Funeral for 10-Year-Old Victim of Bondi Mass Shooting Sparks National Debate on Antisemitism and Hate Crimes…
Published on: 2025-12-18
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Mourners grieve 10-year-old slain in Bondi mass shooting as Australia’s leader pledges new hate laws
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
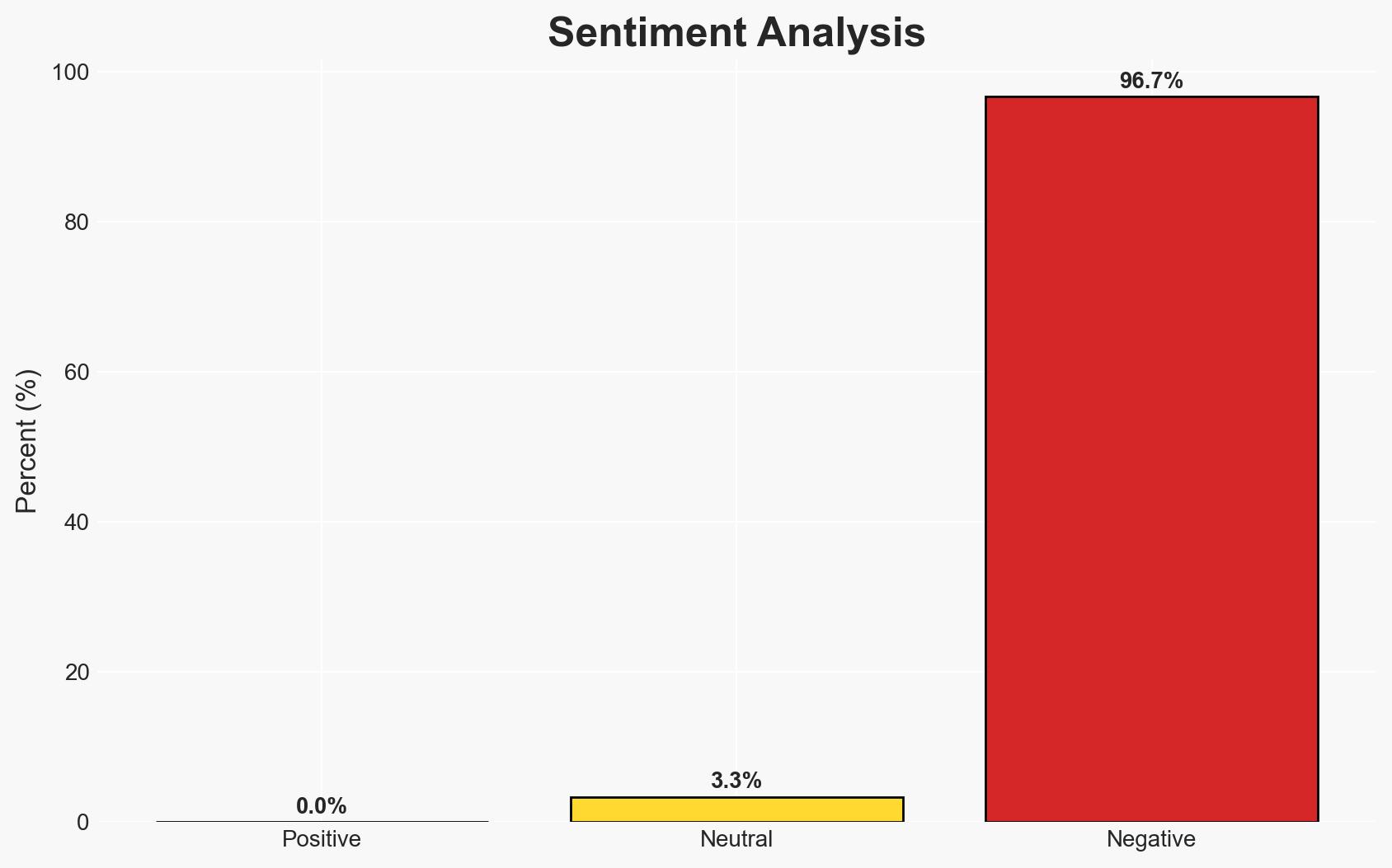
The recent mass shooting in Bondi, targeting Jewish individuals, has prompted a significant national response in Australia, including proposed legislative changes to address hate crimes and radicalization. The attack, linked to Islamic State inspiration, underscores ongoing security challenges. The most likely hypothesis is that the legislative response will face implementation challenges but will ultimately lead to stronger hate crime laws. Confidence in this assessment is moderate due to potential political resistance and public sentiment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The legislative measures proposed by Prime Minister Albanese will be effectively implemented, leading to a reduction in hate crimes and radicalization. This is supported by the government’s commitment to addressing antisemitism and existing strong gun control laws. However, the timeline and legal complexity pose uncertainties.
