US Pursues Third Tanker Near Venezuela Amid Intensified Oil Blockade Against Maduro’s Regime
Published on: 2025-12-21
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Breaking US Intercepts Third Tanker Near Venezuela
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
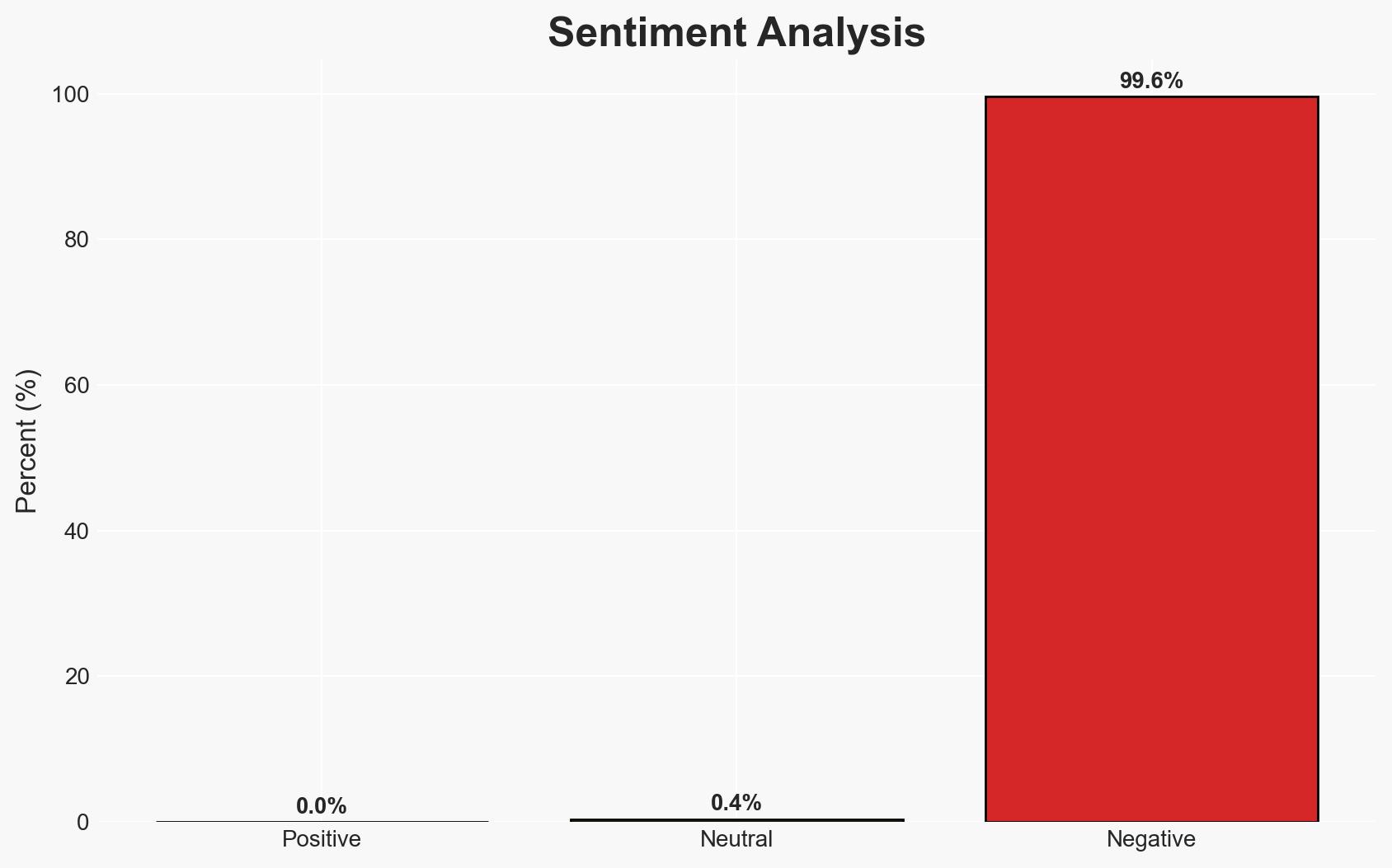
The United States is intensifying its blockade against Venezuela by intercepting oil tankers, aiming to pressure Nicolás Maduro’s regime economically. The most likely hypothesis is that the US seeks to cripple Venezuela’s oil revenue, which could lead to significant economic and social instability in Venezuela. This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to incomplete information on the broader geopolitical implications.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The US is intercepting tankers to economically isolate the Maduro regime, forcing a political change by crippling its oil-dependent economy. Supporting evidence includes the US’s judicial seizure orders and the strategic timing of the interceptions. However, the lack of public sanctions on some vessels introduces uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The US actions are primarily aimed at enforcing international sanctions against illegal oil trade and drug trafficking linked to the Maduro regime. This is supported by the designation of the Maduro government as a foreign terrorist organization. Contradicting evidence includes the potential for these actions to escalate geopolitical tensions without clear evidence of immediate illegal activity by the intercepted tankers.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the strategic focus on economic pressure and the direct impact on Venezuela’s oil exports. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of direct links between the tankers and illicit activities or a change in US diplomatic posture.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The Maduro regime is heavily reliant on oil exports; US actions are primarily economic rather than military; intercepted tankers are directly linked to Venezuelan oil exports.
