China’s Rare Earth Resources Enhance Strategic Dominance Amid Tight Security and Rapid Industry Growth
Published on: 2025-12-21
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Chinas rare earths El Dorado gives strategic edge
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
China’s control over rare earth elements provides a significant strategic advantage, impacting global supply chains and geopolitical dynamics. The most likely hypothesis is that China will continue to leverage this dominance to influence international trade and political negotiations. This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to limited transparency and potential for strategic deception.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: China is using its rare earth dominance primarily as a geopolitical tool to gain leverage in international negotiations. This is supported by China’s historical use of rare earths in trade discussions and recent easing of export controls. However, the lack of transparency and potential for strategic misinformation are key uncertainties.
- Hypothesis B: China’s rare earth strategy is primarily economically driven, focusing on maximizing revenue and industrial growth. The expansion of processing facilities and continuous mining operations support this view, but it contradicts China’s strategic use of rare earths in past geopolitical contexts.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to China’s historical pattern of using rare earths as a bargaining chip in geopolitical contexts. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in export policies or significant investments in alternative supply chains by other nations.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: China will continue to prioritize rare earths as a strategic resource; global demand for rare earths will remain high; alternative supply chains will not be established quickly.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on China’s rare earth reserves and production capabilities; insights into China’s long-term strategic plans for rare earths.
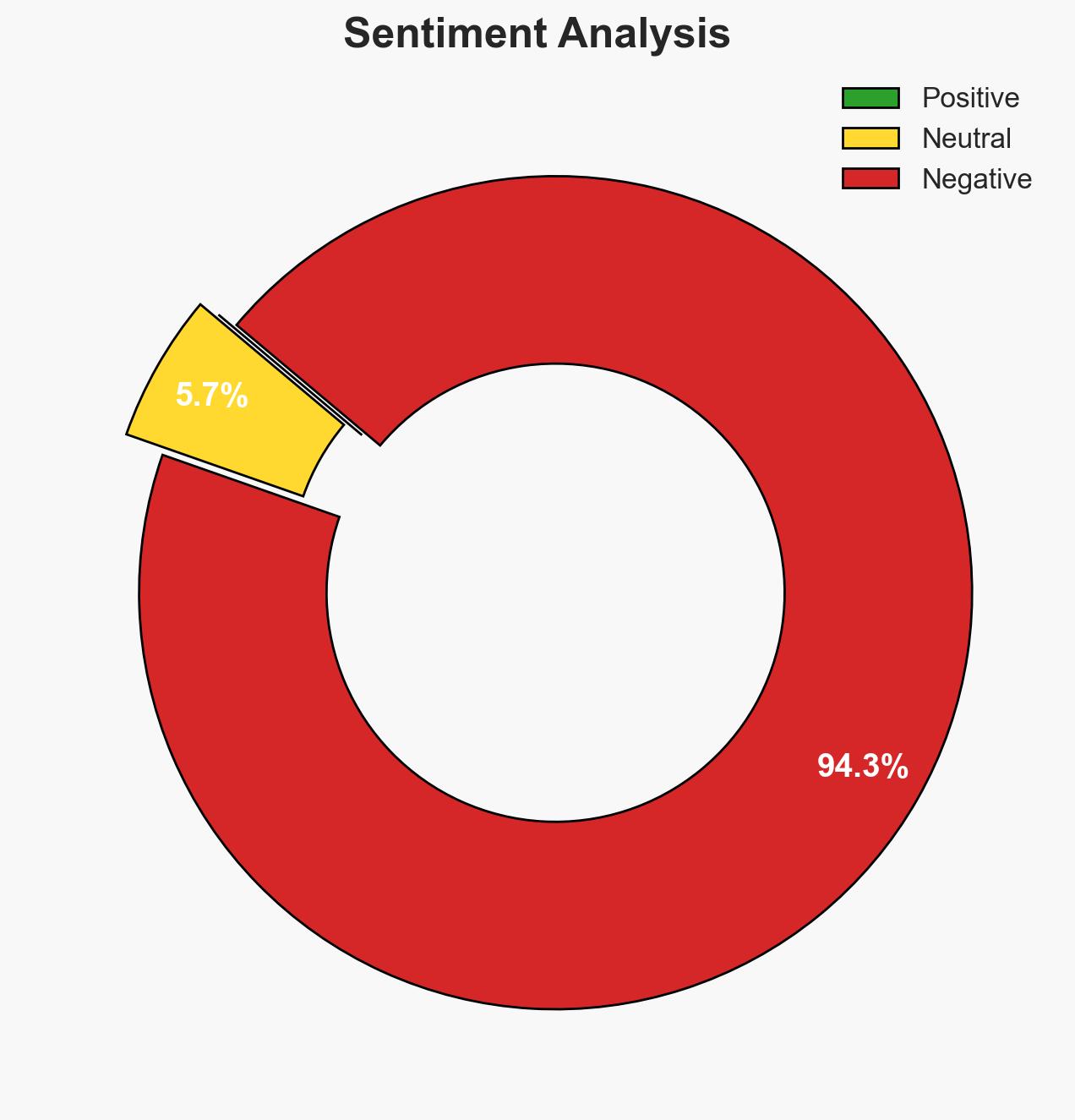
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential for Chinese state-controlled narratives to obscure true strategic intentions; Western sources may overemphasize threat perceptions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development of China’s rare earth industry could lead to increased geopolitical tensions and economic dependencies. Over time, this may influence global trade policies and security alliances.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased leverage in trade negotiations and influence over countries dependent on rare earth imports.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of supply chain disruptions affecting defense and technology sectors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possibility of cyber operations targeting rare earth supply chains or related industries.
