CISA warns of critical Asus Live Update vulnerability; agencies urged to act by January 7.
Published on: 2025-12-18
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: CISA reveals warning on Asus software flaw here’s what you need to do to stay safe
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
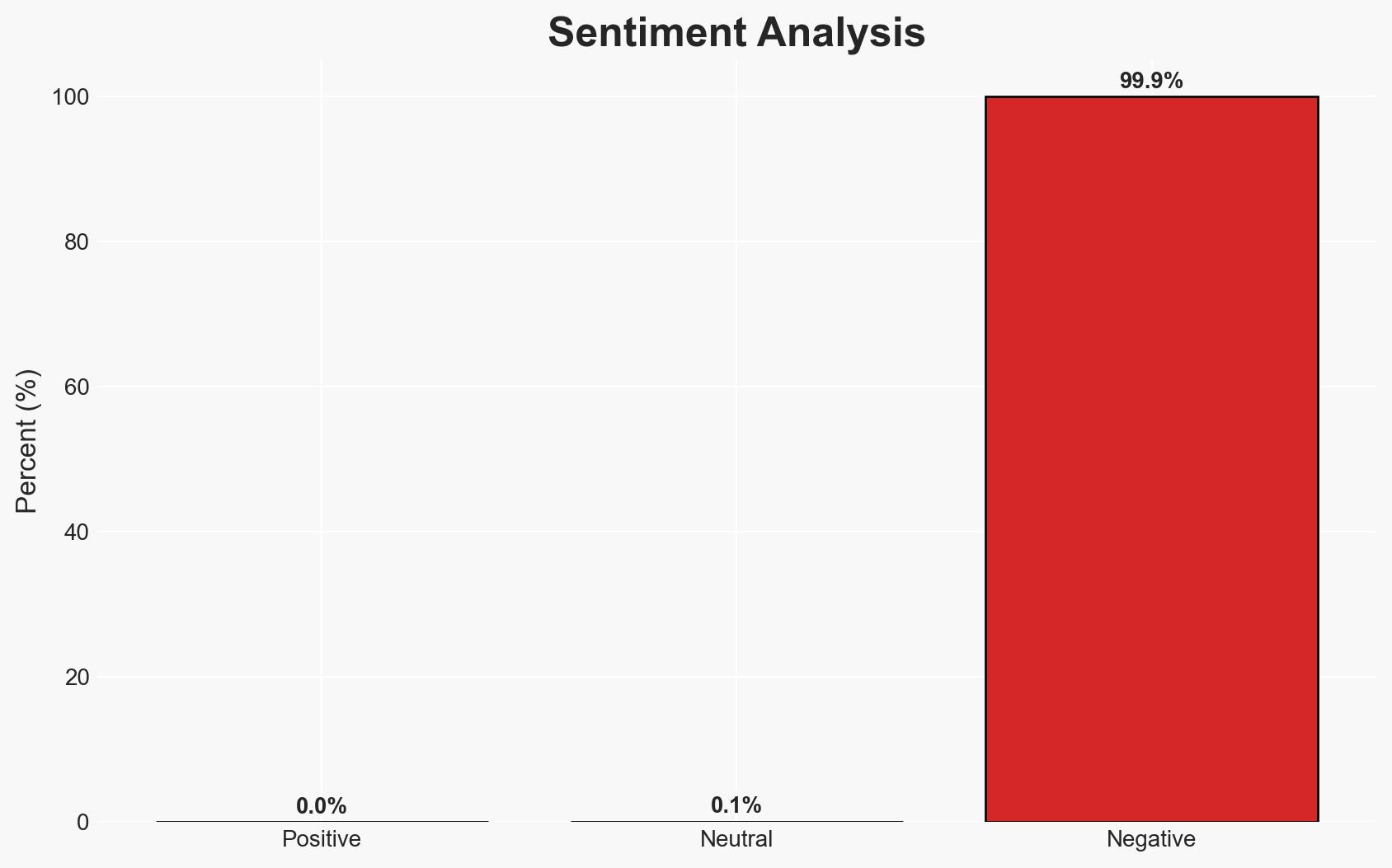
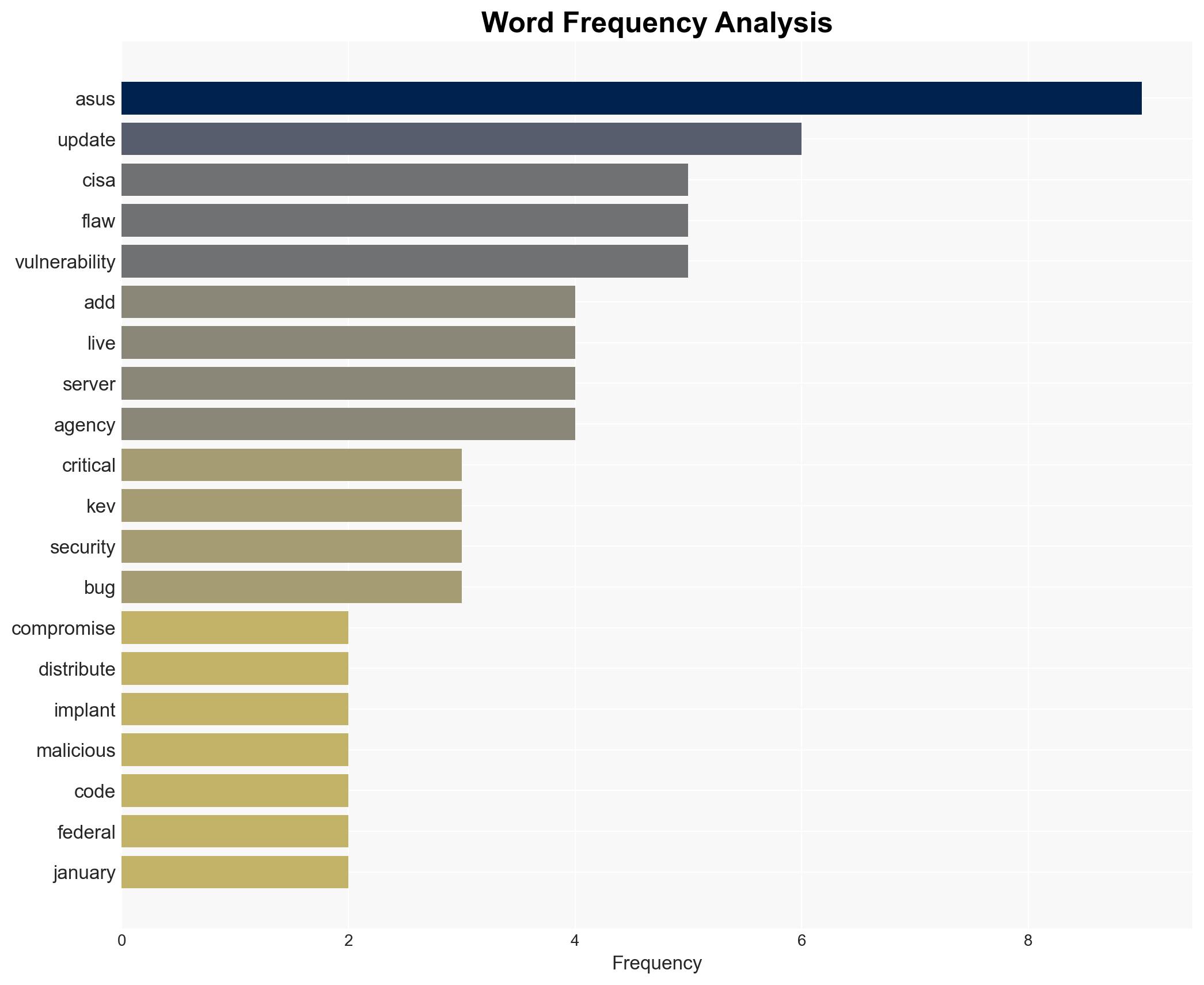
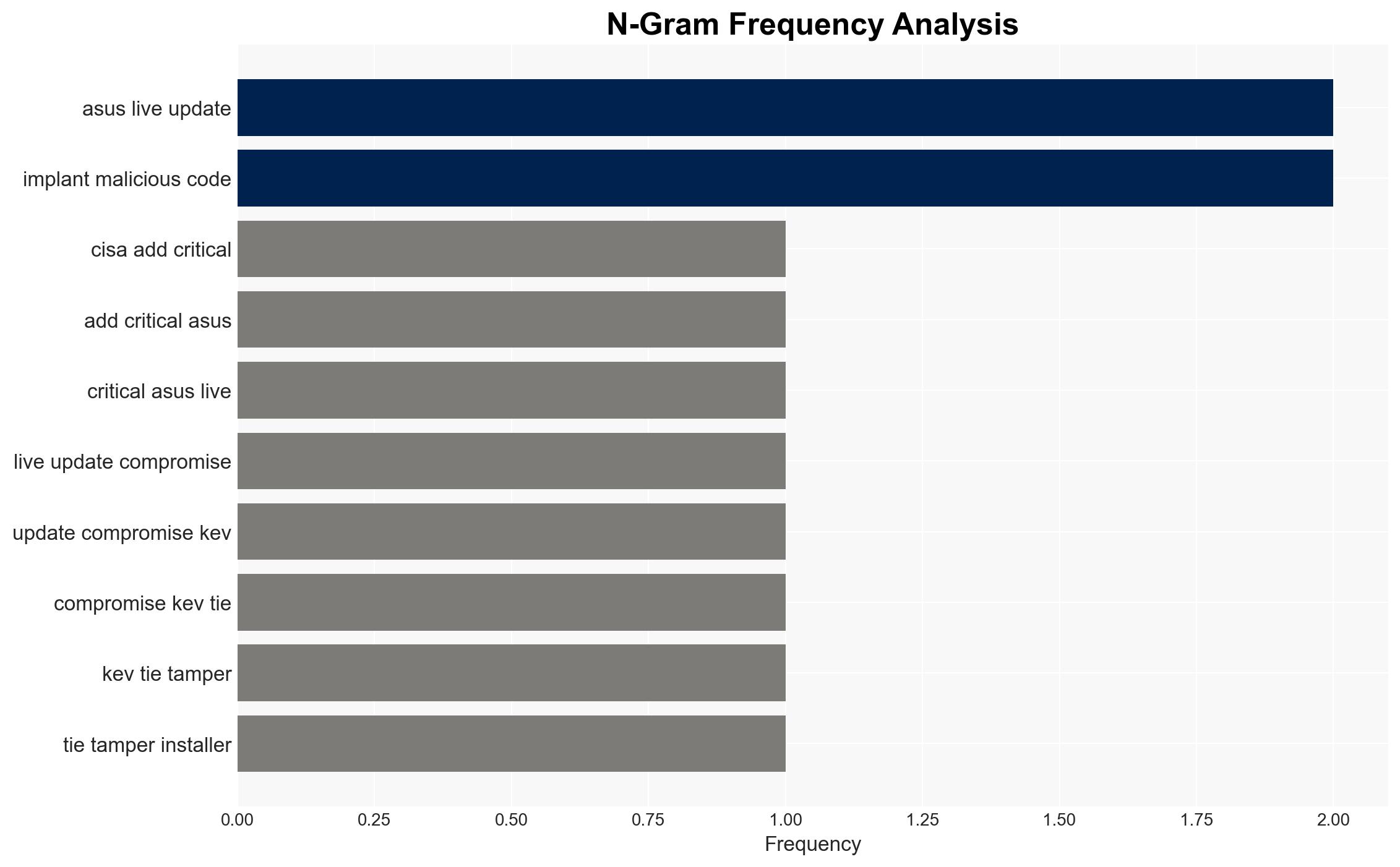
The addition of the Asus Live Update vulnerability (CVE-2025-59374) to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog indicates a significant cyber threat, primarily affecting Asus device users and federal agencies. The most likely hypothesis is that this vulnerability continues to be exploited by threat actors targeting specific user groups. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to historical context and current threat landscape.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerability is actively exploited by advanced persistent threat (APT) groups to target specific high-value individuals or organizations. This is supported by historical evidence of APT involvement and the specificity of the targeting. However, the exact current exploitation scale is uncertain due to limited recent data.
