Israel Should Consider Counterinsurgency Tactics if Conflict with Hamas Resumes in Gaza
Published on: 2025-12-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: If War Returns to Gaza Israel Should Try Counterinsurgency
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
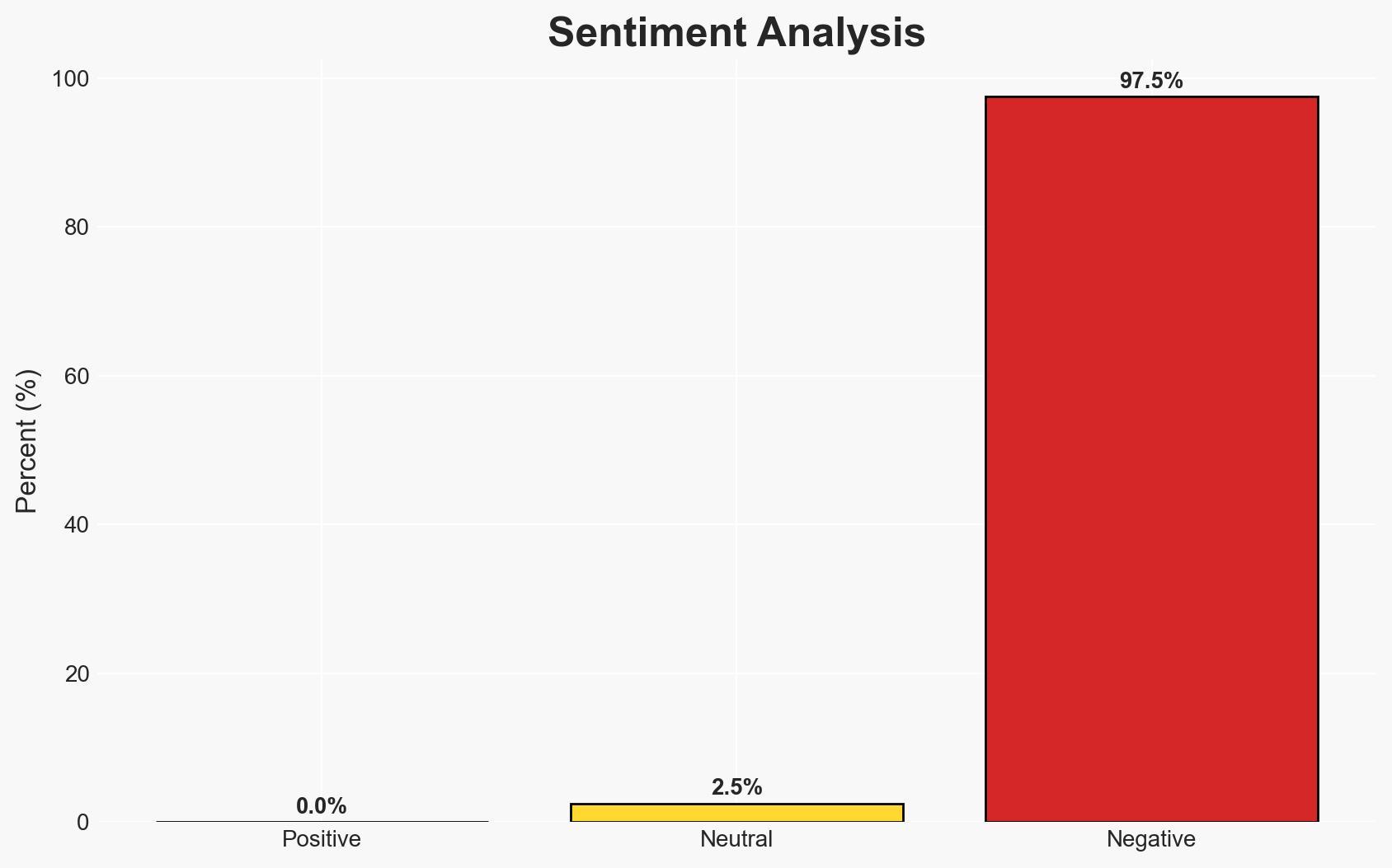
The current cease-fire in Gaza is fragile, with Hamas remaining armed and rejecting disarmament. If conflict resumes, a counterinsurgency strategy involving an International Stabilization Force (ISF) could be more effective than Israel’s previous military campaigns. This approach is likely to succeed due to Hamas’ unpopularity and the potential for a technocratic government to emerge. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Israel’s renewed military efforts will fail to eliminate Hamas due to the group’s ability to regroup and the lack of a sustainable governance plan in cleared areas. This is supported by past failures and the persistence of Hamas’ influence.
- Hypothesis B: Implementing a counterinsurgency strategy with ISF involvement will lead to a sustainable peace in Gaza by establishing a non-Hamas government. This is supported by the potential effectiveness of the “Oil Spot” strategy and international backing for the ISF.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the historical ineffectiveness of Israel’s military campaigns and the potential for international support to stabilize cleared areas. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in Hamas’ military capabilities or international diplomatic dynamics.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Hamas will continue to reject disarmament; the ISF will receive adequate international support; local populations will accept ISF governance; Israel will not commit to long-term governance in Gaza.
