Cybersecurity Threats to Industrial Automation in North and South America: Q3 2025 Analysis
Published on: 2025-12-23
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Threat landscape for industrial automation systems South and North America Canada Q3 2025
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
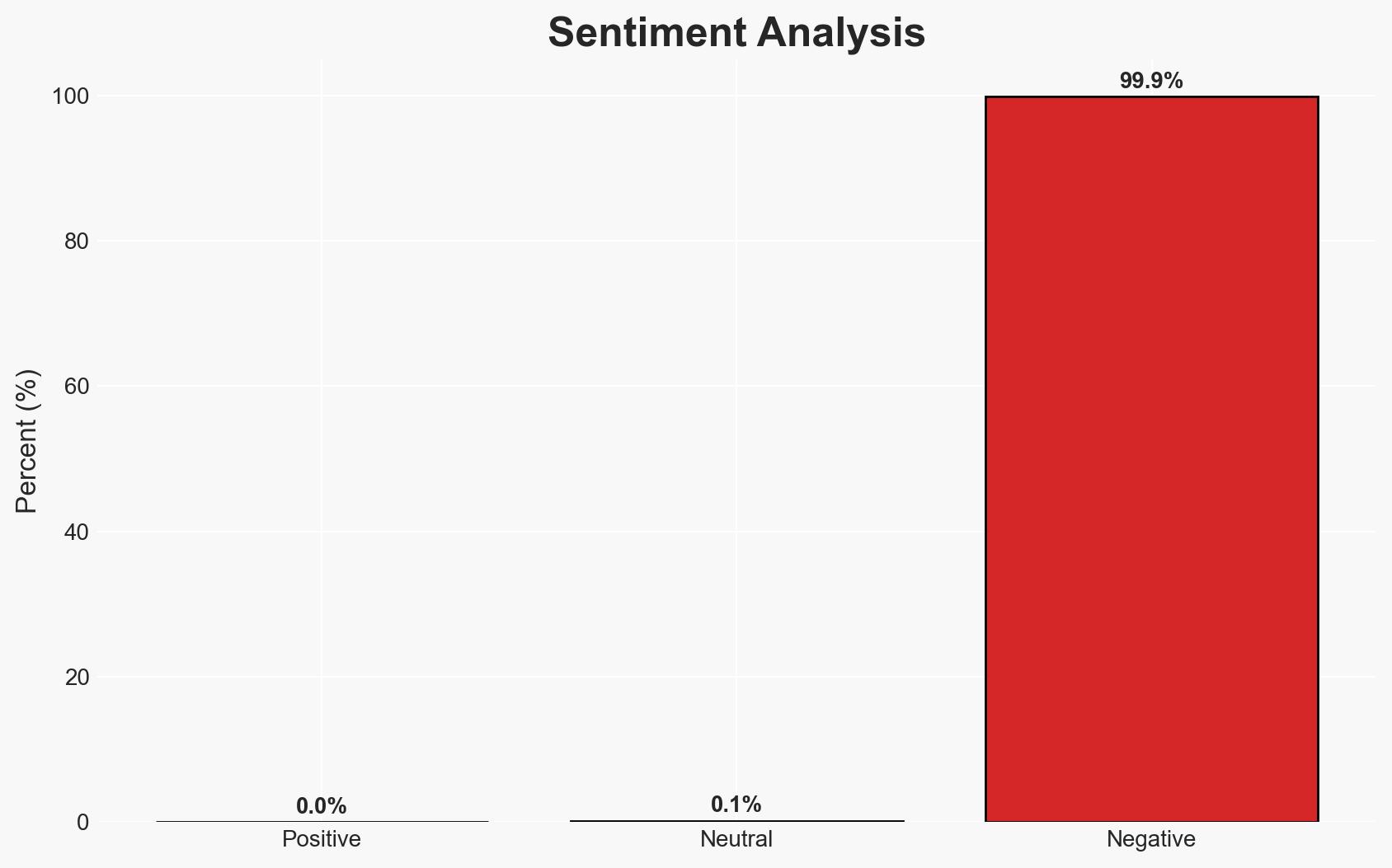
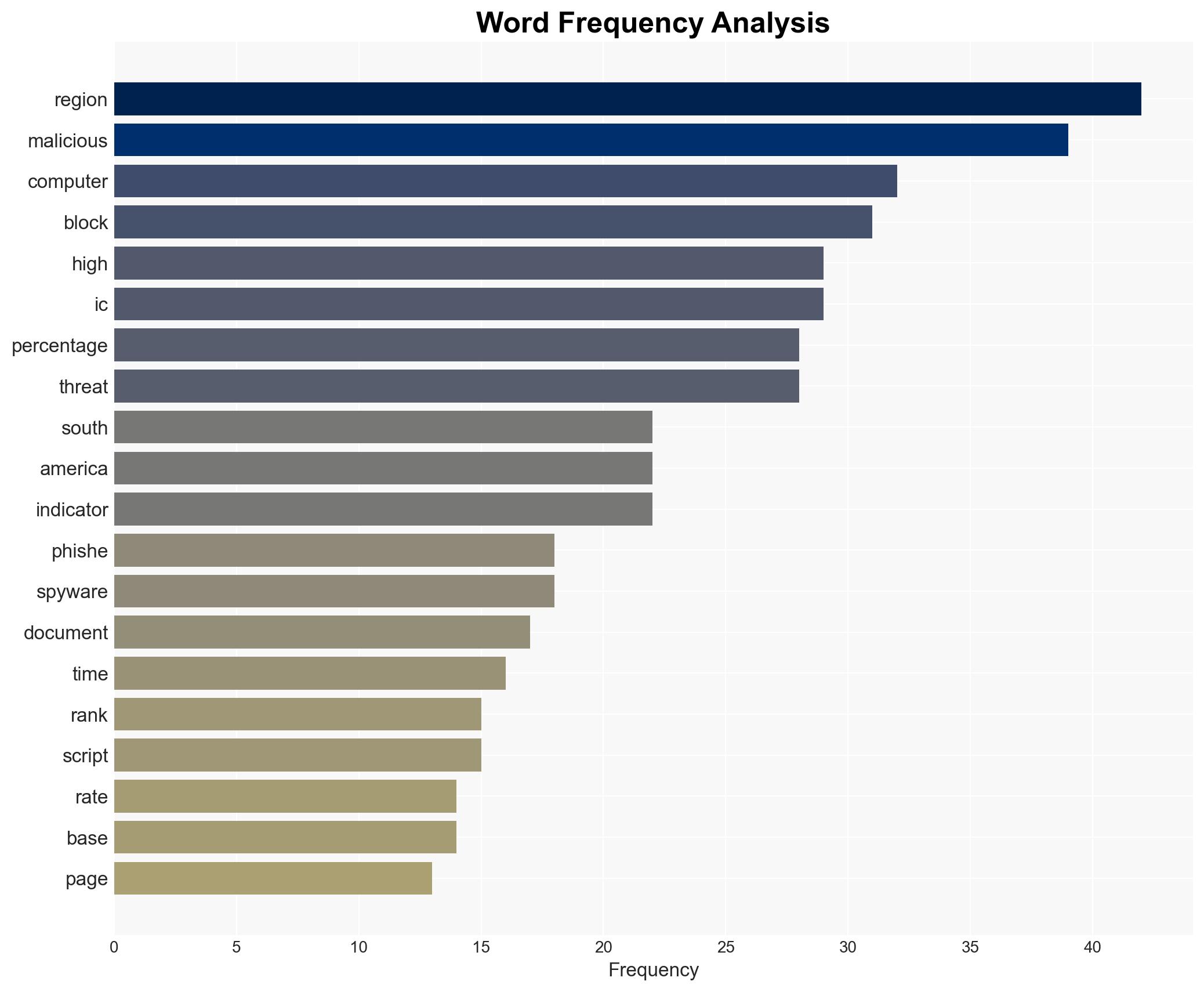
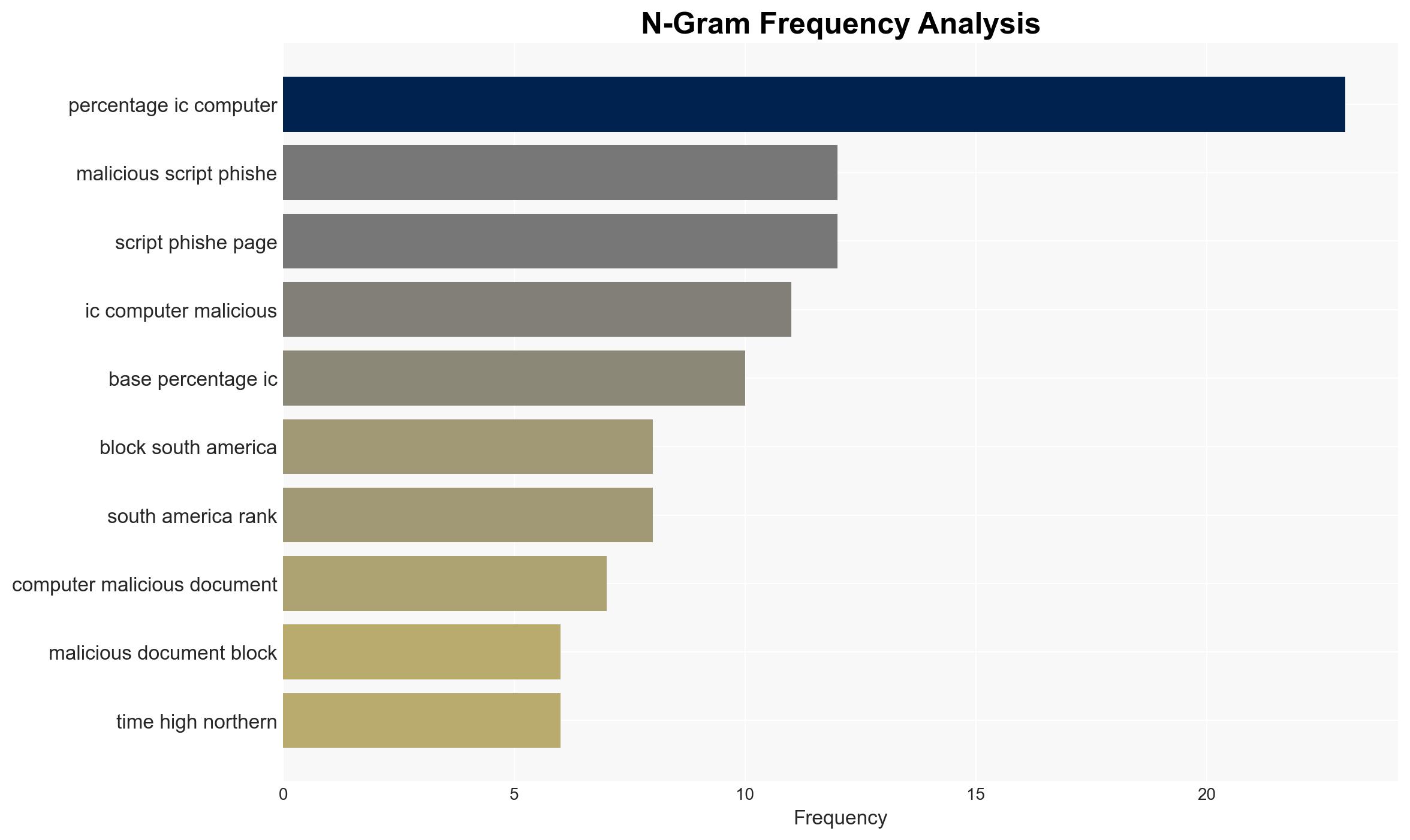
The industrial automation systems in South America are facing a significant cybersecurity threat landscape, characterized by a high incidence of phishing, spyware, and malicious document attacks. The region’s exposure is notably higher than the global average, indicating a targeted focus by threat actors. This situation poses a substantial risk to industrial operations and data integrity. Overall confidence in this judgment is moderate, given the available data.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The high rate of cybersecurity incidents in South America is primarily due to targeted campaigns by sophisticated threat actors exploiting regional vulnerabilities. This is supported by the high incidence of phishing and malicious documents, often using localized and business-like communication.