- Hypothesis B: The vulnerability is not currently being exploited at scale, and the inclusion in the KEV catalog is precautionary. This is contradicted by CISA’s action, which typically indicates active exploitation, but could be supported if no new incidents have been reported since the initial compromise.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to CISA’s inclusion of the vulnerability in the KEV catalog, which implies observed exploitation. Indicators such as new incident reports or changes in targeting patterns could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The vulnerability is primarily exploited by APT groups; Federal agencies will comply with CISA’s remediation deadline; Private sector organizations will heed CISA’s advisory.
- Information Gaps: Current data on the scale and scope of exploitation; Identification of specific threat actors involved; Detailed impact assessment on affected devices.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in threat reporting due to reliance on historical incidents; Risk of underestimating the vulnerability’s impact if new exploitation tactics are not detected.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased scrutiny of supply chain vulnerabilities and influence future cybersecurity policies. The evolution of this threat may impact various domains as follows:
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential strain on US-China relations if linked to Chinese APTs; Increased international cooperation on supply chain security.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened alert for targeted attacks on critical infrastructure or government entities.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on securing software supply chains; Possible rise in similar vulnerabilities being exploited.
- Economic / Social: Potential financial losses for affected organizations; Erosion of consumer trust in Asus products.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Federal agencies should prioritize patching affected systems; Private sector organizations should conduct vulnerability assessments and apply necessary updates.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for information sharing on supply chain threats; Invest in enhanced monitoring and response capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Vulnerability is fully mitigated with no further incidents; increased resilience against supply chain attacks.
- Worst: Widespread exploitation leads to significant data breaches and operational disruptions.
- Most-Likely: Continued targeted exploitation with gradual mitigation as patches are applied.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)
- Asus
- Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) groups (not specifically identified)
- Federal Civilian Executive Branch agencies
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, supply chain security, cyber vulnerability, APT, federal cybersecurity, software patching, threat mitigation, information security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us