Critical RCE Vulnerability in WatchGuard Firebox Firewalls Actively Exploited; Urgent Patching Required
Published on: 2025-12-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: New critical WatchGuard Firebox firewall flaw exploited in attacks
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The critical remote code execution vulnerability in WatchGuard Firebox firewalls, identified as CVE-2025-14733, poses a significant threat to small and mid-sized companies globally, particularly those using IKEv2 VPN configurations. The vulnerability is actively exploited, with over 75,000 devices previously found vulnerable to a similar flaw. The most likely hypothesis is that threat actors are leveraging this vulnerability for cyber-espionage or financial gain. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to incomplete data on the attackers’ identities and objectives.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerability is being exploited primarily by cybercriminal groups seeking financial gain through ransomware or data theft. Supporting evidence includes the low-complexity nature of the attacks and the widespread use of WatchGuard devices in small and mid-sized enterprises, which are common targets for such groups. However, there is uncertainty regarding the specific groups involved.
- Hypothesis B: Nation-state actors are exploiting the vulnerability for cyber-espionage purposes, targeting sensitive information within affected organizations. This is supported by the active exploitation and the previous involvement of CISA in similar vulnerabilities, indicating potential national security concerns. Contradicting evidence includes the lack of specific attribution to state actors in the current advisory.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the nature of the targets and the attack’s characteristics. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include attribution to a known nation-state actor or evidence of targeted attacks on critical infrastructure.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
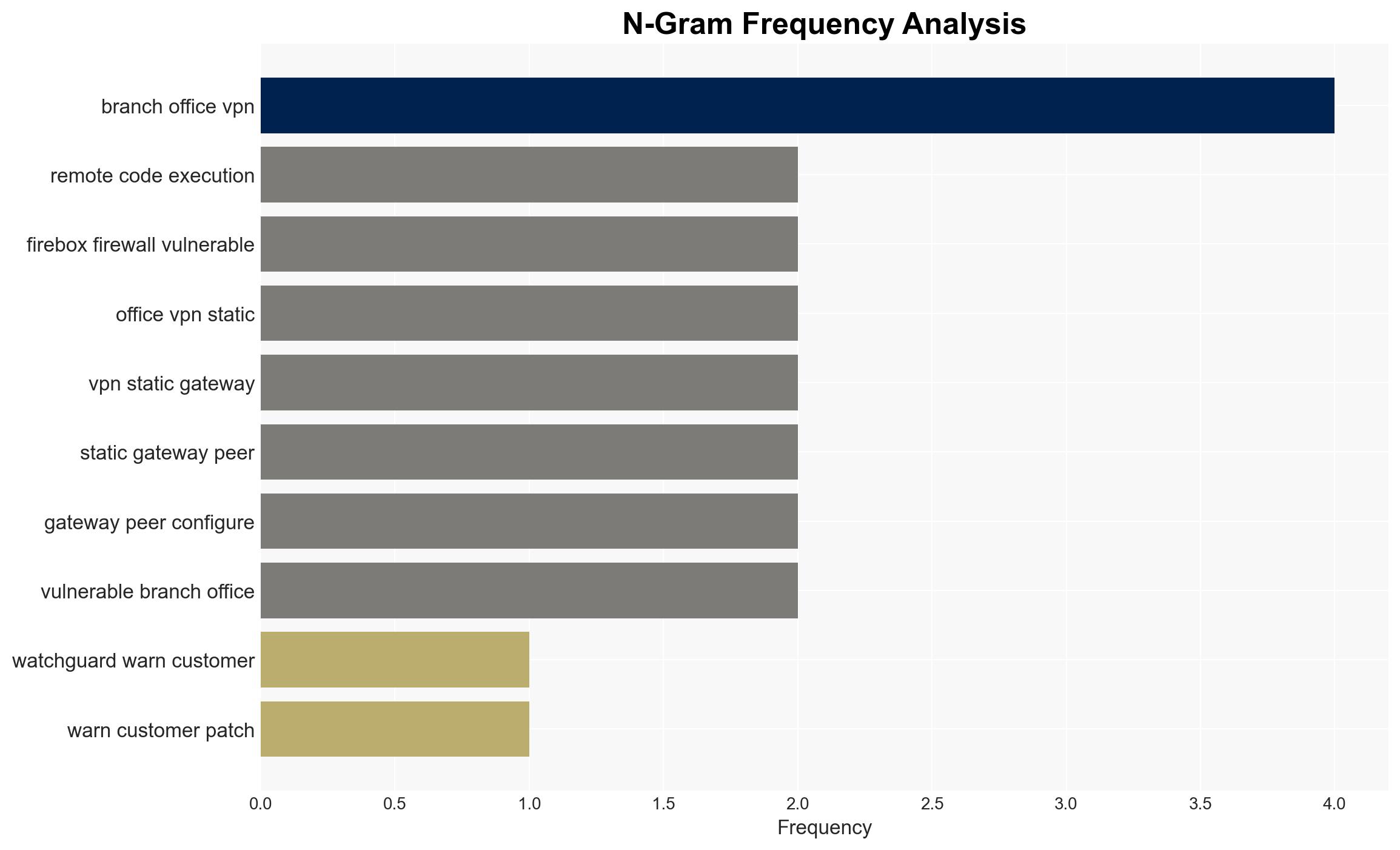
- Assumptions: The vulnerability is primarily exploited through IKEv2 VPN configurations; WatchGuard’s advisory accurately reflects the threat landscape; affected organizations have not yet fully implemented the recommended patches or workarounds.