- Information Gaps: Details on the composition and mandate of the ISF; the level of international commitment to support the ISF; Hamas’ internal strategic decisions.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in overestimating international willingness to engage; underestimating Hamas’ resilience and adaptability; possible manipulation of public opinion by involved parties.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The situation in Gaza could significantly impact regional stability and international relations. A successful counterinsurgency could lead to a lasting peace, while failure could exacerbate tensions.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased international involvement could alter regional power dynamics and influence peace negotiations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: A shift in strategy could reduce Hamas’ operational capabilities but may also provoke retaliatory actions.
- Cyber / Information Space: Information operations by Hamas or other actors could influence public perception and international support.
- Economic / Social: Stabilization efforts could improve economic conditions, but ongoing conflict risks further humanitarian crises.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor international diplomatic efforts regarding the ISF; assess Hamas’ military and political strategies; engage with potential ISF contributors to clarify roles and commitments.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with international stakeholders; enhance intelligence capabilities to track Hamas’ activities; support economic and governance initiatives in Gaza.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Successful ISF deployment leads to peace and governance reform. Worst: Renewed conflict with increased regional instability. Most-Likely: Partial success with ongoing challenges in governance and security.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Hamas
- Israel Defense Forces (IDF)
- International Stabilization Force (ISF)
- Potential contributing countries (e.g., Indonesia)
7. Thematic Tags
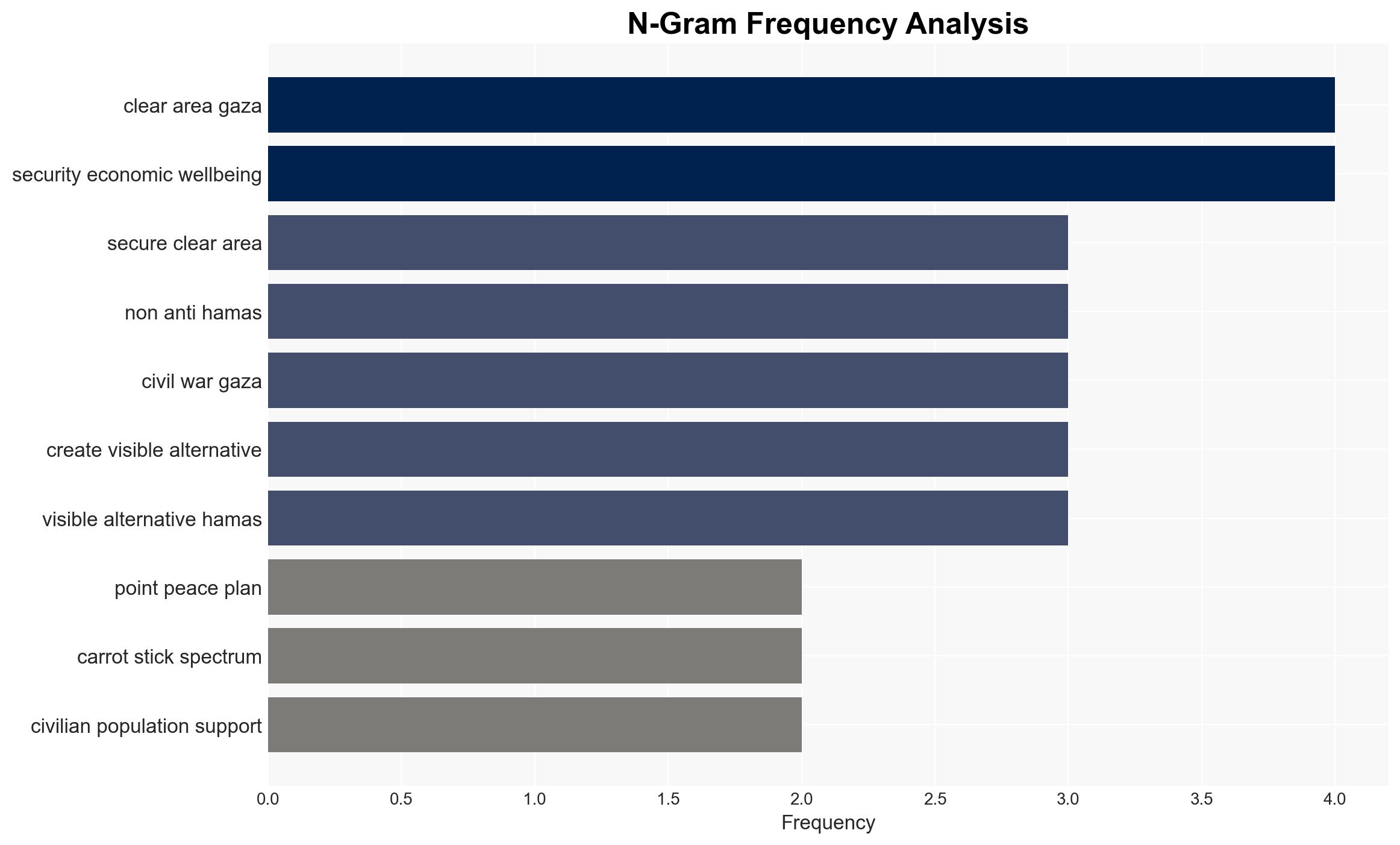
Counter-Terrorism, counterinsurgency, Gaza conflict, international stabilization, Hamas, Israeli military strategy, peacekeeping, regional security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us