- Economic / Social: Economic pressure on countries reliant on Chinese rare earths; potential for social unrest if supply disruptions occur.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of China’s rare earth export policies; engage with allies to assess alternative supply chain options.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with countries possessing rare earth reserves; invest in domestic processing capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Diversified global supply chains reduce dependency on China.
- Worst: China restricts exports, causing global shortages and economic instability.
- Most-Likely: Gradual diversification of supply chains with continued Chinese influence.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
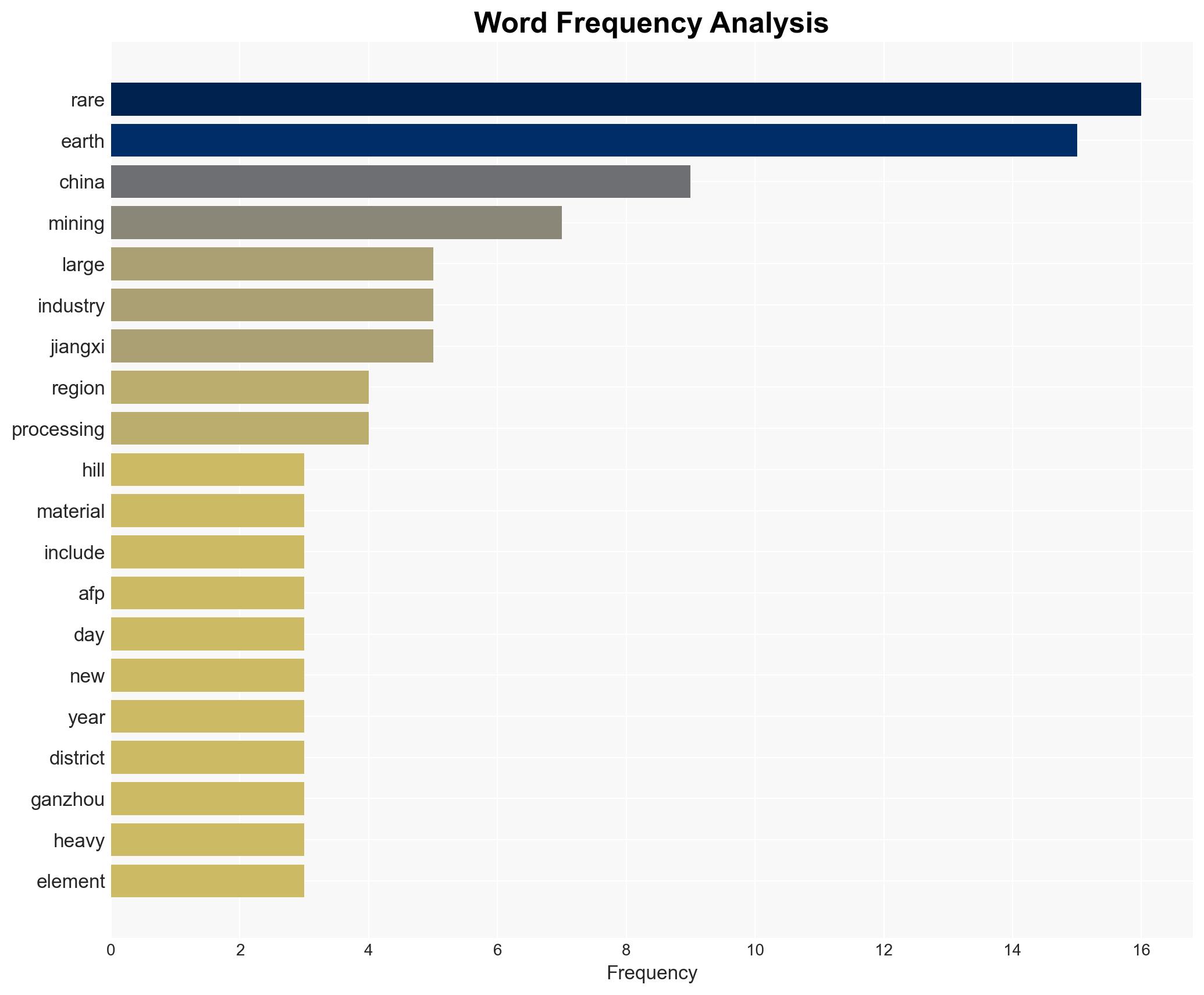
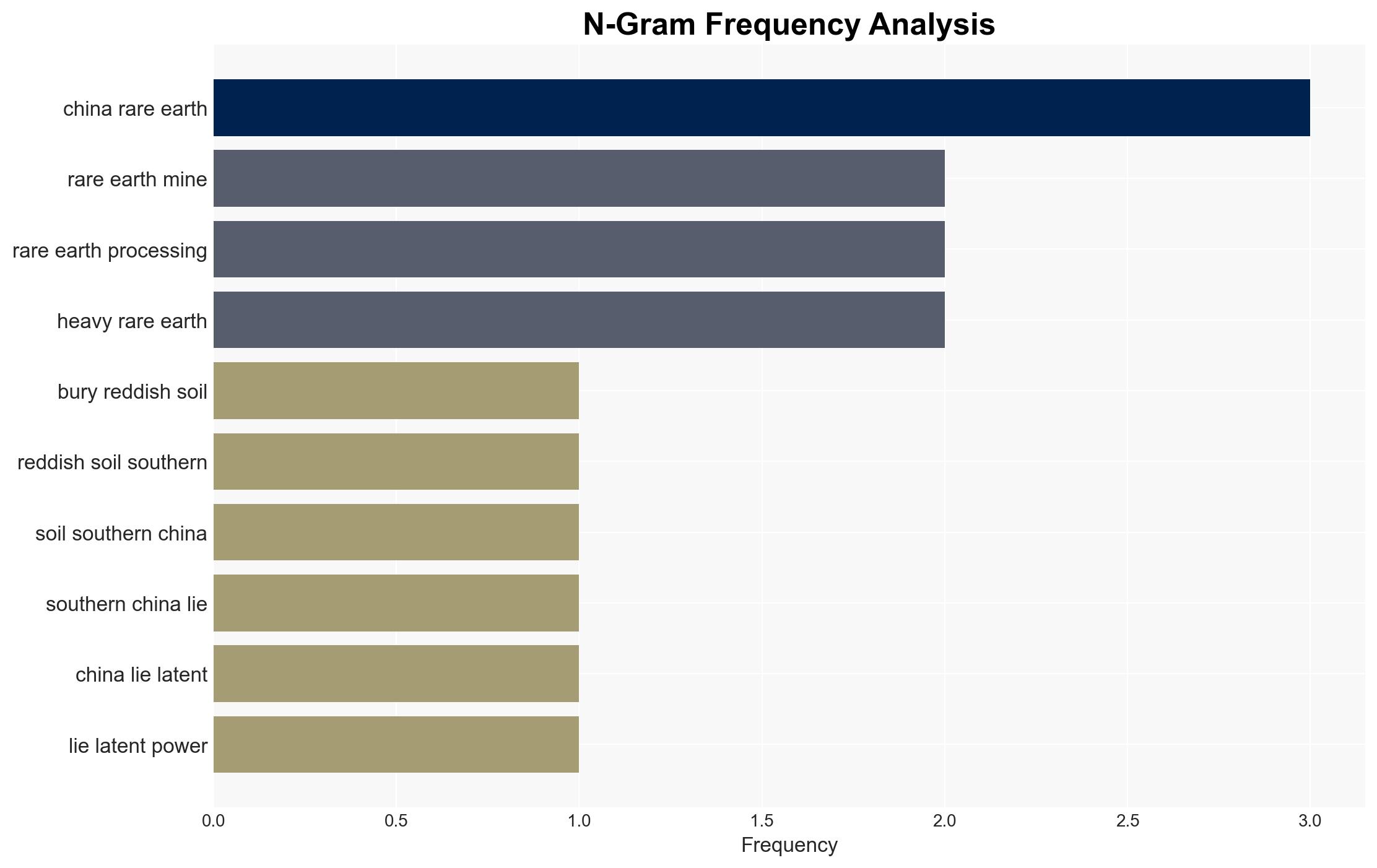
regional conflicts, rare earths, geopolitical strategy, supply chain, economic leverage, China, trade negotiations, strategic resources
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us