- Hypothesis B: The proposed legislative changes will face significant political and public resistance, delaying or diluting their effectiveness. This is supported by the lack of immediate timeline and potential backlash from communities concerned about civil liberties.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the political momentum following the attack and the government’s track record on gun control. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include public opinion shifts and legislative hurdles.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The Australian government has the political will to implement the proposed changes; public support for stronger hate crime laws will remain steady; the legislative process will not be unduly delayed.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on the legislative proposals and their timelines; the extent of public and political support or opposition.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in media reporting on public sentiment; risk of underestimating opposition from civil liberties groups.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development could lead to a strengthened legal framework against hate crimes, but also risks exacerbating tensions if perceived as infringing on civil liberties. The situation may influence broader regional security dynamics and domestic political landscapes.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased political polarization; influence on Australia’s international reputation regarding human rights.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced focus on domestic radicalization and hate groups; potential for increased security measures at public events.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible increase in online hate speech and radicalization efforts; need for monitoring digital platforms.
- Economic / Social: Social cohesion challenges; potential economic impact from increased security measures and public protests.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor legislative developments and public sentiment; engage with community leaders to mitigate tensions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with tech companies to combat online hate; enhance community resilience programs.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Effective implementation of laws leading to reduced hate crimes. Worst: Legislative failure leading to increased societal tensions. Most-Likely: Gradual implementation with mixed public reception.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Prime Minister Anthony Albanese
- Rabbi Dovid Slavin
- Australian law enforcement agencies
- Islamic State-inspired suspects (father and son)
7. Thematic Tags
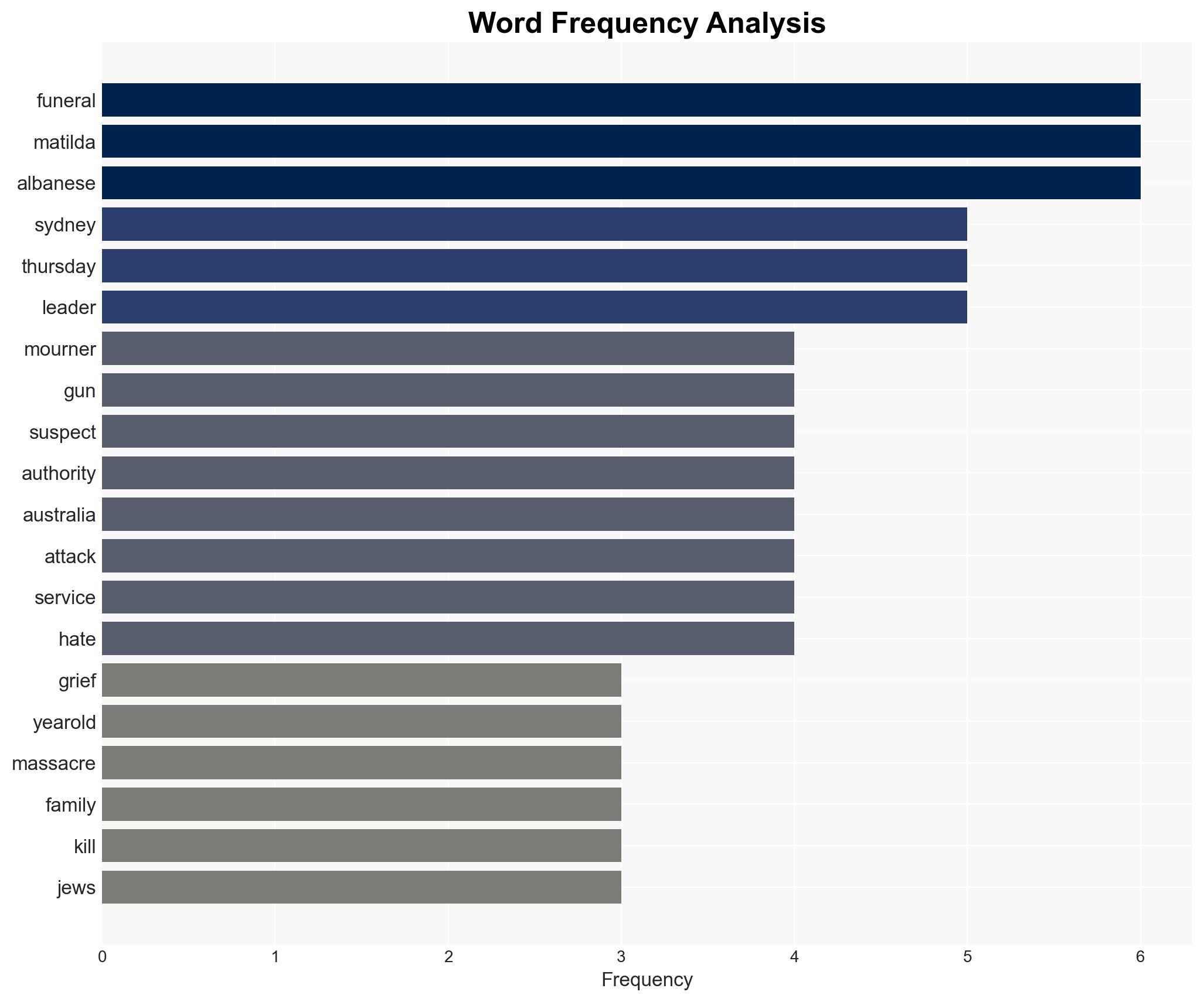
national security threats, counter-terrorism, hate crimes, legislative reform, radicalization, antisemitism, public safety, national security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us