Sanctions Oversight Lacks Credibility Without Effective Ground Results, Security Council Subsidiary Chairs Wa…
Published on: 2025-12-17
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Sanctions Oversight Mechanisms Risk Losing Credibility Without Results on Ground Chairs of Subsidiary Bodies Tell Security Council
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
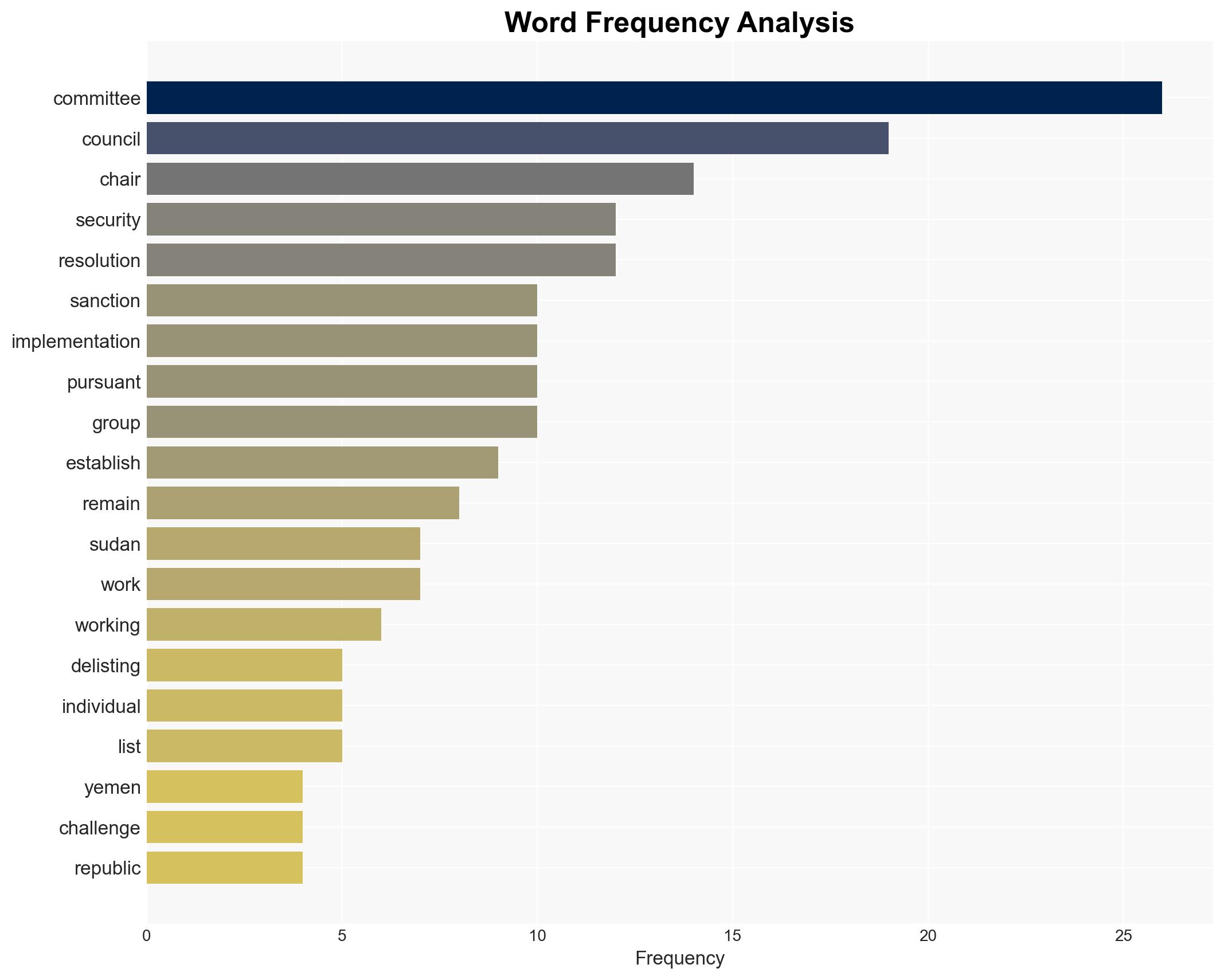
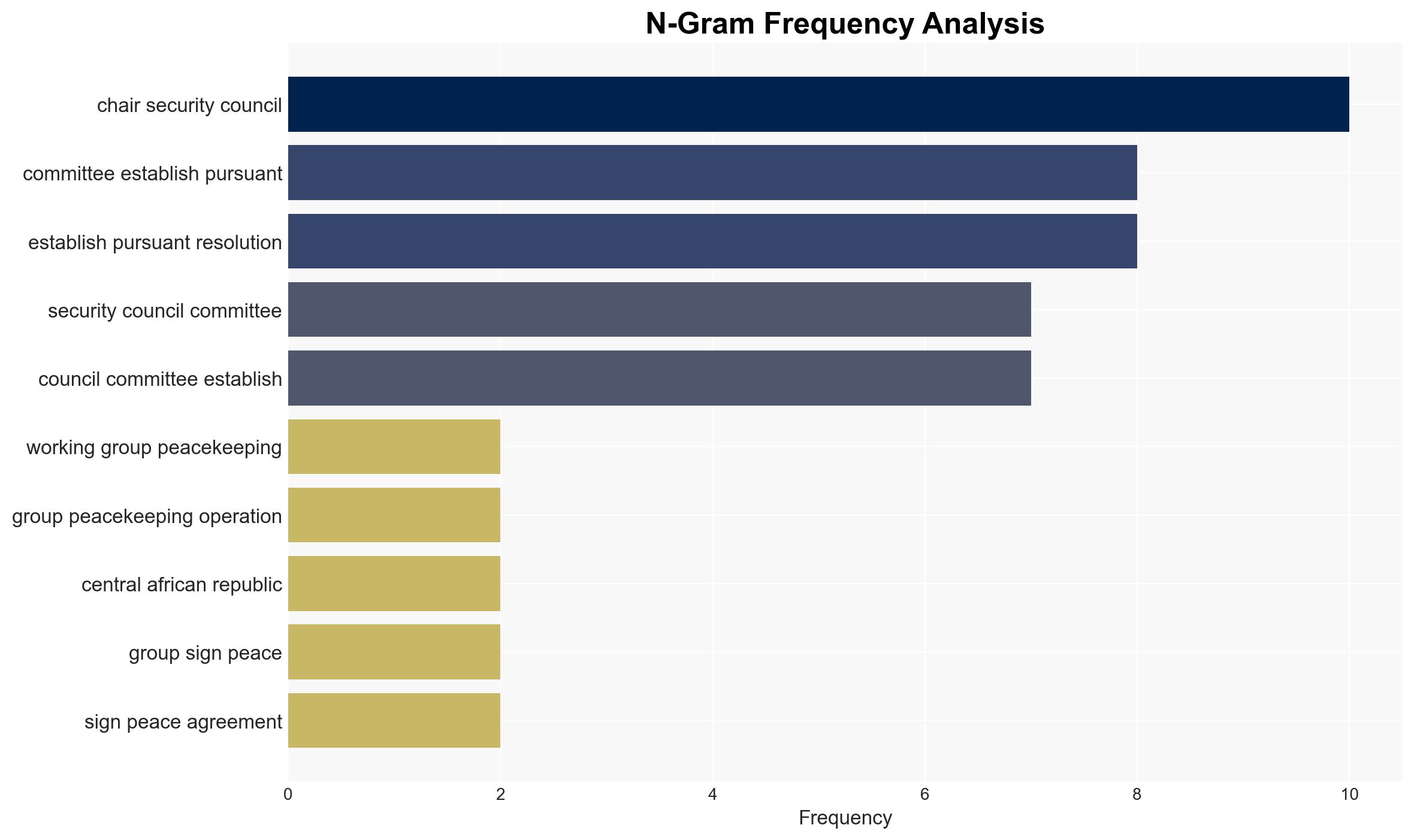
The credibility of UN Security Council sanctions and oversight mechanisms is at risk due to implementation challenges and procedural inefficiencies, particularly in Yemen and Sudan. The lack of timely results and staffing issues undermine these efforts, potentially affecting international security and counter-terrorism initiatives. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The current inefficiencies in sanctions implementation are primarily due to procedural delays and staffing shortages, as indicated by the delayed Chair appointments and expert staffing issues. This is supported by the reported operational consequences and the need for credible monitoring.
- Hypothesis B: The challenges in sanctions implementation are driven more by geopolitical complexities and resistance from affected states, rather than procedural inefficiencies alone. This is suggested by the complex political and security environments in regions like Sudan and Yemen.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to explicit mentions of procedural and staffing issues as significant factors. However, geopolitical dynamics could shift this judgment, particularly if resistance from affected states becomes more evident.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Sanctions are an effective tool for international security; Staffing and procedural efficiency directly impact sanctions’ effectiveness; Political will exists to resolve these issues.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the specific impacts of sanctions in Yemen and Sudan; Insights into the geopolitical motivations of affected states.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from Security Council members; Risk of states exaggerating procedural issues to deflect from non-compliance.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
Failure to address these challenges could lead to diminished credibility of international sanctions regimes, affecting global security and counter-terrorism efforts.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential erosion of trust in UN mechanisms, leading to unilateral actions by member states.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of unchecked violence and terrorism in regions like Sudan and Yemen.
- Cyber / Information Space: Limited direct impact, but potential for misinformation campaigns exploiting perceived inefficiencies.
- Economic / Social: Prolonged sanctions without results could exacerbate humanitarian crises and economic instability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Expedite staffing and Chair appointments; Enhance monitoring and reporting mechanisms.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with regional organizations to improve implementation; Invest in capacity-building for sanctions enforcement.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Efficient implementation leads to improved compliance and reduced violence.
- Worst: Continued inefficiencies result in sanctions being ignored, escalating conflicts.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in implementation with ongoing challenges due to geopolitical factors.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Sangjin Kim, Chair of the Security Council Committee on Yemen and Sudan
- Amar Bendjama, Chair of the Security Council Committees on Counter-Terrorism and Central African Republic
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet for other key individuals.
7. Thematic Tags
Counter-Terrorism, sanctions, international security, UN Security Council, geopolitical dynamics, procedural inefficiencies, humanitarian impact
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us