Mast Proposes AI OVERWATCH Act to Strengthen U.S. Oversight and Export of Military-Enhancing AI Technologies
Published on: 2025-12-20
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Chairman Mast Introduces AI OVERWATCH Act to Secure America’s Technological Dominance
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
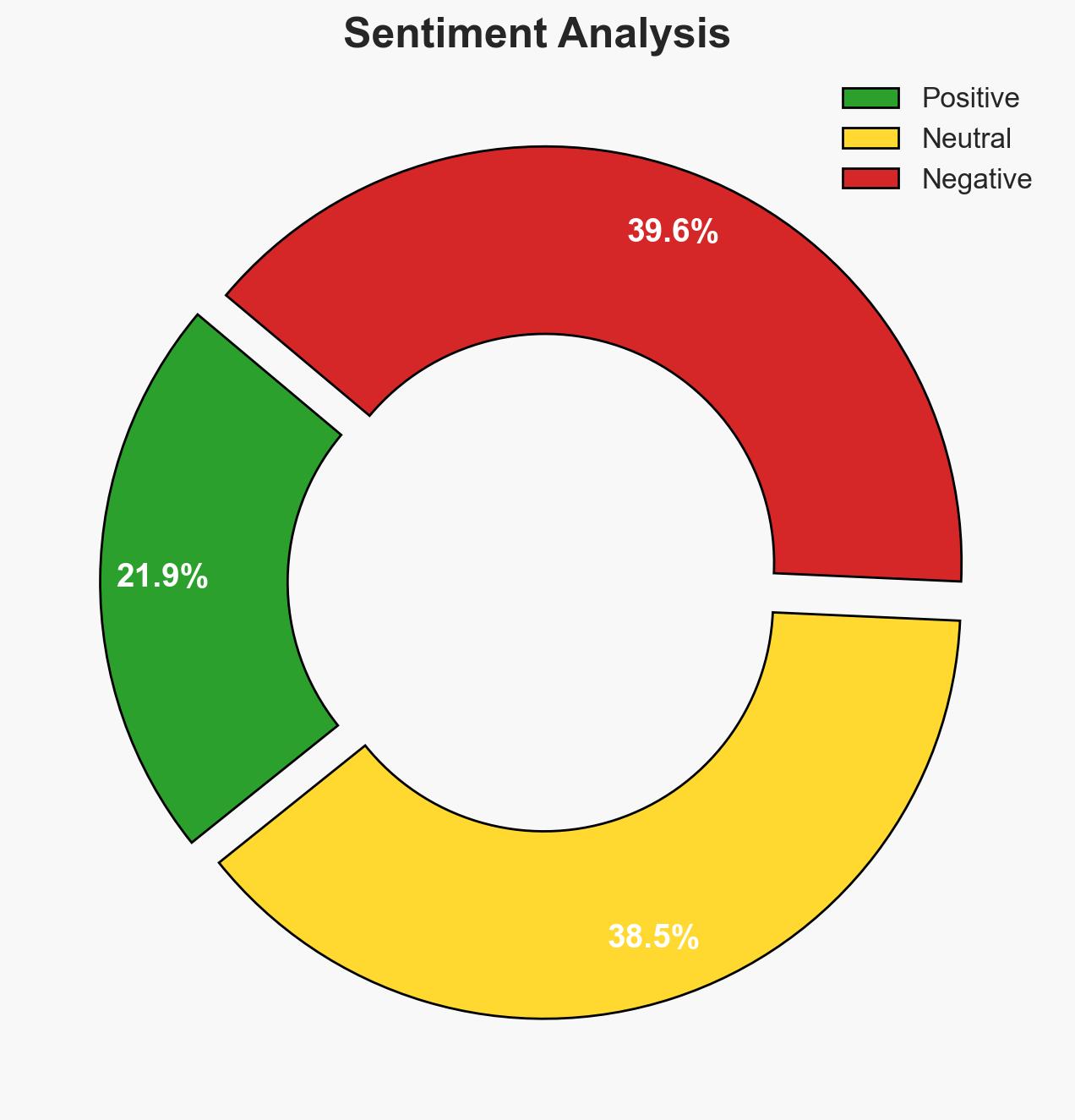
The introduction of the AI OVERWATCH Act aims to enhance U.S. congressional oversight on AI chip exports, particularly to adversary nations, while promoting exports to allies. This legislative move is likely to impact U.S. technological leadership and national security dynamics. The most likely hypothesis is that the Act will strengthen U.S. control over AI technology proliferation, with moderate confidence in this assessment due to existing geopolitical tensions and technological dependencies.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The AI OVERWATCH Act will effectively prevent adversary nations from acquiring advanced AI technologies, thereby securing U.S. technological dominance. Supporting evidence includes the bill’s provisions for congressional oversight and export controls. However, uncertainties remain regarding enforcement mechanisms and potential loopholes.
- Hypothesis B: The Act may inadvertently slow down U.S. technological innovation and competitiveness by imposing stringent export controls, potentially leading allies to seek alternative suppliers. This hypothesis is supported by historical instances where over-regulation has stifled innovation. Contradicting evidence includes the Act’s provisions for accelerated exports to allies.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the strategic focus on oversight and safeguarding national security. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in global AI market dynamics or significant diplomatic pushback from allies.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The U.S. maintains its technological edge in AI; adversary nations lack indigenous capabilities to rapidly develop equivalent technologies; allies remain aligned with U.S. strategic goals.
- Information Gaps: Detailed enforcement strategies and potential international responses to the Act are not specified.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in assuming all adversary nations are equally incapable of developing AI independently; risk of underestimating adversaries’ countermeasures or alternative strategies.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The AI OVERWATCH Act could reshape global AI technology flows and influence geopolitical alliances. Over time, it may lead to increased tensions with adversary nations while strengthening ties with allies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential escalation in U.S.-China tech rivalry; reinforcement of alliances through technology sharing.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced U.S. capability to monitor and control AI technology proliferation, potentially reducing adversary military enhancements.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on securing AI supply chains and preventing cyber espionage related to AI technologies.
- Economic / Social: Possible economic impacts on U.S. tech companies due to export restrictions; social implications if technological innovation is perceived to be hindered.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Establish a task force to monitor the implementation of the Act; engage with allies to ensure alignment and address concerns.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for U.S. tech companies; foster partnerships with allied nations to enhance cooperative AI development.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Strengthened U.S. technological leadership and international cooperation.
- Worst: Strained alliances and accelerated adversary technological advancements through alternative means.
- Most-Likely: Incremental strengthening of U.S. export controls with moderate ally cooperation.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Brian Mast, John Moolenaar, Bill Huizenga, Keith Self, Young Kim, Rick Crawford, Darin LaHood
- FDD Action, American Compass, Americans for Responsible Innovation
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, AI technology, congressional oversight, export controls, U.S. national security, geopolitical strategy, technological innovation, international alliances
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us