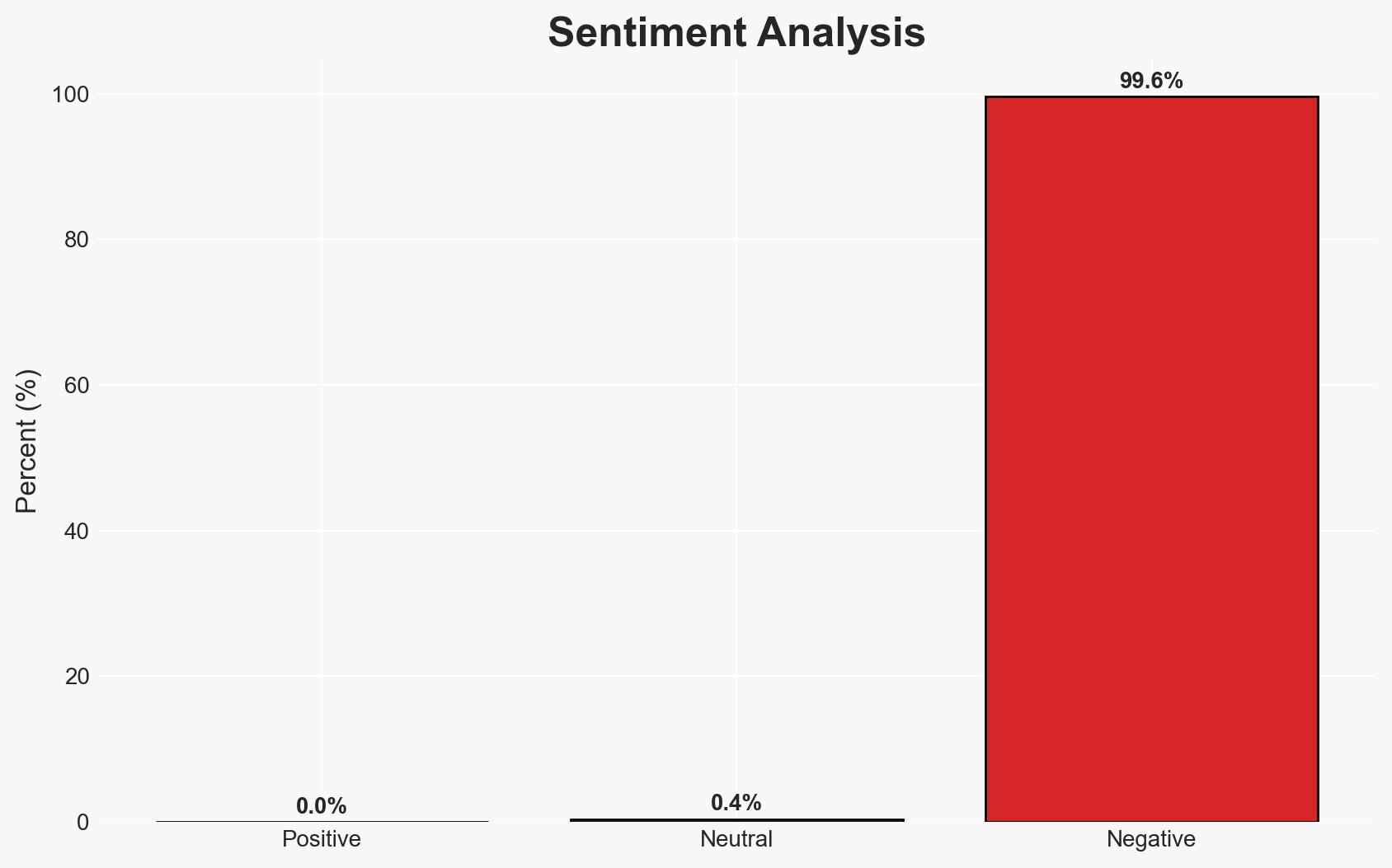
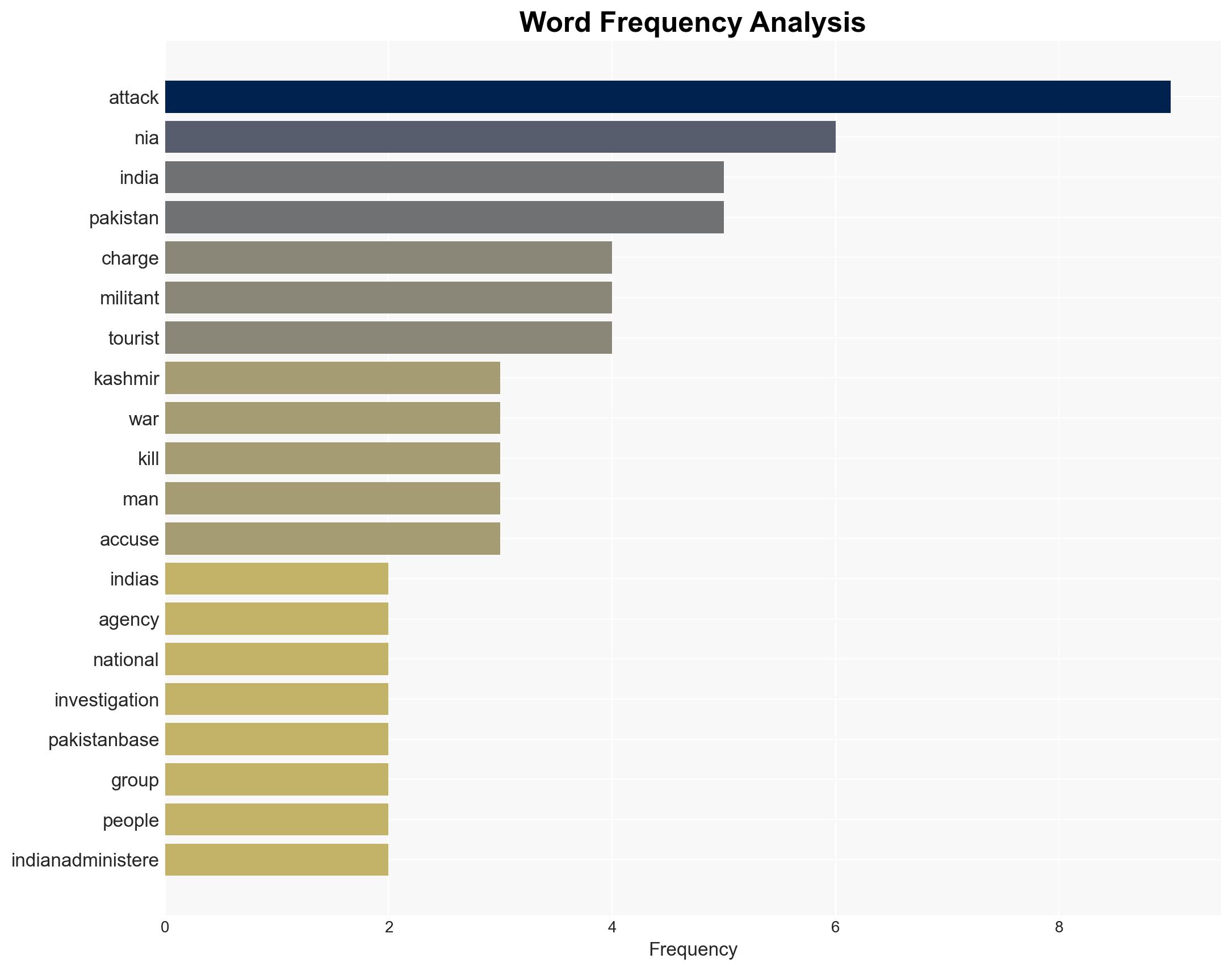
The National Investigation Agency (NIA) of India has charged Pakistan-based militant groups Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT) and The Resistance Front (TRF) with orchestrating the Pahalgam attack in Indian-administered Kashmir, escalating tensions between India and Pakistan. The charges have significant implications for regional security and bilateral relations. The overall confidence level in this assessment is moderate, given the ongoing investigation and lack of response from Pakistan.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The Pahalgam attack was planned and executed by Pakistan-based militant groups LeT and TRF, as charged by the NIA. Supporting evidence includes the NIA’s chargesheet and confessions from detained individuals. Contradicting evidence includes TRF’s initial claim and subsequent denial of involvement, and Pakistan’s denial of responsibility. Key uncertainties include the extent of state involvement or support from Pakistan.
- Hypothesis B: The attack was carried out by local insurgents or rogue elements without direct coordination from Pakistan-based groups. This hypothesis is supported by the complex dynamics within Kashmir and the possibility of local grievances being exploited. However, there is limited direct evidence to support this, and the NIA’s investigation points towards external involvement.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the detailed chargesheet and confessions aligning with the NIA’s narrative. Indicators that could shift this judgment include new evidence of local group involvement or credible denials from Pakistan with supporting evidence.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The NIA’s investigation is thorough and unbiased; Pakistan-based groups have the capability and intent to conduct such attacks; India and Pakistan’s responses are based on strategic calculations rather than immediate emotional reactions.
