FCC Prohibits Foreign Drones and Components to Mitigate National Security Threats
Published on: 2025-12-23
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: FCC Bans Foreign-Made Drones and Key Parts Over US National Security Risks
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
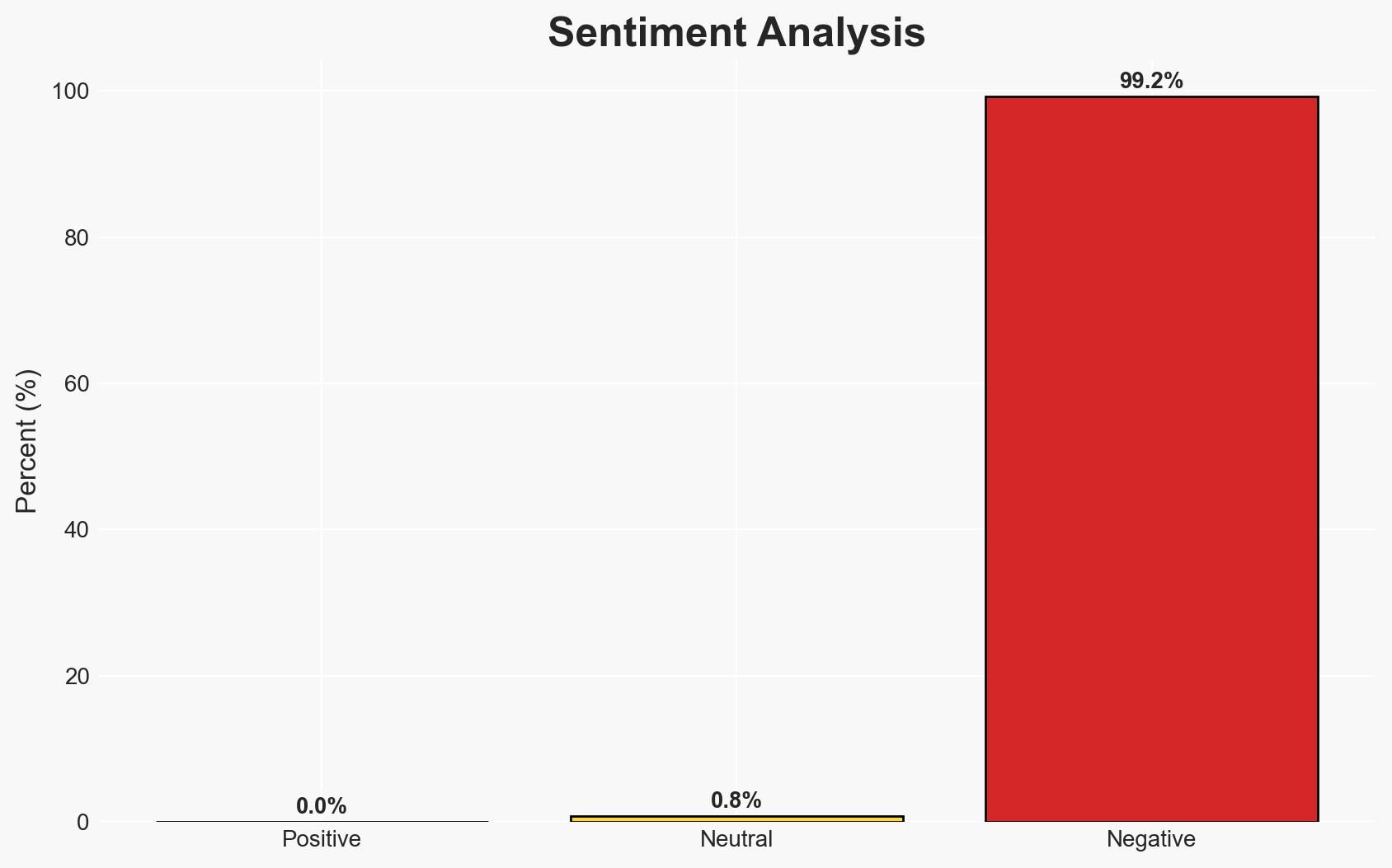
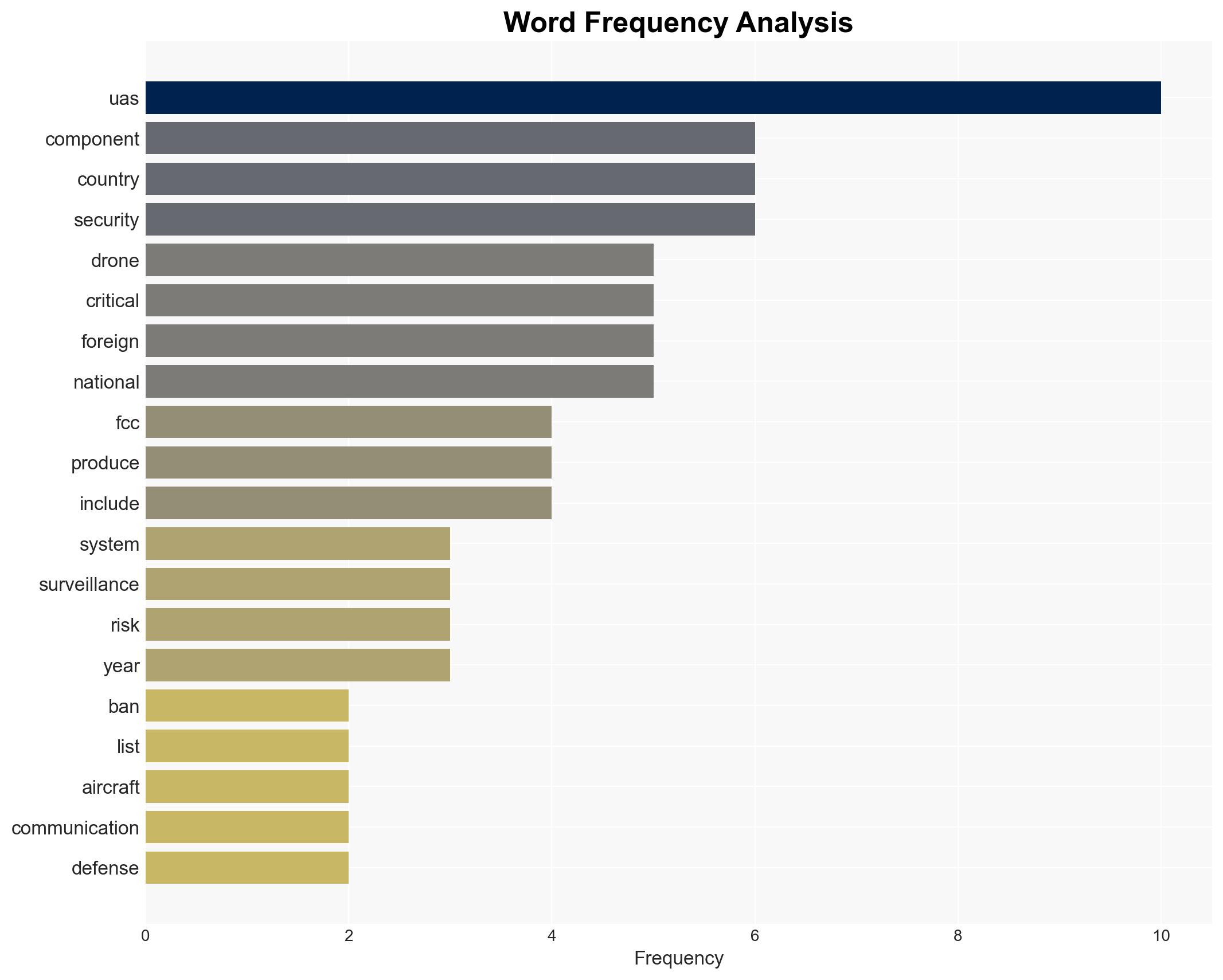
The FCC’s ban on foreign-made drones and components, primarily targeting Chinese manufacturers, aims to mitigate national security risks associated with potential misuse by hostile actors. This policy affects manufacturers, importers, and users of such drones in the U.S. The decision is underpinned by concerns over unauthorized surveillance and data exfiltration. Overall, the assessment is made with moderate confidence due to existing information gaps and potential geopolitical ramifications.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The ban is primarily a security measure to prevent espionage and cyber threats from foreign-made drones. Supporting evidence includes the FCC’s emphasis on national security risks and the potential for drones to be weaponized. Contradicting evidence includes the lack of specific incidents cited that directly link these drones to security breaches.
- Hypothesis B: The ban is a strategic move to bolster domestic drone manufacturing and reduce dependency on foreign technology. This is supported by the FCC’s statement on the need for U.S.-produced components. However, the immediate security rationale provided by the FCC suggests a more urgent threat perception.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the explicit national security concerns outlined by the FCC and the interagency review’s findings. Indicators that could shift this judgment include new evidence of economic motivations or changes in U.S.-China relations.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The ban will effectively reduce national security risks; U.S. manufacturers can meet demand for compliant drones; foreign-made drones pose a significant security threat.