- Information Gaps: Specific identities and motivations of the threat actors exploiting the vulnerability; comprehensive data on the geographical distribution of affected devices; effectiveness of the recommended mitigations in preventing exploitation.
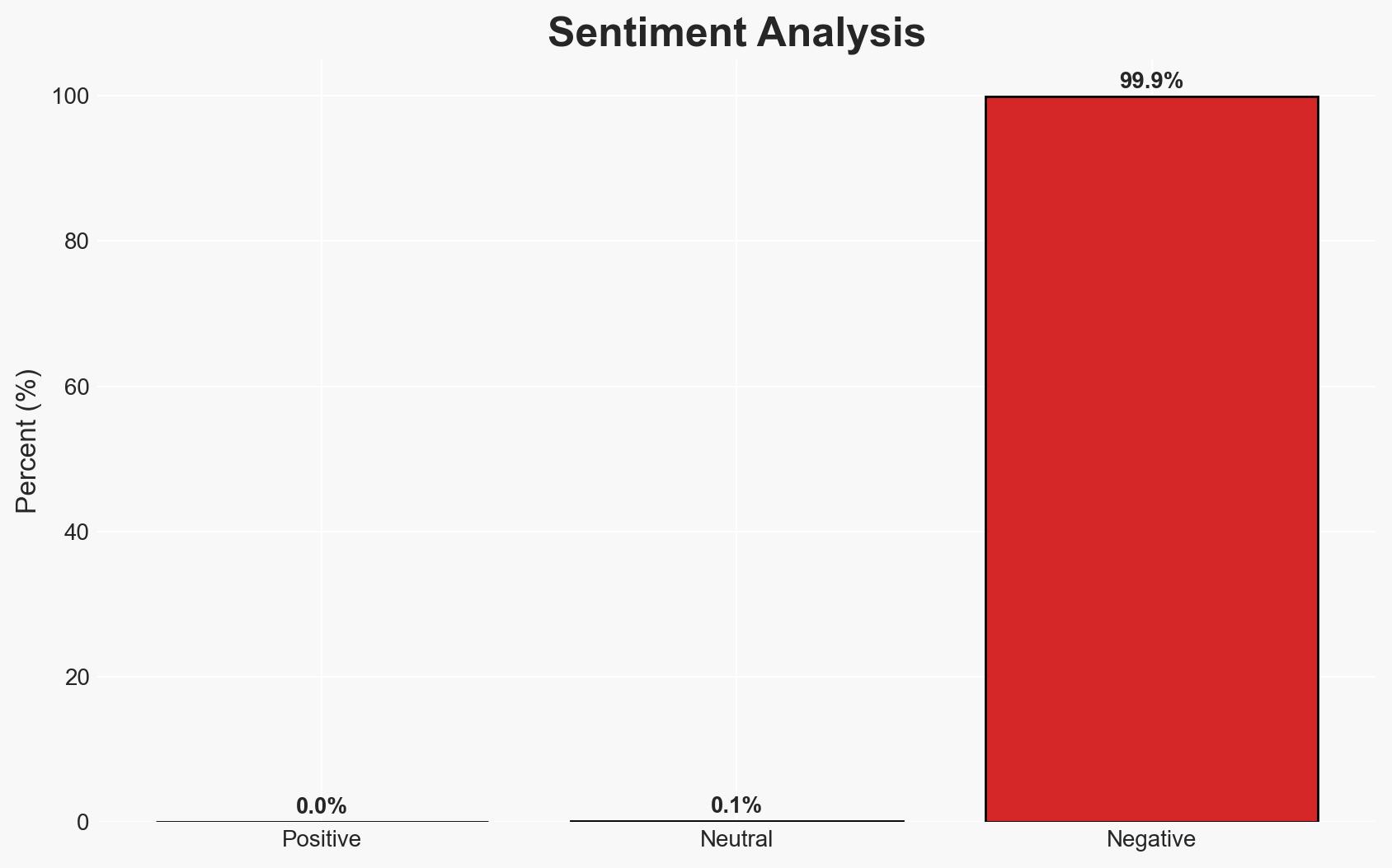
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting due to WatchGuard’s vested interest in promoting the urgency of patching; the possibility of threat actors using misinformation to obscure their activities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This vulnerability could lead to increased cyber incidents affecting small and mid-sized enterprises, potentially resulting in financial losses and data breaches. Over time, this may erode trust in WatchGuard’s security solutions and prompt regulatory scrutiny.
