North Korea’s Crypto Theft Surges to $2 Billion in 2025, Marking Record High for State-Sponsored Cybercrime
Published on: 2025-12-18
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Kim’s crypto thieving reached a record 2B in 2025
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
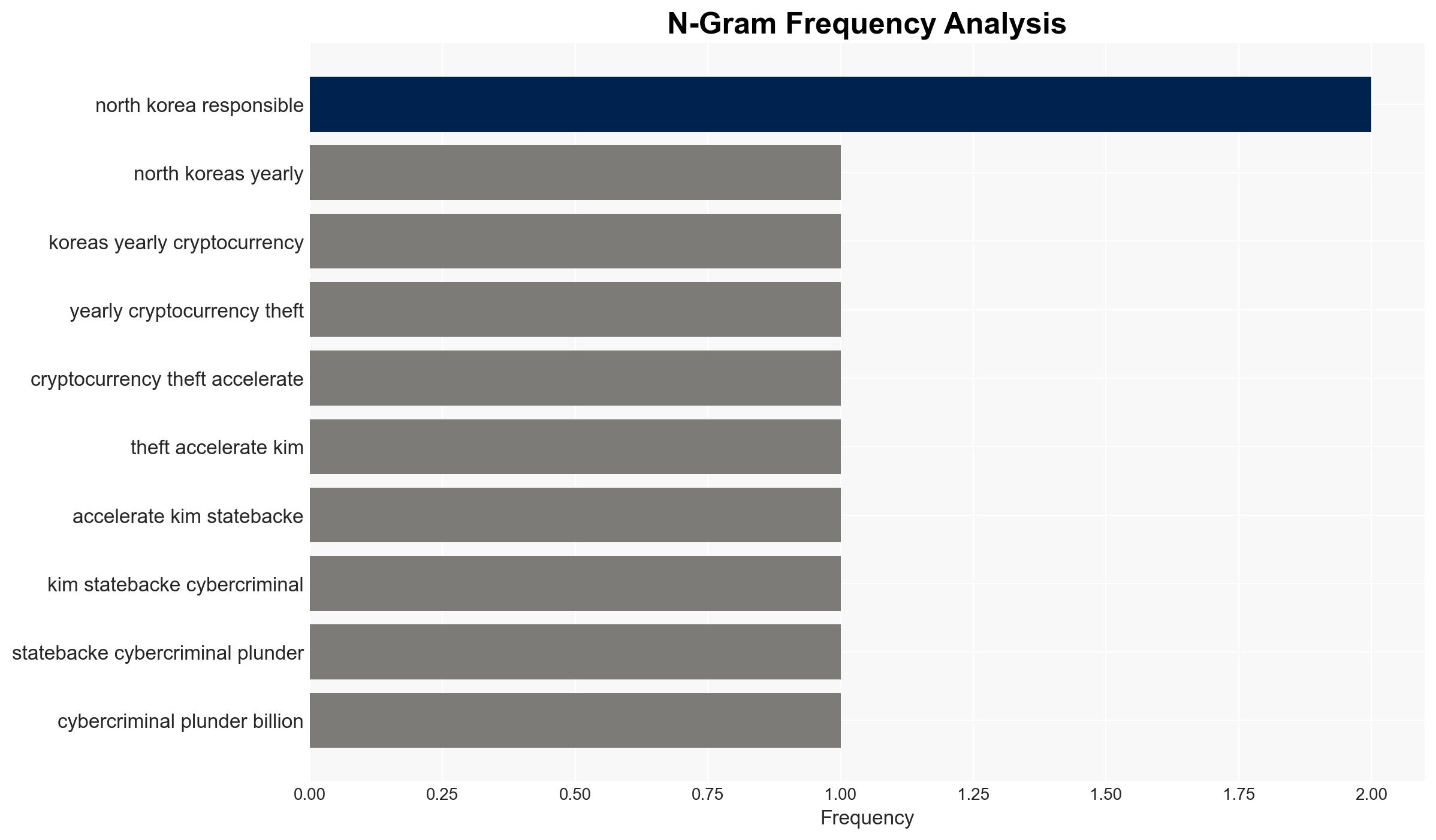
North Korea’s state-sponsored cybercriminals have escalated their cryptocurrency theft operations, achieving a record $2 billion in 2025. This represents a significant increase in both the scale and sophistication of their activities, with implications for global financial security and cyber defense strategies. The most likely hypothesis is that North Korea is intensifying these activities to circumvent international sanctions and fund its regime. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the reliance on open-source data and potential for deception.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: North Korea is increasing cryptocurrency theft to fund its regime amidst tightening international sanctions. This is supported by the significant increase in theft value and the strategic targeting of high-value assets and personal wallets. However, the exact allocation of these funds remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The increase in thefts is primarily driven by opportunistic criminal elements within North Korea, acting independently of state directives. While plausible, this is less supported due to the scale and coordination of the attacks, which suggest state-level involvement.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the organized nature of the operations and alignment with North Korea’s historical use of cybercrime to evade sanctions. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of decentralized operations or changes in North Korea’s geopolitical strategy.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: North Korea’s cyber operations are centrally coordinated; the regime prioritizes cryptocurrency theft as a key revenue stream; international sanctions remain a significant pressure point for North Korea.
