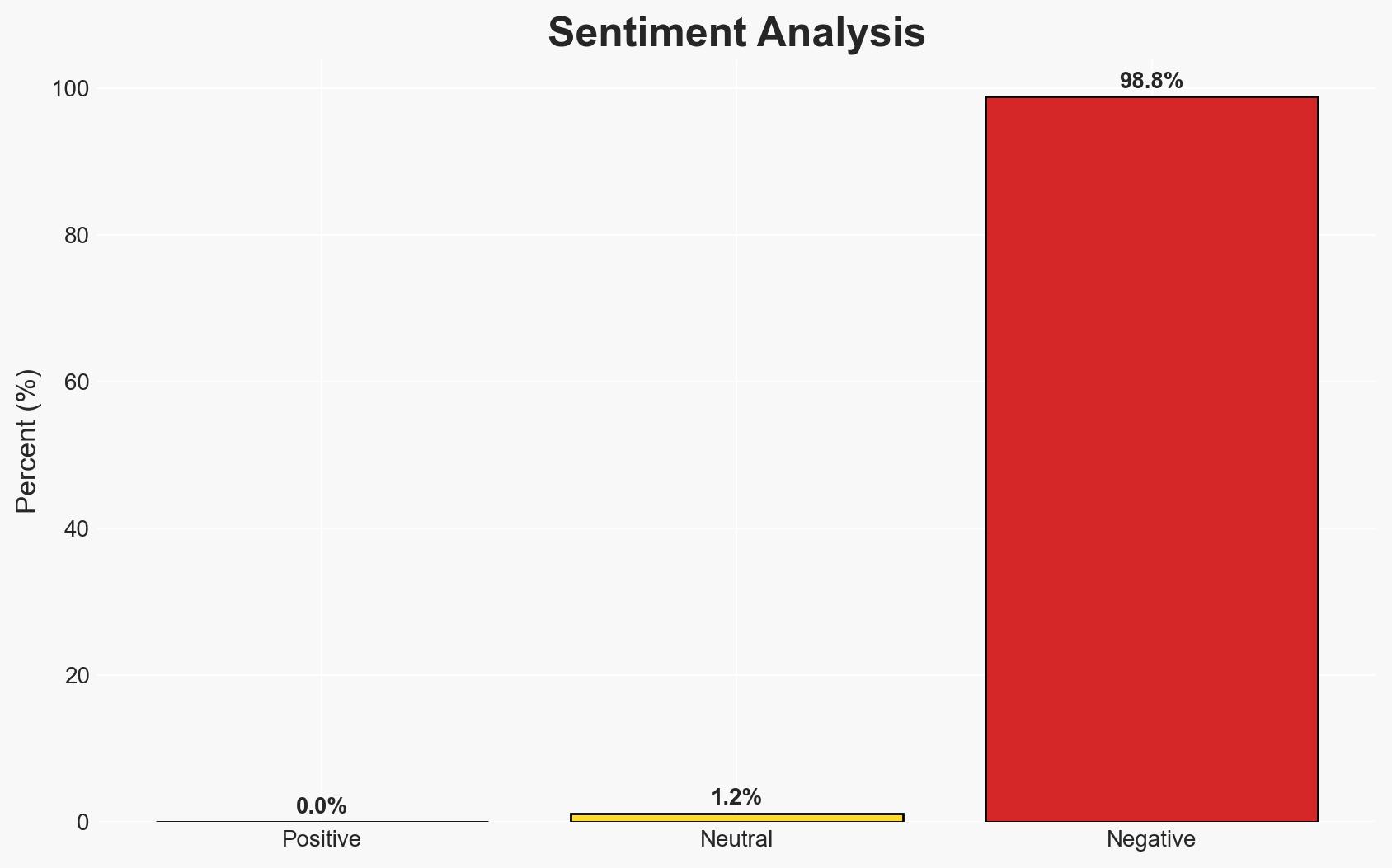
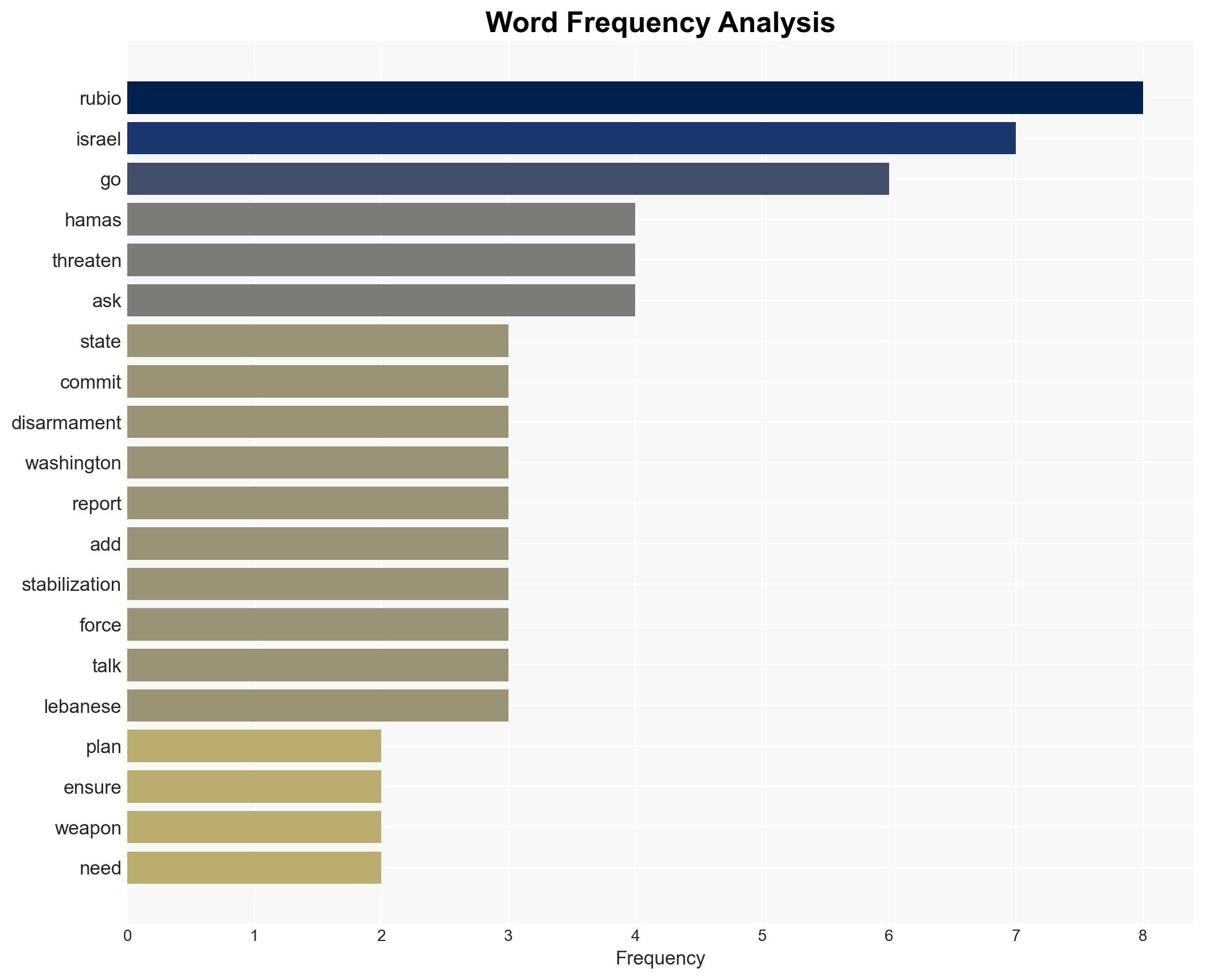
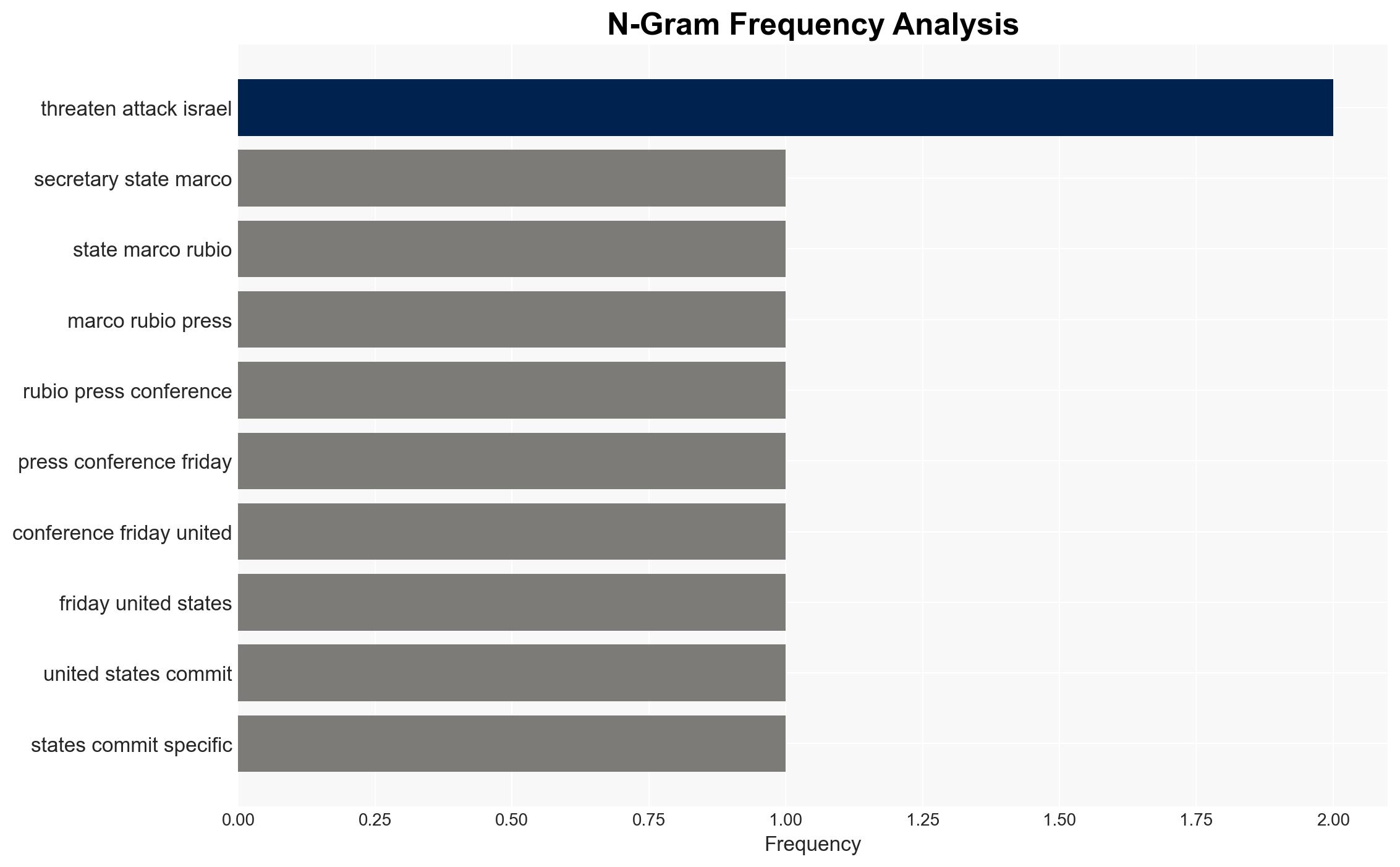
Rubio: Lasting peace hinges on preventing Hamas from threatening Israel with future attacks
Published on: 2025-12-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Rubio No peace if Hamas retains the ability to attack Israel
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The United States, under Secretary of State Marco Rubio, emphasizes the necessity of Hamas disarmament to ensure peace and economic investment in Gaza. The most likely hypothesis is that the U.S. will pursue a disarmament plan that aligns with Israeli security needs, though specific terms remain undefined. This affects regional stability and international diplomatic efforts, with moderate confidence in this assessment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The U.S. will support a comprehensive disarmament plan for Hamas, including both heavy and light weapons, to ensure long-term peace and security for Israel. This is supported by Rubio’s emphasis on preventing any future threat to Israel. However, the lack of specific terms and the complexity of negotiations are key uncertainties.
- Hypothesis B: The U.S. may accept a partial disarmament plan, allowing Hamas to retain some lighter weapons, to facilitate quicker diplomatic progress and reduce immediate tensions. This is contradicted by Rubio’s focus on comprehensive disarmament as a baseline for peace.