Trump’s Executive Order Accelerates U.S. Lunar Base Plans and Nuclear Power Deployment in Space by 2030
Published on: 2025-12-21
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: A new mandate for the Final Frontier Trump orders lunar base and nuclear power in space
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
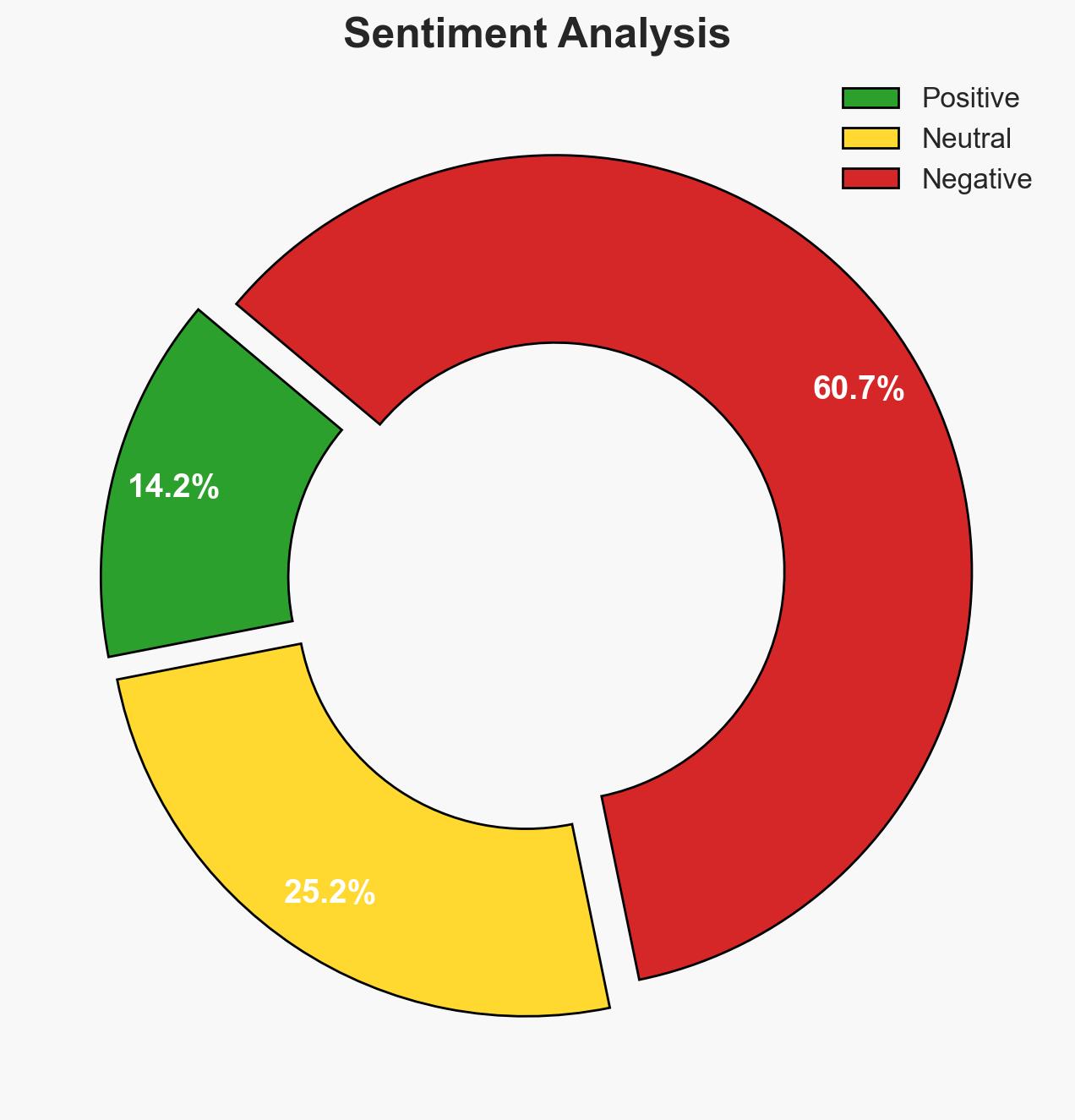
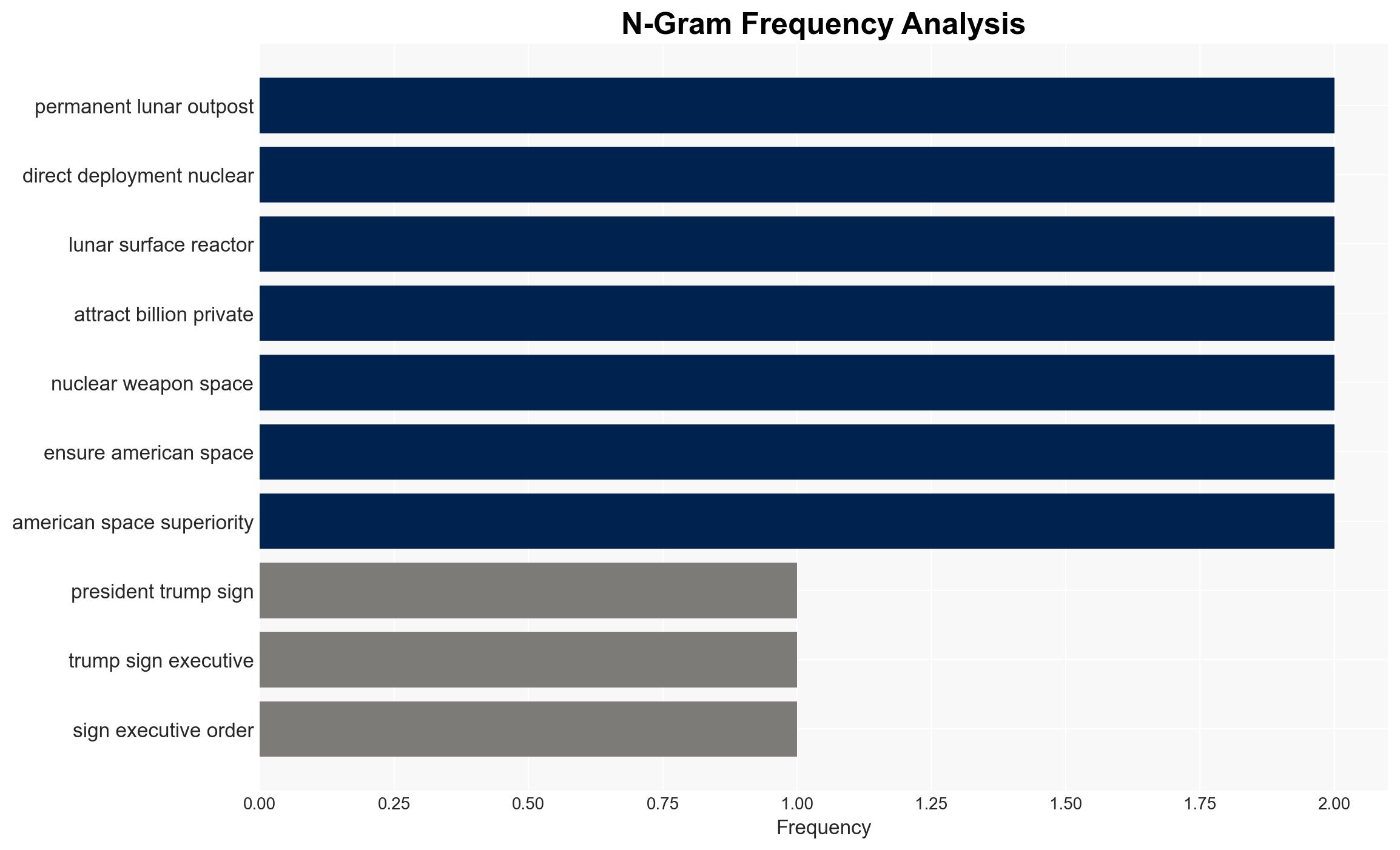
The executive order signed by President Trump mandates a strategic shift in U.S. space policy, focusing on establishing a permanent lunar base powered by nuclear energy by 2030. This move is aimed at securing national security and commercial dominance in space, with significant implications for geopolitical competition, particularly with China. The overall confidence level in this assessment is moderate, given the ambitious timelines and technological challenges involved.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The U.S. will successfully establish a permanent lunar base by 2030, leveraging private investment and technological advancements. This is supported by the executive order’s clear directives and the mobilization of private capital. However, uncertainties include technological feasibility and sustained political support.
- Hypothesis B: The U.S. will face significant delays or fail to meet the 2030 deadline for a lunar base due to technological, financial, or geopolitical challenges. This is supported by historical precedents of delays in large-scale space projects and potential geopolitical tensions.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the strong policy directive and potential for private sector engagement. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include technological setbacks or shifts in political priorities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The U.S. government will maintain consistent funding and political support for the lunar base project; private sector investment will be sufficiently mobilized; technological advancements will proceed as planned.
- Information Gaps: Detailed timelines and technological milestones for the lunar base project; specific private sector commitments and partnerships.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential overestimation of technological readiness; political bias in portraying the initiative as a guaranteed success; adversarial misinformation campaigns.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development of a U.S. lunar base could significantly alter geopolitical dynamics, particularly in relation to China and other space-faring nations. The initiative may lead to an arms race in space and increased militarization of space assets.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential escalation of space competition with China and Russia; diplomatic tensions over space resource utilization.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased focus on space-based missile defense systems; potential vulnerabilities to space-based assets.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened risk of cyber-attacks on space infrastructure; information warfare targeting space initiatives.