- Information Gaps: Detailed allocation of stolen funds within North Korea; specific identities of key operatives; comprehensive understanding of North Korea’s cyber capabilities and infrastructure.
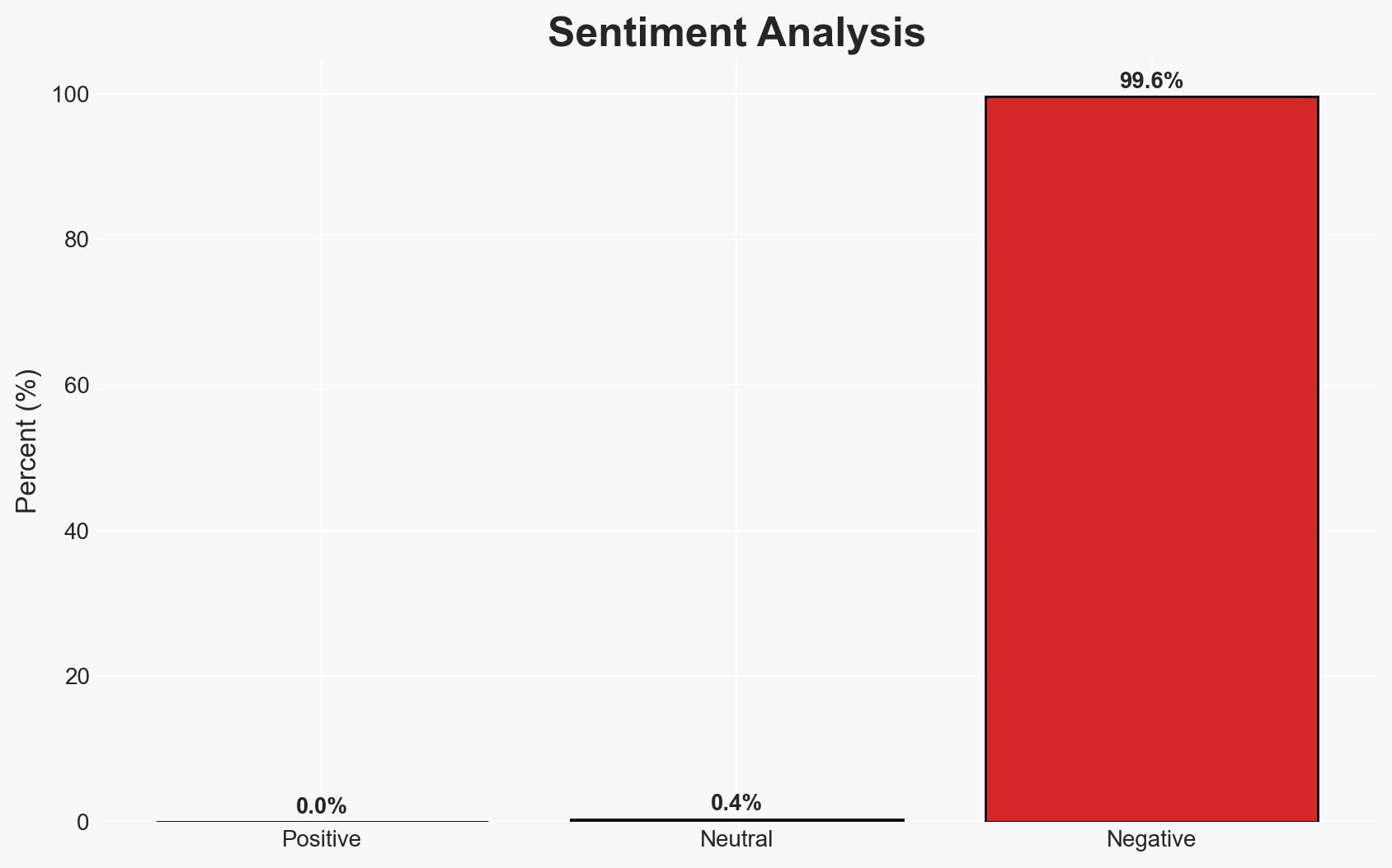
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in source data from Chainalysis; risk of North Korean misinformation or obfuscation of true operational scale and intent.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The increase in North Korean cryptocurrency theft could exacerbate tensions in international relations, particularly with countries targeted by these operations. This development may also prompt enhanced cybersecurity measures globally, affecting financial institutions and cryptocurrency platforms.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased sanctions or diplomatic actions against North Korea; strain on international relations with affected countries.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment for financial and cyber infrastructures; increased need for international cooperation in cyber defense.
