Microsoft to Phase Out RC4 Cipher After 26 Years Amid Security Concerns and Criticism
Published on: 2025-12-16
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Microsoft Will Finally Kill Obsolete Cipher That Has Wreaked Decades of Havoc
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
Microsoft’s decision to deprecate the RC4 cipher, due to its vulnerabilities, marks a significant shift in cybersecurity practices affecting organizations reliant on legacy systems. This move is likely to enhance network security but may pose challenges for entities with outdated infrastructure. The overall confidence level in this assessment is moderate, given the potential for unforeseen complications in legacy system adaptations.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The deprecation of RC4 will significantly enhance security across Windows networks by eliminating a known vulnerability. Supporting evidence includes the historical exploitation of RC4 and Microsoft’s commitment to strengthening encryption standards. However, uncertainties remain regarding the readiness of organizations to transition away from RC4.
- Hypothesis B: The deprecation of RC4 may lead to operational disruptions for organizations reliant on legacy systems, potentially creating new vulnerabilities. This is supported by the continued use of RC4 in some critical systems and the complexity of updating legacy infrastructure. Contradicting evidence includes Microsoft’s provision of tools to facilitate the transition.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to Microsoft’s proactive measures and the clear security benefits of eliminating RC4. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include widespread reports of transition difficulties or new vulnerabilities emerging from the update process.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Organizations will prioritize updating their systems; Microsoft’s tools will be effective in identifying RC4 dependencies; the transition will not introduce new vulnerabilities.
- Information Gaps: The extent of reliance on RC4 in critical systems across different sectors; the readiness of organizations to implement necessary changes.
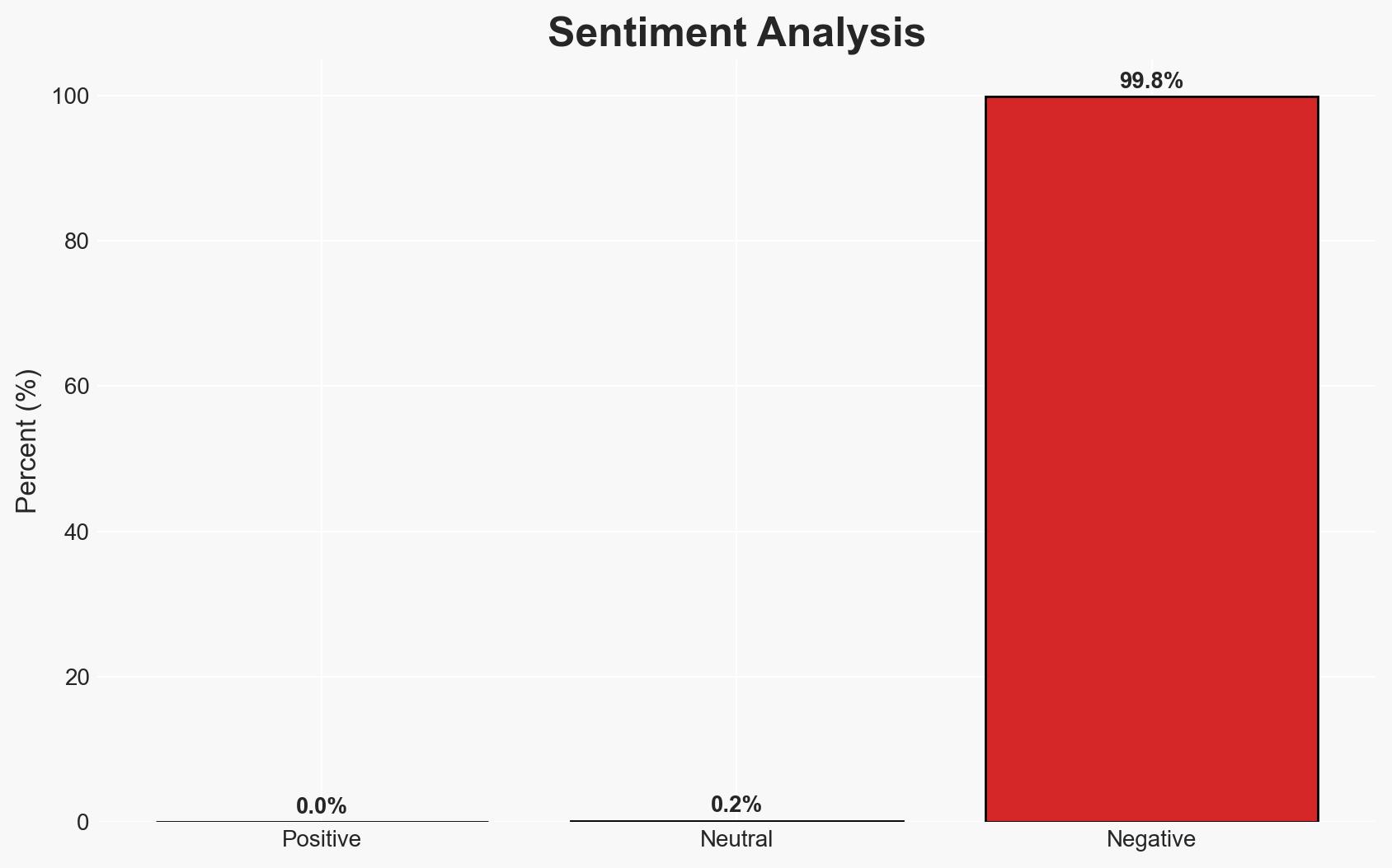
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting the effectiveness of Microsoft’s transition tools; underreporting of transition challenges by organizations due to reputational concerns.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to a more secure digital environment but may also expose gaps in organizational preparedness for cybersecurity updates. The interaction with broader dynamics includes potential shifts in cyber threat landscapes and organizational IT strategies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Limited direct implications; however, improved cybersecurity may indirectly influence national security postures.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced security could reduce the risk of cyber intrusions, indirectly supporting counter-terrorism efforts by protecting critical infrastructure.
- Cyber / Information Space: The deprecation of RC4 may prompt adversaries to seek alternative vulnerabilities, potentially leading to a temporary increase in cyber reconnaissance activities.
- Economic / Social: Organizations may incur costs related to system updates, but long-term benefits include reduced risk of costly breaches.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Organizations should conduct audits to identify RC4 dependencies and begin transition planning. Monitor for any emerging vulnerabilities during the transition period.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures by updating legacy systems and investing in cybersecurity training for IT staff. Foster partnerships with cybersecurity firms for support.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Smooth transition with enhanced security and no significant disruptions.
- Worst: Major operational disruptions and new vulnerabilities emerge, leading to increased cyber threats.
- Most-Likely: Gradual transition with manageable challenges and improved security posture.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Microsoft, Matthew Palko (Microsoft principal program manager), Organizations using Windows networks
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, encryption, legacy systems, Microsoft, network security, RC4 deprecation, IT infrastructure
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us