- Information Gaps: Specific incidents of security breaches involving foreign-made drones; detailed criteria used by DHS for exemptions.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential for confirmation bias in assessing threat levels; geopolitical bias against specific countries influencing policy decisions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased tensions with countries whose manufacturers are affected, particularly China, and may prompt retaliatory measures. The ban may also drive innovation in domestic drone technology but could disrupt current market dynamics.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential escalation in U.S.-China trade tensions and diplomatic friction.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced security posture against drone-based threats; potential gaps during the transition to domestic production.
- Cyber / Information Space: Reduced risk of data exfiltration and unauthorized surveillance; possible increase in cyber espionage attempts as a countermeasure.
- Economic / Social: Short-term market disruptions; potential job creation in domestic manufacturing; consumer pushback due to limited product availability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor compliance with the ban; engage with domestic manufacturers to assess production capabilities; enhance surveillance of potential retaliatory actions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships to strengthen domestic supply chains; invest in R&D for drone technology; establish clear guidelines for exemptions.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Successful transition to domestic production with minimal disruption.
- Worst Case: Significant geopolitical backlash and market instability.
- Most-Likely: Gradual adaptation with ongoing diplomatic tensions and market adjustments.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- FCC (Federal Communications Commission)
- DHS (Department of Homeland Security)
- DJI
- Autel Robotics
- U.S. Executive Branch Interagency Body
- U.S. President Donald Trump
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, national security, drone technology, U.S.-China relations, trade policy, domestic manufacturing, airspace sovereignty
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us