Emergence of DIG AI: Unregulated Darknet Assistant Fuels Criminal Activities and Threats Ahead of Major Events
Published on: 2025-12-22
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
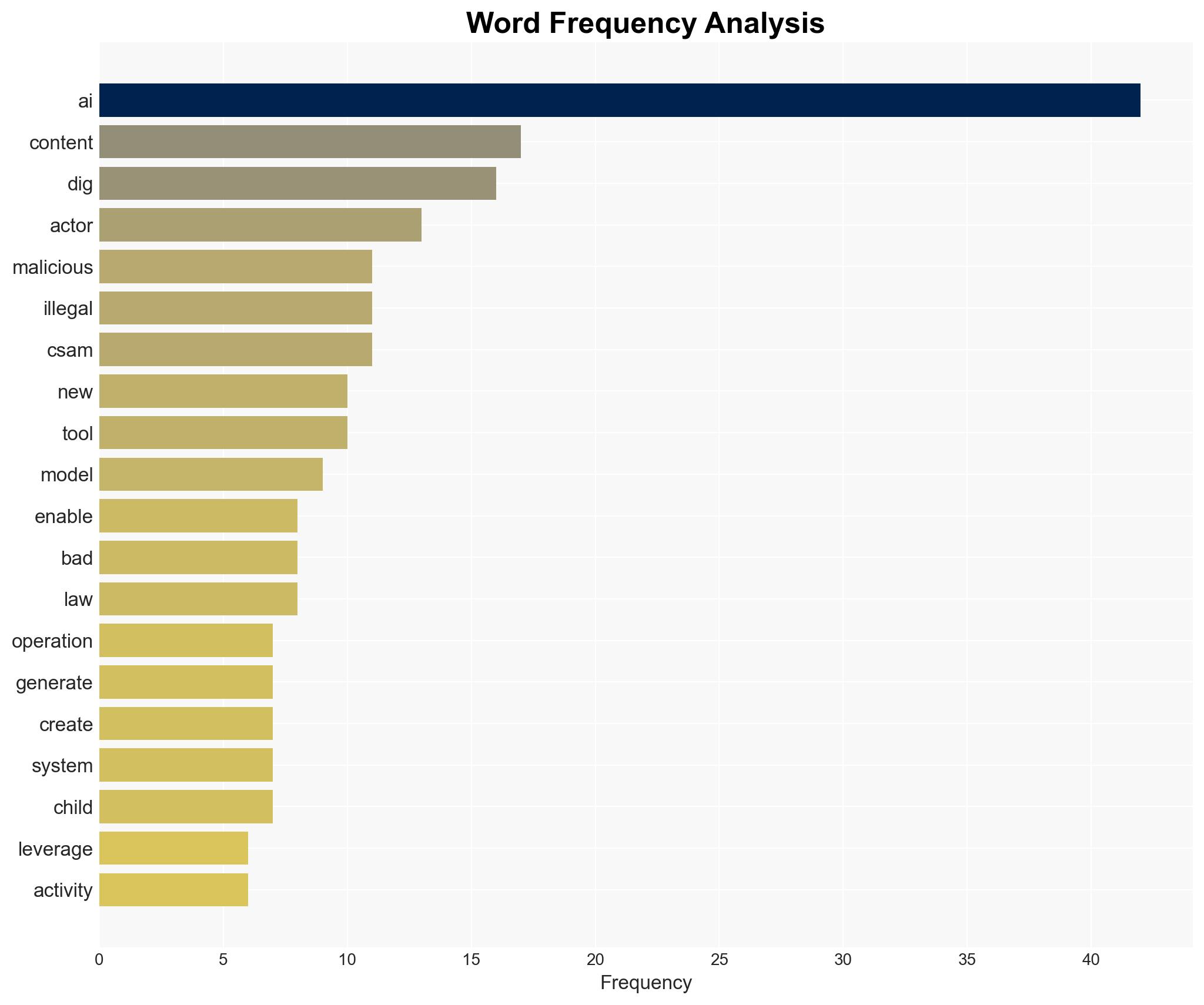
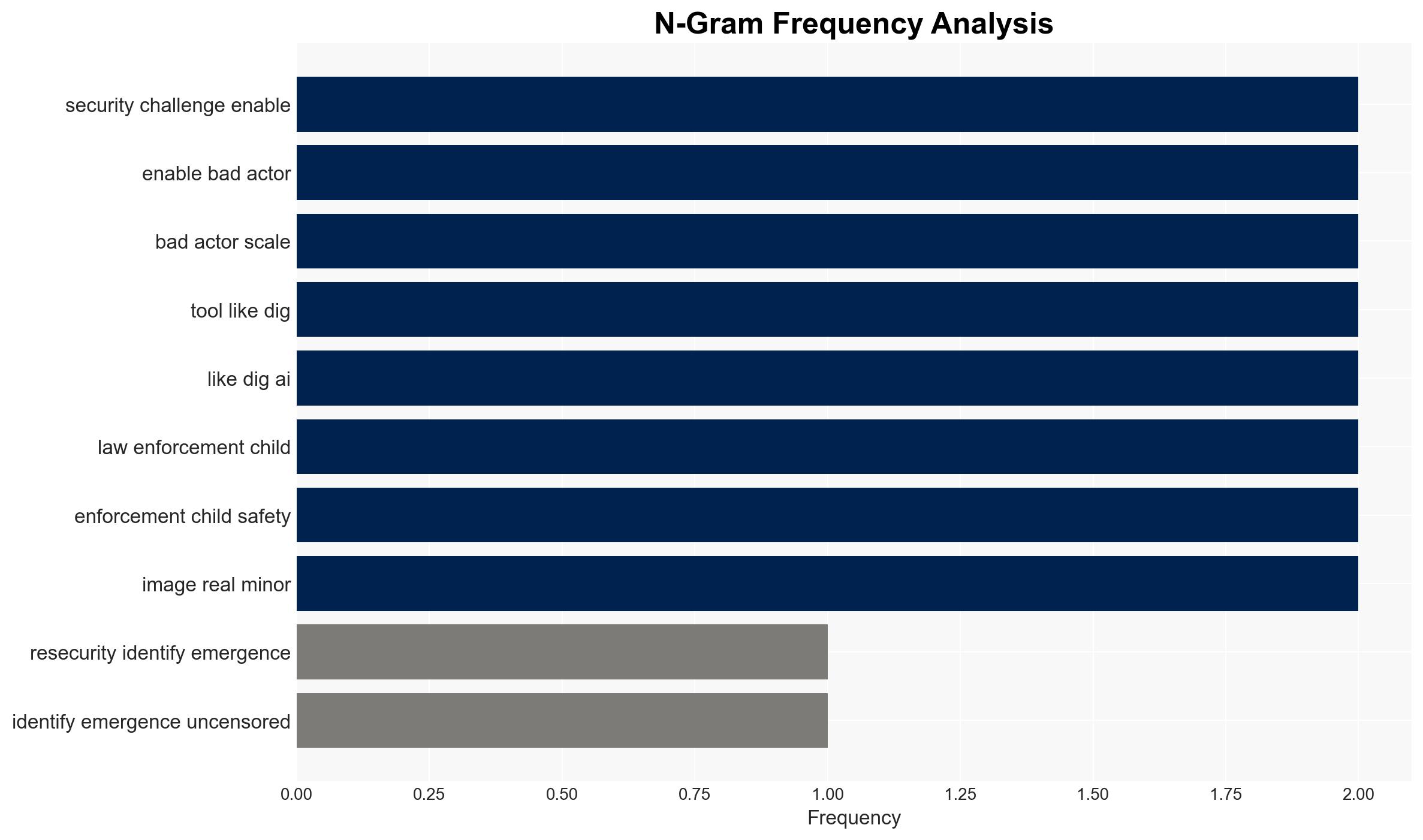
Intelligence Report: DIG AI Uncensored darknet AI assistant at the service of criminals and terrorists
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
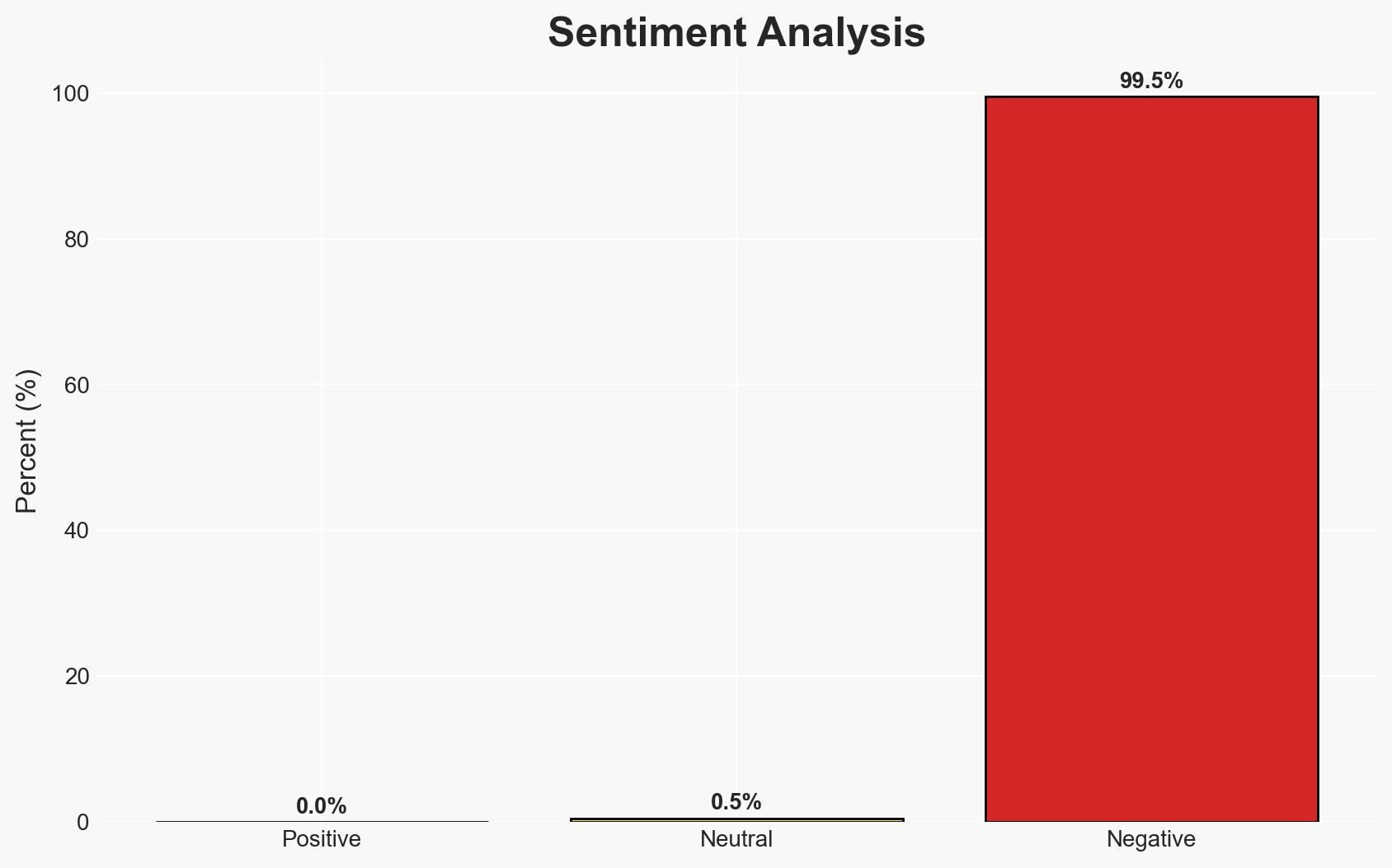
The emergence of DIG AI, an uncensored darknet AI assistant, represents a significant threat to national security, enabling cybercriminals and terrorists to enhance their operations. The tool’s accessibility and capabilities to facilitate illegal activities pose substantial risks, particularly with upcoming global events in 2026. We assess with moderate confidence that DIG AI will continue to proliferate among malicious actors, potentially leading to increased cybercrime and extremist activities.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: DIG AI will primarily be used by cybercriminals to automate and scale existing criminal activities. This is supported by the tool’s popularity in cybercriminal forums and its ability to bypass content protection policies. However, the extent of its use by terrorists remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: DIG AI will be adopted by both cybercriminals and terrorist organizations to conduct a broader range of malicious activities, including extremism and misinformation campaigns. The tool’s capabilities and ease of access support this hypothesis, but there is limited direct evidence of terrorist use.