- Hypothesis B: The elevated threat levels are a result of inadequate cybersecurity measures and awareness among industrial enterprises in South America, making them easy targets for opportunistic attacks. This is contradicted by the sophisticated nature of the attacks, which suggests deliberate targeting rather than random exploitation.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the targeted nature of the attacks and the use of specific exploits and localized phishing tactics. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of widespread security lapses or increased incidents in other regions with similar vulnerabilities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The threat actors have advanced capabilities; regional cybersecurity defenses are insufficient; the data reflects a comprehensive view of the threat landscape.
- Information Gaps: Detailed attribution of threat actors, specific industries most affected, and the effectiveness of current defensive measures.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on reported data from cybersecurity firms, which may have commercial biases; possibility of threat actors using deception to mask true intentions or origins.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolving threat landscape in South America could lead to increased operational disruptions and data breaches in industrial sectors, potentially affecting regional economic stability and investor confidence.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state-sponsored actors are implicated, leading to diplomatic strains.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of industrial espionage and sabotage, requiring enhanced security measures.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased need for robust cybersecurity frameworks and information-sharing initiatives.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact due to operational disruptions and loss of sensitive data, affecting social trust in technology.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of phishing and malware campaigns; conduct awareness training for employees; review and update security protocols.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop regional cybersecurity partnerships; invest in advanced threat detection technologies; strengthen incident response capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful mitigation reduces threat levels, leading to improved regional cybersecurity resilience.
- Worst: Escalation of attacks causes significant industrial disruptions and economic damage.
- Most-Likely: Continued targeted attacks with gradual improvements in defensive measures and awareness.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, industrial automation, phishing, spyware, South America, threat actors, information security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us