- Information Gaps: Details on the planning and execution of the attack, Pakistan’s internal communications regarding the incident, and independent verification of the NIA’s findings.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential confirmation bias in the NIA’s investigation, political bias in public statements from both India and Pakistan, and possible misinformation campaigns by involved parties.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could exacerbate tensions between India and Pakistan, potentially leading to further military confrontations and destabilizing the region.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased diplomatic strain, potential for international mediation efforts, and shifts in alliances or support from global powers.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened security measures in Kashmir, potential for retaliatory attacks, and increased counter-terrorism operations.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible increase in cyber-attacks or propaganda efforts by state or non-state actors to influence public perception.
- Economic / Social: Economic disruptions due to instability, impact on tourism in Kashmir, and heightened communal tensions within India.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance intelligence-sharing mechanisms, increase diplomatic engagement with international partners, and monitor for retaliatory actions or misinformation campaigns.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen regional security alliances, invest in counter-terrorism capabilities, and pursue confidence-building measures with Pakistan.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: De-escalation through diplomatic channels, leading to renewed peace talks.
- Worst: Escalation into a broader military conflict, drawing in regional powers.
- Most-Likely: Continued low-intensity conflict with sporadic diplomatic engagements.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT)
- The Resistance Front (TRF)
- National Investigation Agency (NIA)
- Sajid Jatt (alleged Pakistani terrorist handler)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Counter-Terrorism, India-Pakistan relations, Kashmir conflict, regional security, militant groups, geopolitical tensions, intelligence operations
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us