- Cyber / Information Space: Escalation in cyber warfare tactics; potential for retaliatory cyber operations by affected states.
- Economic / Social: Potential destabilization of cryptocurrency markets; increased scrutiny and regulation of digital assets.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of cryptocurrency transactions; strengthen cybersecurity protocols in financial institutions; engage in diplomatic discussions to address the threat.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop international partnerships for cyber threat intelligence sharing; invest in cybersecurity infrastructure and workforce training; explore regulatory measures for cryptocurrency exchanges.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: International collaboration leads to effective deterrence and reduction in cyber theft incidents.
- Worst: North Korea escalates cyber operations, causing significant financial and infrastructural damage.
- Most-Likely: Continued high-level cyber theft operations with incremental improvements in global cyber defense measures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Kim Jong-un (North Korean leader)
- Chainalysis (Blockchain analysis company)
- Bybit (Cryptocurrency exchange)
- Solana (Cryptocurrency platform)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet for specific operatives or groups.
7. Thematic Tags
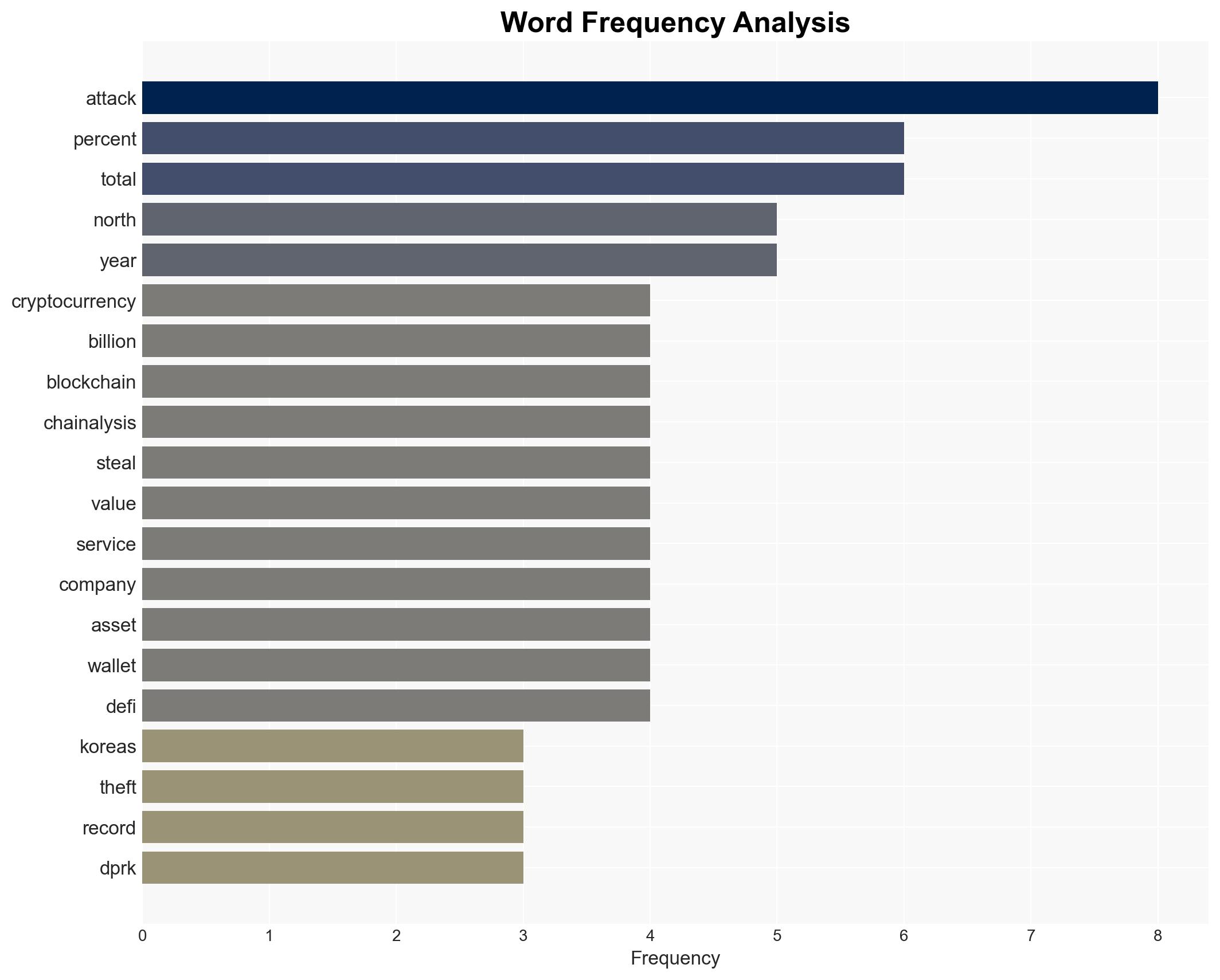
cybersecurity, cryptocurrency, North Korea, sanctions, cybercrime, international relations, financial security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us