Critical UEFI Firmware Vulnerability Found in Major Motherboard Brands, Exposing Systems to DMA Attacks
Published on: 2025-12-23
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: New UEFI Firmware Flaw Exposes Popular Motherboards To Attacks
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
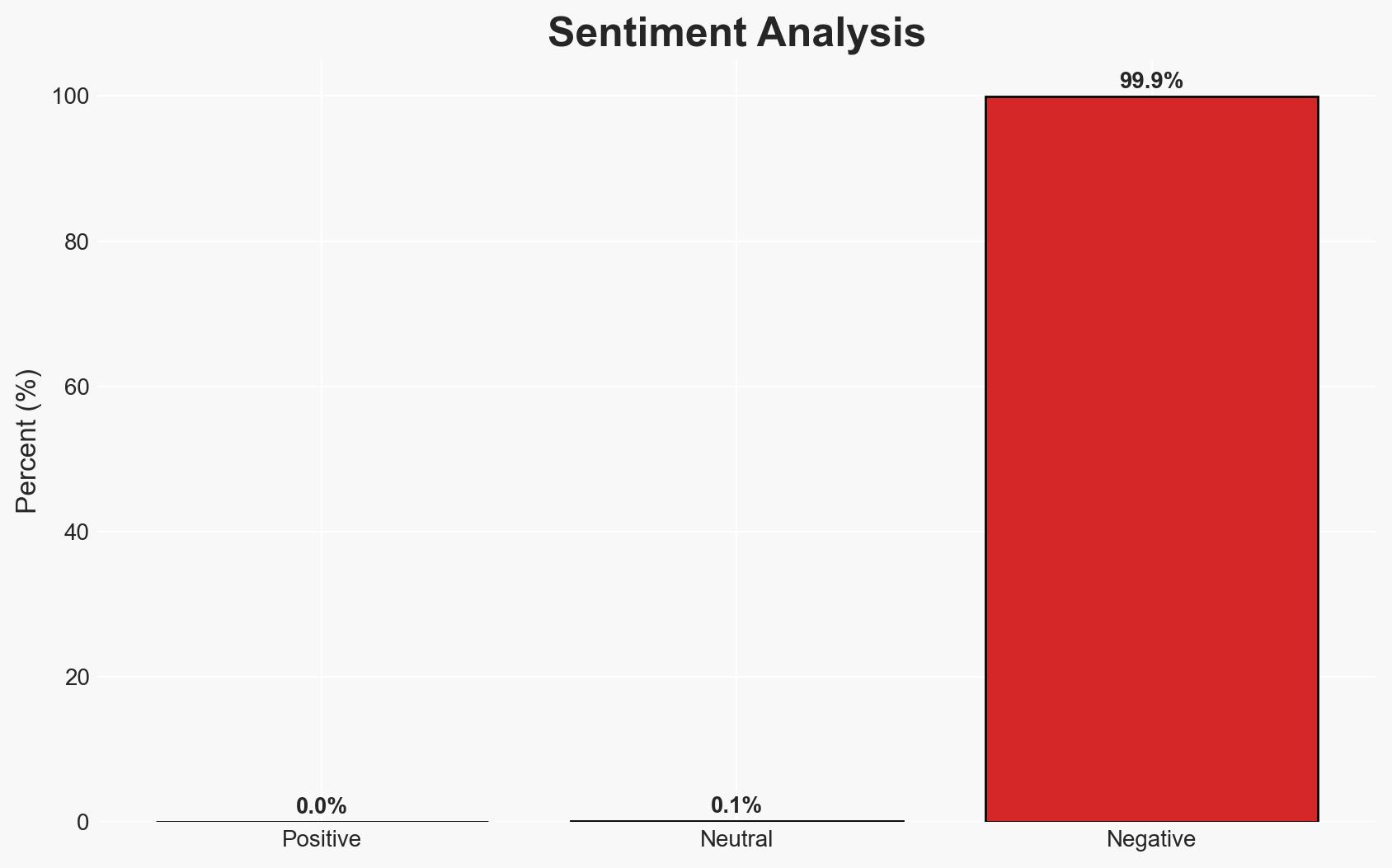
A newly discovered UEFI firmware flaw exposes motherboards from major manufacturers to potential DMA attacks, posing a significant security risk. The vulnerability affects systems from Gigabyte, MSI, ASUS, and ASRock, with potential for deep and persistent unauthorized access. However, the requirement for physical access limits widespread exploitation. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerability will primarily affect high-value targets with physical access risks, such as corporate or government systems, due to the physical access requirement for exploitation. Supporting evidence includes the need for pre-boot access to connect malicious devices. Key uncertainties involve the potential for remote exploitation techniques to emerge.
- Hypothesis B: The vulnerability will have limited impact due to the physical access requirement, making widespread exploitation unlikely. Contradicting evidence includes the potential for advanced threat actors to develop new methods of exploitation. Key uncertainties include the speed and effectiveness of firmware patch deployment by manufacturers.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the physical access prerequisite, which significantly reduces the likelihood of widespread exploitation. Indicators that could shift this judgment include reports of remote exploitation or significant delays in patch deployment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The vulnerability requires physical access for exploitation; manufacturers will release timely patches; affected users will apply updates promptly.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on the vulnerability’s potential for remote exploitation; timelines for patch releases from all affected manufacturers.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential underestimation of threat actors’ capabilities to bypass physical access requirements; reliance on manufacturer disclosures for patch timelines.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This vulnerability could lead to targeted attacks on high-value systems, particularly if physical access can be obtained. The broader impact is mitigated by the physical access requirement, but delays in patch deployment could increase risk exposure.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for exploitation in espionage activities targeting government or corporate entities.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of targeted attacks on critical infrastructure if physical access is feasible.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber espionage activities; heightened awareness and scrutiny of firmware vulnerabilities.
- Economic / Social: Possible disruption to businesses reliant on affected hardware; increased costs related to security patching and system upgrades.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor for firmware updates from manufacturers; advise high-risk entities to review physical security controls.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with hardware vendors for timely vulnerability disclosures; enhance capabilities for detecting unauthorized physical access attempts.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid patch deployment mitigates risk; no significant exploitation occurs.
- Worst: Delays in patching lead to exploitation by advanced threat actors; remote exploitation techniques emerge.
- Most-Likely: Limited exploitation due to physical access constraints; gradual patch deployment reduces risk over time.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Gigabyte, MSI, ASUS, ASRock (motherboard manufacturers)
- Riot Games (researchers who identified the vulnerability)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, firmware vulnerability, hardware security, DMA attacks, UEFI, motherboard manufacturers, patch management
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us