- Economic / Social: Significant economic opportunities for the private sector; potential public debate over the prioritization of space over domestic issues.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Establish a task force to monitor progress and challenges; engage with private sector stakeholders to secure commitments.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for space infrastructure; foster international partnerships to mitigate geopolitical tensions.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful establishment of a lunar base by 2030, enhancing U.S. dominance in space.
- Worst: Project delays lead to loss of strategic advantage and increased geopolitical tensions.
- Most-Likely: Partial success with some delays, maintaining competitive parity with other nations.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
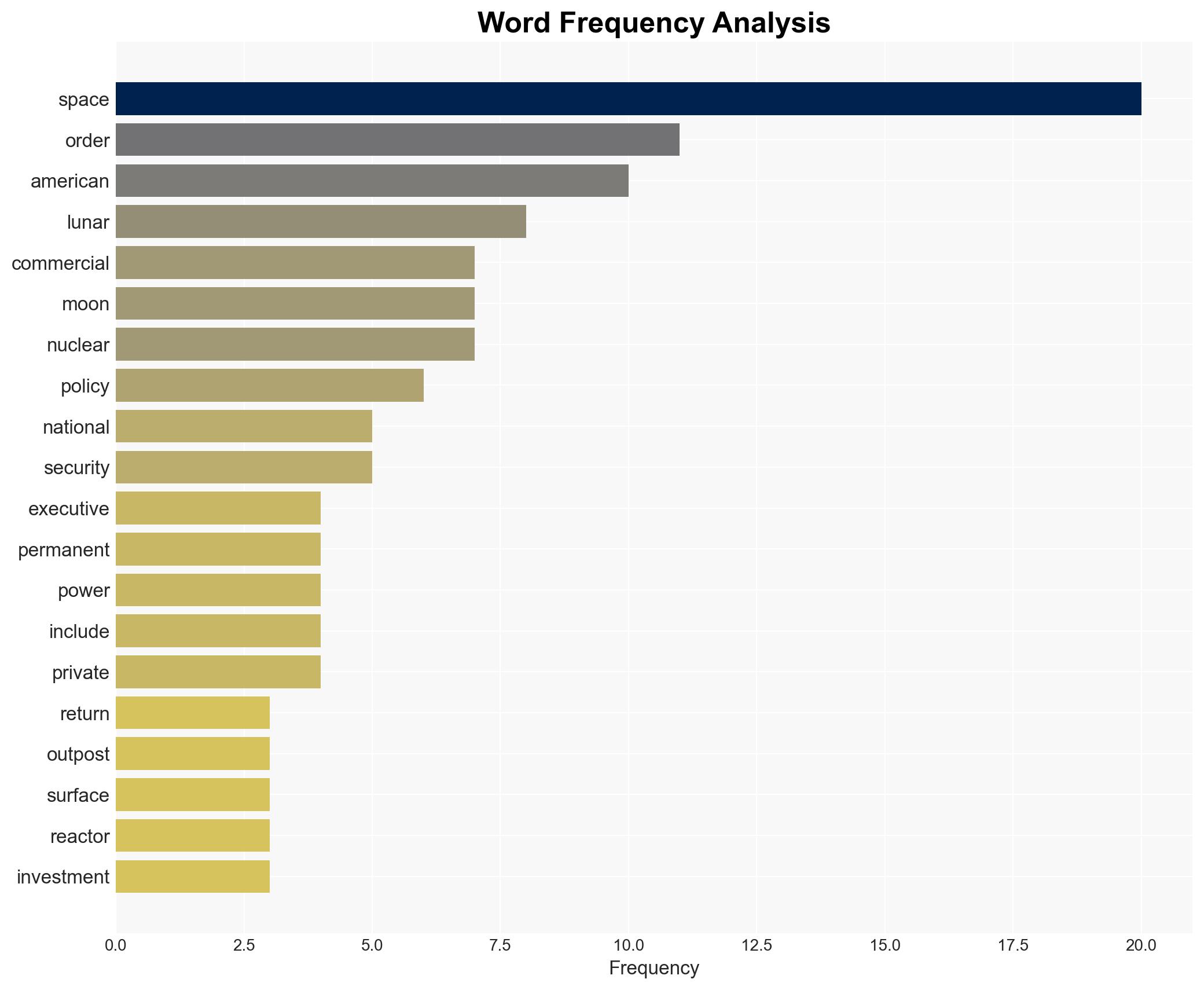
national security threats, space policy, lunar base, nuclear power, geopolitical competition, national security, private investment, space exploration
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us