Fortinet FortiGate Devices Targeted in Active Exploits of Critical SAML SSO Authentication Bypass Flaws
Published on: 2025-12-16
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Fortinet FortiGate Under Active Attack Through SAML SSO Authentication Bypass
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
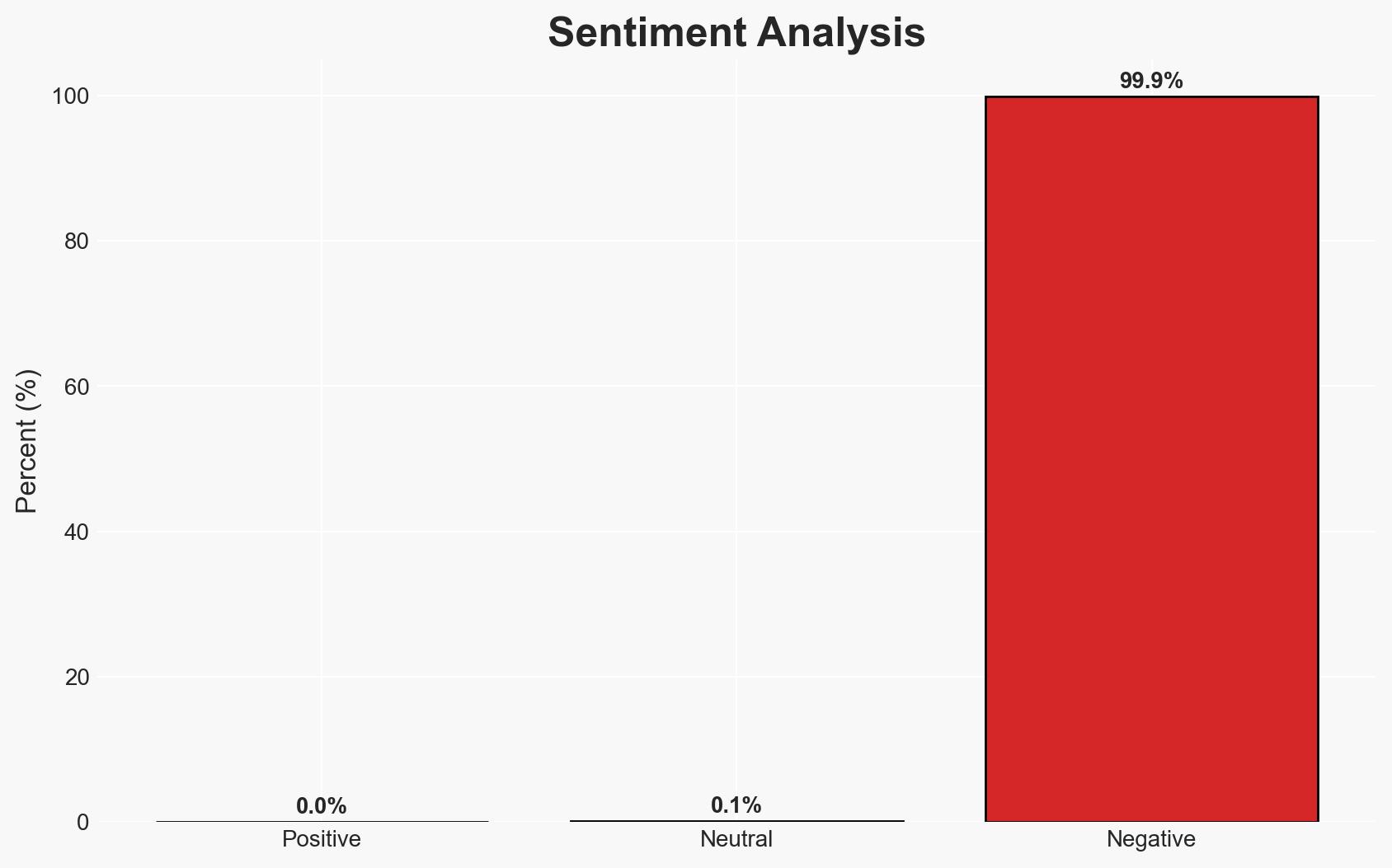
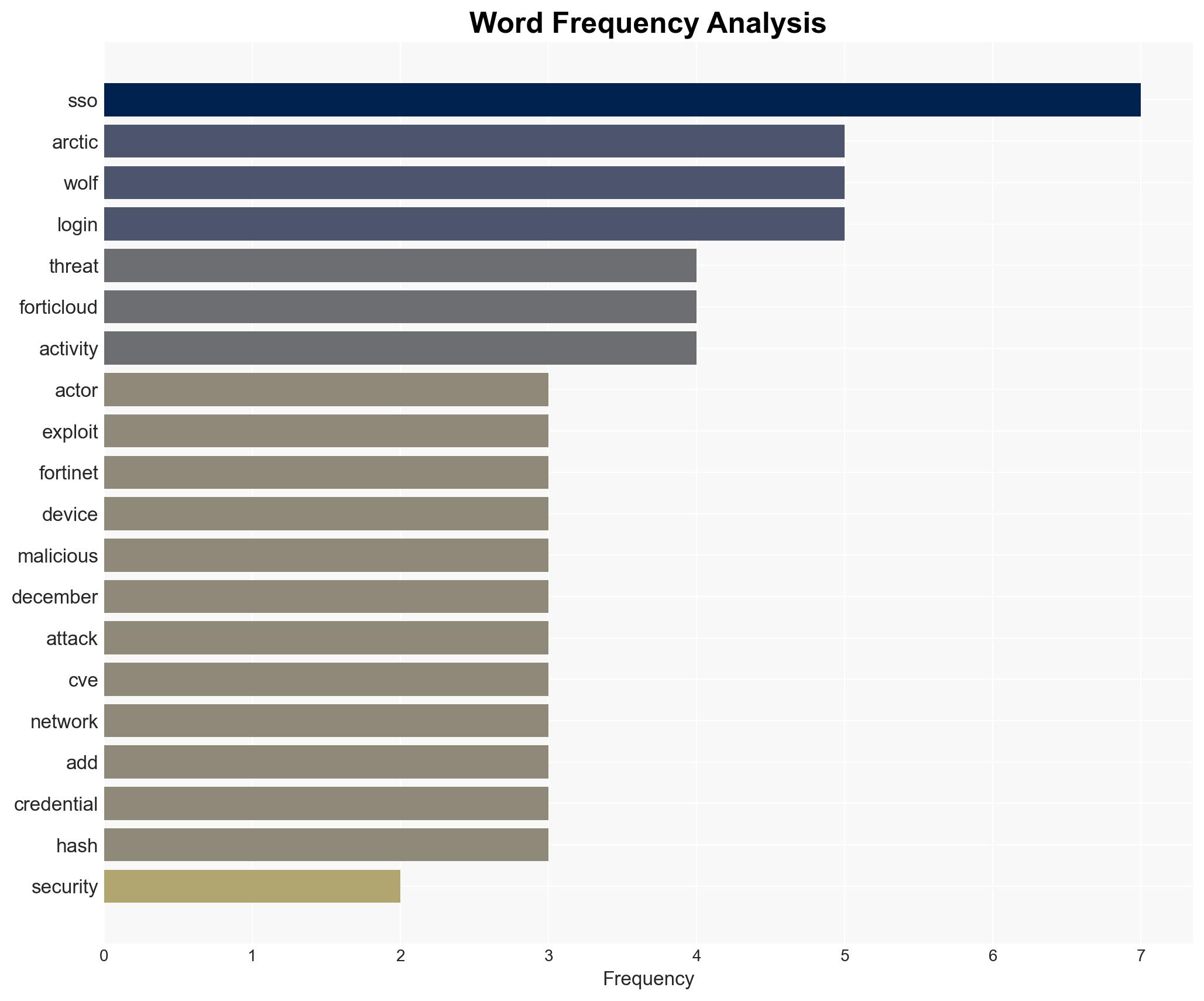
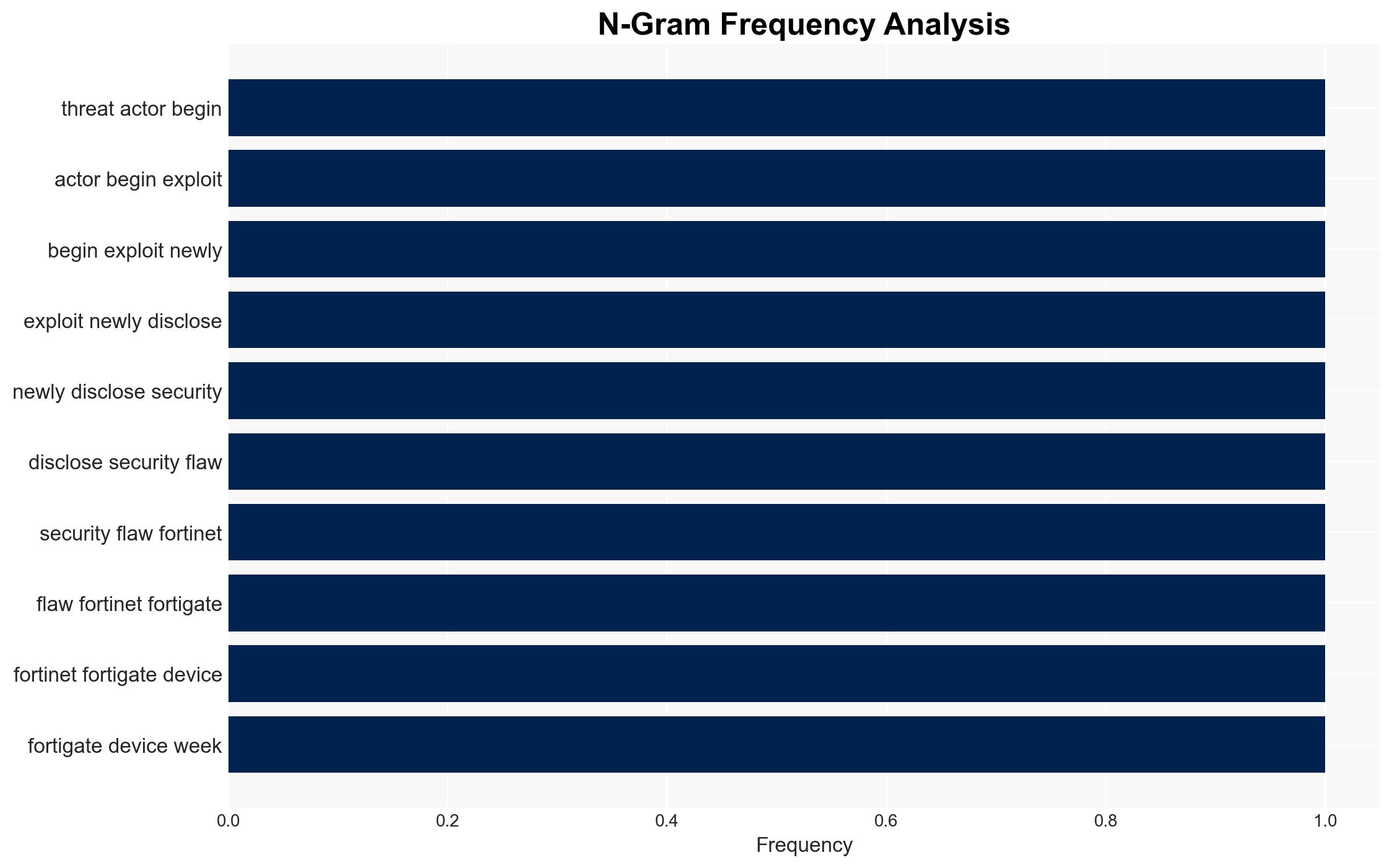
Fortinet FortiGate devices are currently under active attack due to two critical authentication bypass vulnerabilities (CVE-2025-59718 and CVE-2025-59719). The exploitation is opportunistic, affecting a limited number of networks, and involves unauthorized access via SAML SSO. Organizations using these devices should apply patches immediately and disable FortiCloud SSO to mitigate risks. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The attacks are opportunistic, conducted by cybercriminals exploiting the vulnerabilities for financial gain. This is supported by the lack of specific threat actor attribution and the use of common hosting providers. However, the early stage of the campaign leaves room for uncertainty regarding the attackers’ ultimate objectives.