- Political / Geopolitical: Escalation of cyber tensions if nation-state involvement is confirmed, potentially impacting diplomatic relations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased operational risks for affected organizations, with potential for data leaks or operational disruptions.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened awareness and urgency in cybersecurity practices among small and mid-sized enterprises; potential for increased cyber insurance claims.
- Economic / Social: Financial strain on affected businesses, particularly if they lack resources for rapid mitigation; possible reputational damage to WatchGuard.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Organizations should immediately apply patches and implement WatchGuard’s recommended workarounds; conduct thorough network audits for indicators of compromise.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for enhanced threat intelligence sharing; invest in employee training and incident response capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid patch adoption mitigates the threat with minimal impact.
- Worst: Widespread exploitation leads to significant financial and data losses.
- Most-Likely: Continued exploitation with gradual mitigation as patches are applied.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- WatchGuard Technologies
- U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)
- Shadowserver Foundation
- Not clearly identifiable threat actors from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
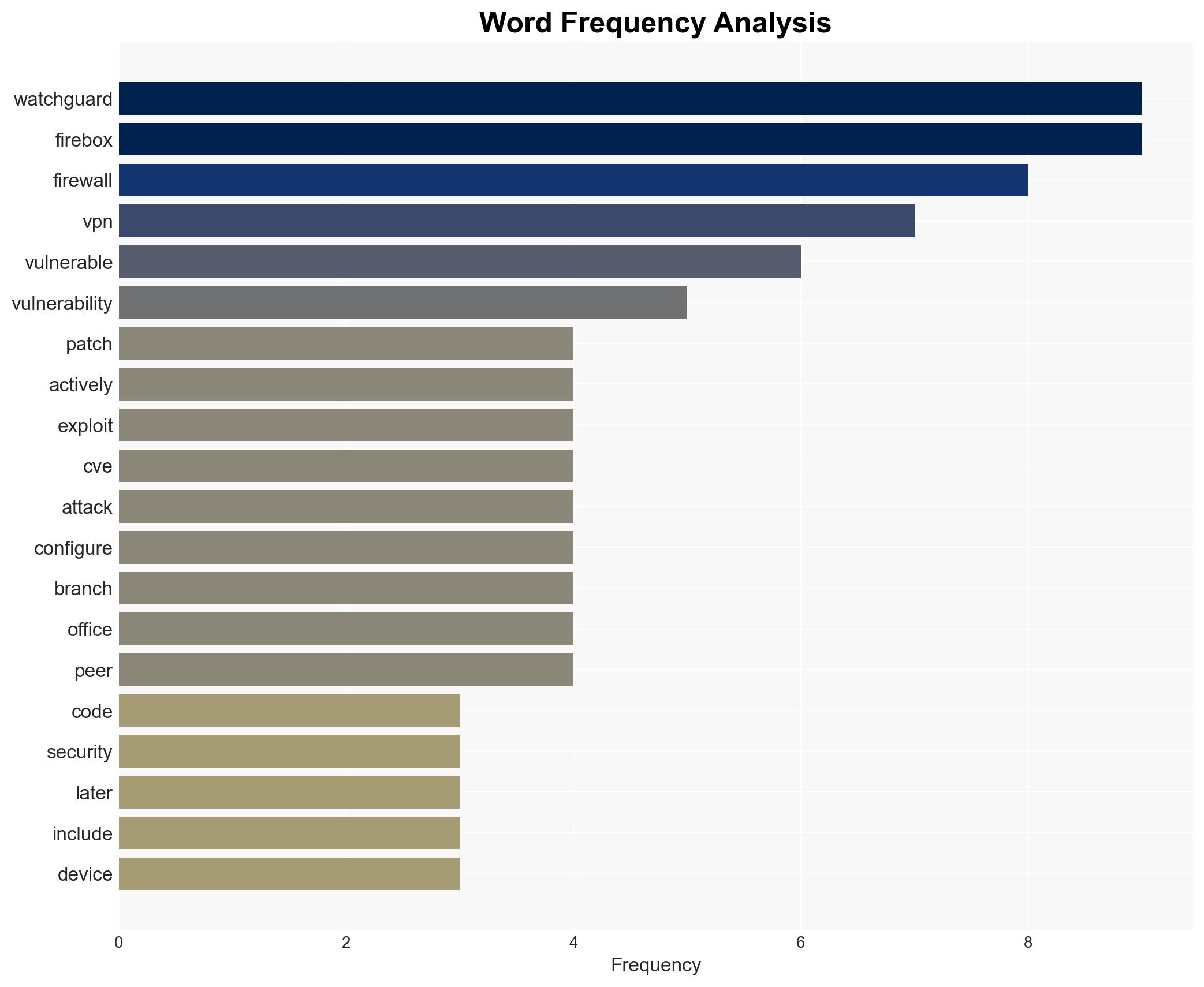
cybersecurity, remote code execution, vulnerability management, WatchGuard Firebox, cyber-espionage, small and mid-sized enterprises, threat mitigation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us