- Information Gaps: Detailed intelligence on the ownership and cargo of the intercepted tankers; the extent of international support or opposition to US actions.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in US sources emphasizing economic motives; Venezuelan government statements may be propaganda or misdirection.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could exacerbate Venezuela’s economic crisis, potentially leading to increased social unrest and migration pressures. It may also strain US relations with countries sympathetic to Venezuela.
- Political / Geopolitical: Risk of escalating tensions with allies of Venezuela, such as China and Russia, potentially leading to broader geopolitical conflicts.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased likelihood of internal unrest in Venezuela, which could destabilize the region.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for cyber retaliation by state or non-state actors aligned with Venezuela; increased propaganda efforts by the Maduro regime.
- Economic / Social: Further deterioration of Venezuela’s economy, leading to humanitarian crises and regional instability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of maritime traffic near Venezuela; engage in diplomatic efforts to clarify US intentions and mitigate international tensions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for potential regional instability; strengthen partnerships with regional allies to manage humanitarian impacts.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: US pressure leads to political reform in Venezuela without major conflict.
- Worst: Escalation leads to military confrontation or severe regional instability.
- Most-Likely: Continued economic pressure results in increased internal unrest and migration.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Nicolás Maduro – President of Venezuela
- Donald Trump – Former President of the United States
- Delcy Rodriguez – Venezuelan Vice President and Oil Minister
- Petróleos de Venezuela SA (PDVSA) – State-owned oil company
- Anna Kelly – White House spokeswoman
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet for tanker ownership and operational command.
7. Thematic Tags
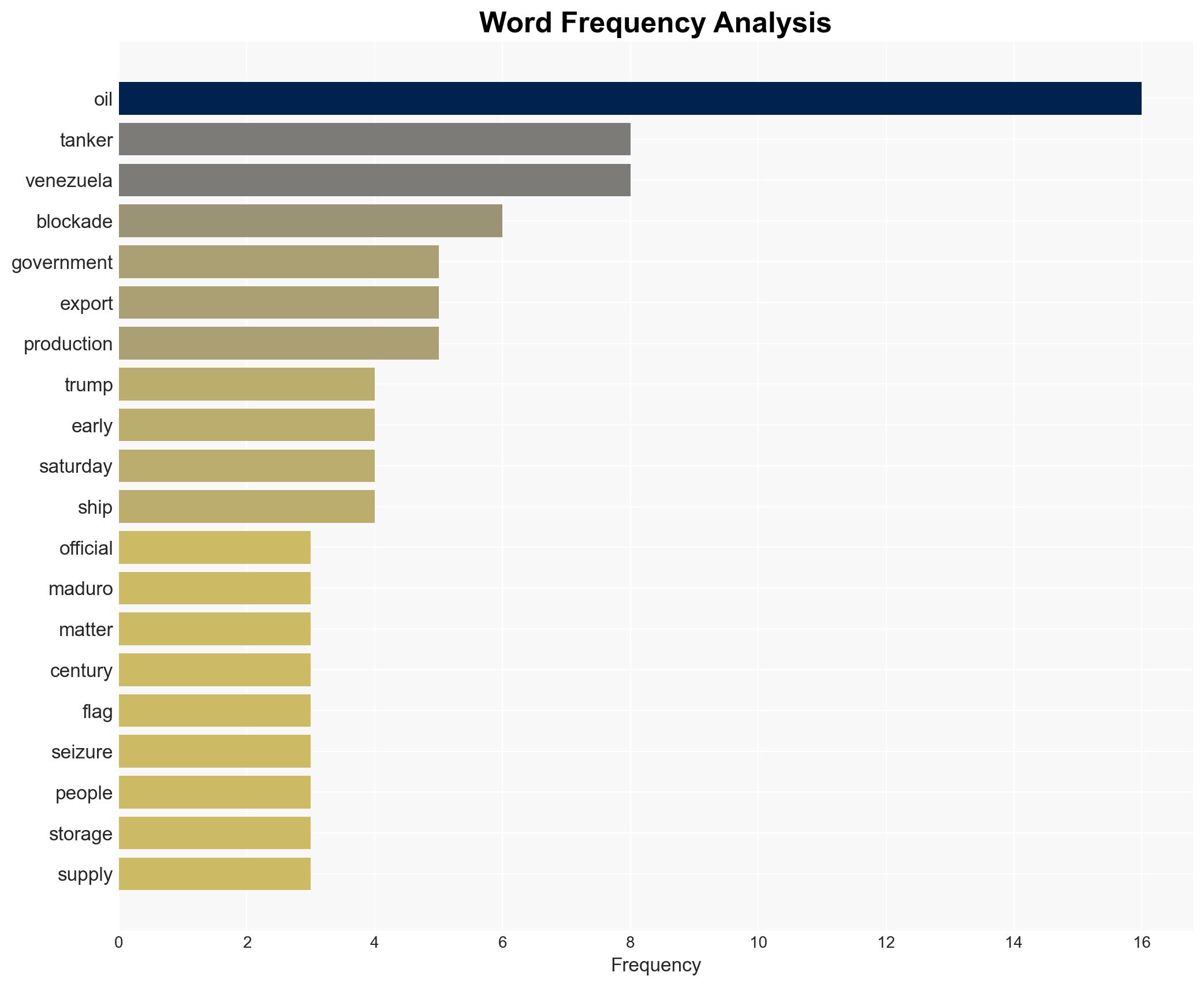
national security threats, sanctions, oil blockade, Venezuela, US foreign policy, economic pressure, geopolitical tensions, maritime security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us