- Hypothesis B: The attacks are a targeted campaign by a sophisticated threat actor aiming to compromise specific organizations for strategic purposes. This hypothesis is less supported due to the opportunistic nature of the attacks and the absence of advanced tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) typically associated with state-sponsored actors.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the opportunistic nature of the attacks and the use of common hosting providers. Indicators that could shift this judgment include the emergence of more sophisticated TTPs or evidence of targeting specific high-value entities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The vulnerabilities are primarily being exploited by financially motivated actors; FortiCloud SSO is enabled in a significant number of vulnerable devices; organizations will promptly apply patches.
- Information Gaps: The identity and motivations of the threat actors; the full scope of affected organizations; potential secondary impacts of the attacks.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias from relying on a single cybersecurity firm’s analysis; the possibility of threat actors using deception to mask their true objectives.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The exploitation of these vulnerabilities could lead to broader security challenges if not contained. The situation may evolve with increased sophistication or targeting, affecting geopolitical stability and economic sectors reliant on Fortinet devices.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state-sponsored actors are involved or if critical infrastructure is affected.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information, potentially impacting national security.
- Cyber / Information Space: Escalation in cyber threat activity, leading to a need for enhanced cybersecurity measures and awareness.
- Economic / Social: Disruption to businesses relying on Fortinet devices, leading to economic losses and potential reputational damage.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Apply patches to affected devices, disable FortiCloud SSO, and monitor for indicators of compromise (IoCs).
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures, enhance cybersecurity partnerships, and invest in threat intelligence capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Vulnerabilities are patched, and attacks subside. Worst: Attacks escalate, targeting critical infrastructure. Most-Likely: Continued opportunistic attacks with moderate impact.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Arctic Wolf Labs
- The Constant Company LLC
- Bl Networks
- Kaopu Cloud HK Limited
- Fortinet
- U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, vulnerability exploitation, Fortinet, SAML SSO, authentication bypass, threat actors, network security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us