Operation Sentinel Leads to 574 Arrests and $3 Million Recovered in Major Cybercrime Crackdown
Published on: 2025-12-23
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Hundreds of Arrests as Operation Sentinel Recovers 3m
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
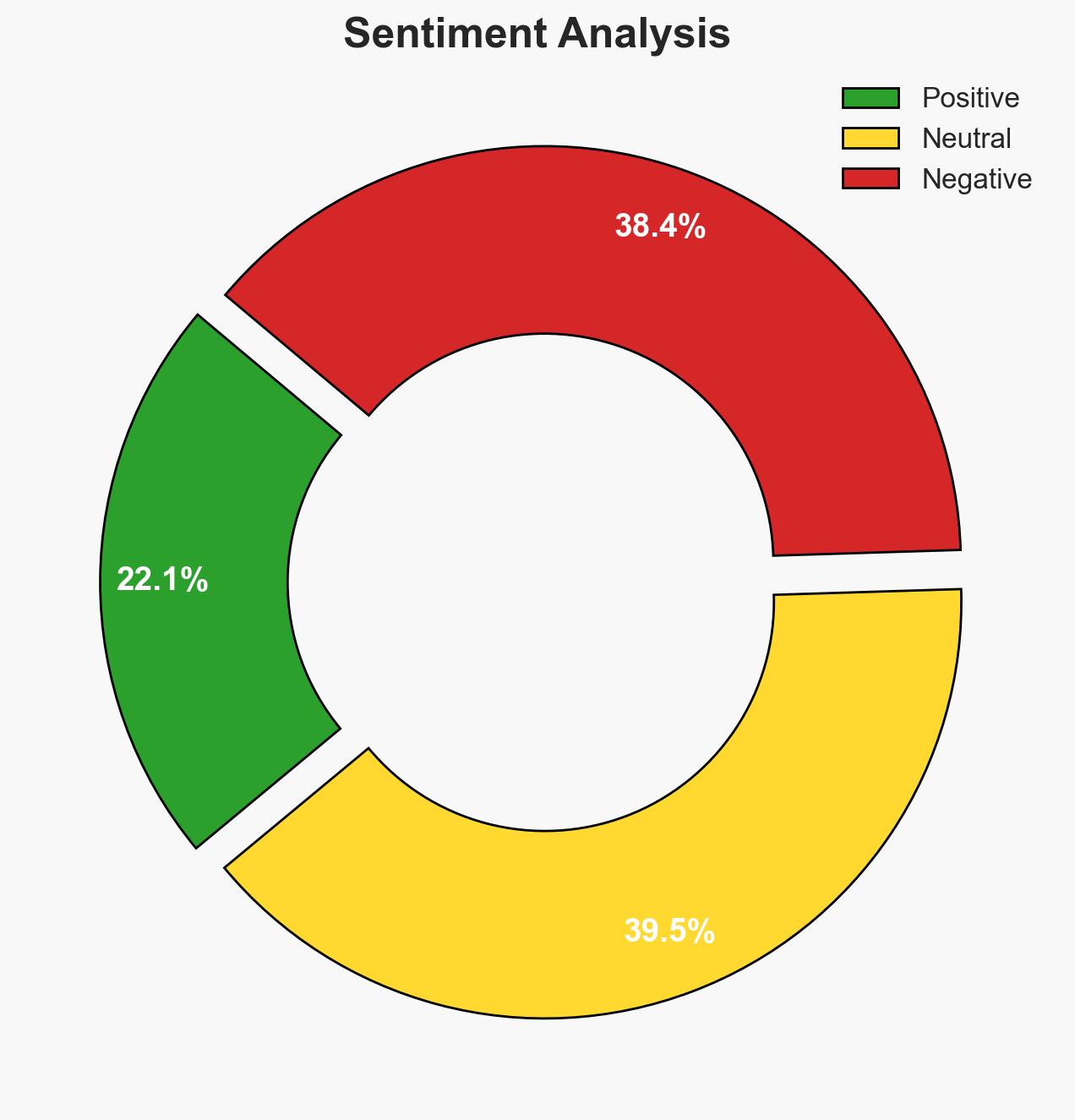
Operation Sentinel, coordinated by Interpol, resulted in 574 arrests and the recovery of $3 million in cybercrime proceeds across Africa. This operation highlights the increasing sophistication and prevalence of cybercrime on the continent, particularly targeting critical sectors. The operation’s success underscores the effectiveness of international collaboration in combating cyber threats. Overall confidence in these findings is moderate due to potential information gaps and biases.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Operation Sentinel’s success is primarily due to effective international collaboration and coordination among African law enforcement agencies. Supporting evidence includes the involvement of multiple international partners and the coordinated actions across several countries. However, the exact contribution of each partner and the sustainability of these efforts remain uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The operation’s success is largely due to the inherent vulnerabilities and lack of preparedness in African cyber infrastructure, which made it easier to identify and dismantle cybercriminal networks. While the rapid increase in cybercrime supports this hypothesis, it does not fully account for the operational successes achieved.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the documented international partnerships and coordinated efforts, which are critical in addressing transnational cybercrime. Indicators such as continued international support and capacity-building in African law enforcement could further substantiate this hypothesis.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: African law enforcement agencies have the capacity to sustain anti-cybercrime operations; international partnerships will continue to support these efforts; cybercrime will remain a priority for African governments.
- Information Gaps: Detailed breakdown of the roles and contributions of international partners; specific methodologies used in the operation; long-term impact on cybercrime rates in the region.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on Interpol’s reporting; possible underreporting of unsuccessful aspects of the operation; cognitive bias towards attributing success to international collaboration.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The success of Operation Sentinel could lead to increased international support and collaboration in combating cybercrime in Africa. However, it may also drive cybercriminals to adapt and evolve their tactics, potentially increasing the sophistication of future attacks.
- Political / Geopolitical: Strengthened international relations and partnerships between African countries and global entities; potential for increased geopolitical influence of supporting nations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced capabilities of African law enforcement could improve overall security and counter-terrorism efforts, though cybercriminals may shift tactics.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible escalation in cyber threats as criminals adapt; increased focus on cybersecurity measures and infrastructure improvements.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic benefits from reduced cybercrime; improved public trust in digital transactions; however, social unrest could arise if cybercriminals target vulnerable populations.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of cybercrime trends; strengthen information-sharing mechanisms among international partners; conduct a comprehensive review of Operation Sentinel’s methodologies.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures and cybersecurity training programs for African law enforcement; foster long-term international partnerships; invest in cybersecurity infrastructure.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Sustained international collaboration leads to a significant reduction in cybercrime across Africa.
- Worst Case: Cybercriminals adapt quickly, leading to more sophisticated attacks and increased economic losses.
- Most-Likely: Continued international efforts result in moderate success, with cybercriminals gradually adapting to new law enforcement strategies.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Interpol
- African Joint Operation against Cybercrime (AFJOC)
- Team Cymru
- The Shadowserver Foundation
- Trend Micro
- TRM Labs
- Uppsala Security
- Neal Jetton, Interpol Director of Cybercrime
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet for specific African law enforcement agencies involved.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, cybercrime, international collaboration, law enforcement, Africa, financial crime, ransomware
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us