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to Rubio’s explicit statements on the necessity of preventing any threat to Israel. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in Israeli or Palestinian positions or new diplomatic pressures.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The U.S. has the diplomatic leverage to influence Hamas disarmament; Israel’s security needs will dictate U.S. policy; international partners will support the ISF mandate.
- Information Gaps: Specific terms of disarmament negotiations; the stance of key regional actors like Egypt and Qatar; the detailed mandate of the ISF.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential U.S. bias towards Israeli security concerns; manipulation of public statements by involved parties to gain negotiation leverage.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to a recalibration of regional alliances and influence the broader Middle East peace process. The success or failure of disarmament efforts will have significant repercussions.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential shifts in U.S.-Middle East relations; increased diplomatic engagement or tensions with regional powers.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Changes in threat levels to Israel and potential for escalated conflict if disarmament fails.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible increase in cyber operations targeting negotiation processes or involved parties.
- Economic / Social: Economic investment in Gaza contingent on perceived security improvements; social stability linked to successful governance structures.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase diplomatic engagement with regional partners; clarify ISF mandate and funding mechanisms; monitor Hamas’s military capabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for potential conflict escalation; strengthen partnerships with key regional actors; enhance intelligence capabilities on Hamas activities.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Successful disarmament and stabilization lead to peace and investment. Worst: Failed negotiations result in renewed conflict. Most-Likely: Partial progress with ongoing tensions and intermittent violence.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Marco Rubio – U.S. Secretary of State
- Hamas – Palestinian militant organization
- Israel – State actor involved in negotiations
- International Stabilization Force (ISF) – Proposed peacekeeping entity
- Pakistan – Potential contributor to ISF
7. Thematic Tags
Counter-Terrorism, Middle East peace process, disarmament, international diplomacy, regional security, economic investment, geopolitical strategy
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us