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to documented use by cybercriminals and the rapid adoption of similar AI tools in these circles. Indicators such as increased mentions in extremist forums could shift this judgment towards Hypothesis B.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: DIG AI’s capabilities will continue to evolve; cybercriminals will prioritize AI tools that enhance operational efficiency; law enforcement will face challenges in detecting and mitigating darknet activities.
- Information Gaps: Specific data on the extent of DIG AI’s use by terrorist organizations; detailed technical capabilities of DIG AI; effectiveness of current countermeasures.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on cybercriminal forums as primary sources; risk of underestimating the adaptability of law enforcement; possible misinformation from threat actors to exaggerate capabilities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The proliferation of DIG AI could lead to a significant increase in cybercrime and potentially enable terrorist activities, challenging existing security frameworks. Its evolution may influence broader dynamics in technology misuse and digital security.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased international pressure on darknet regulation and AI governance.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced operational capabilities for threat actors, complicating counter-terrorism efforts.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased sophistication and volume of cyber-attacks; potential for misinformation campaigns.
- Economic / Social: Potential destabilization of financial systems through cybercrime; erosion of public trust in digital platforms.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of darknet forums; enhance collaboration with international cybercrime units; develop rapid response protocols.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Invest in AI detection and countermeasure technologies; strengthen public-private partnerships; conduct regular threat assessments.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful international cooperation leads to effective suppression of DIG AI and similar tools.
- Worst: Widespread adoption by terrorists results in significant global security incidents.
- Most-Likely: Continued use by cybercriminals with gradual adoption by extremists, leading to increased cyber threats.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, cybercrime, darknet, artificial intelligence, counter-terrorism, digital security, misinformation, international cooperation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model hostile behavior to identify vulnerabilities.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us