Major Cyber Crime Incidents of 2025: AI Exploitation and High-Profile Targets in the UK
Published on: 2025-12-24
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Top 10 cyber crime stories of 2025
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
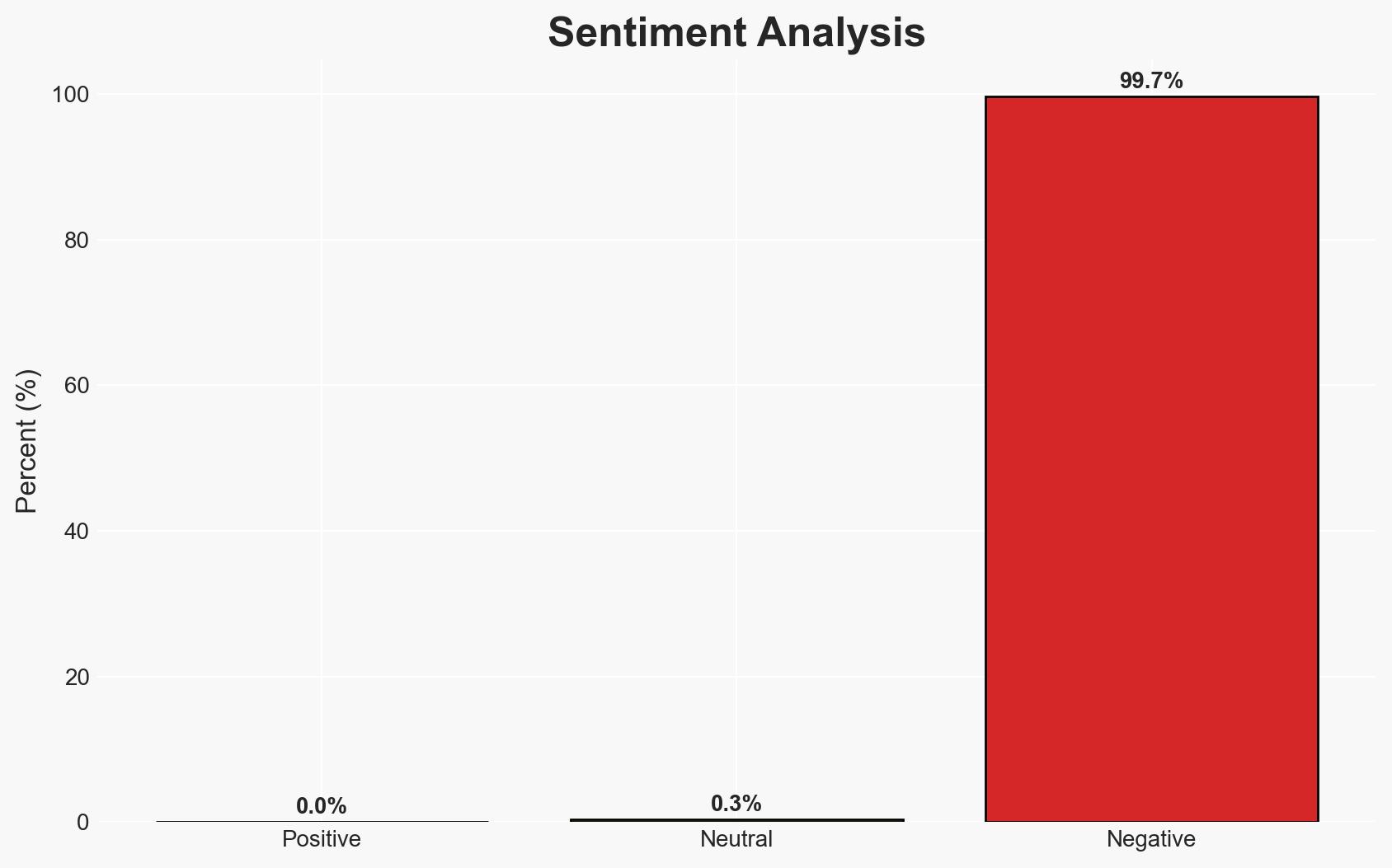
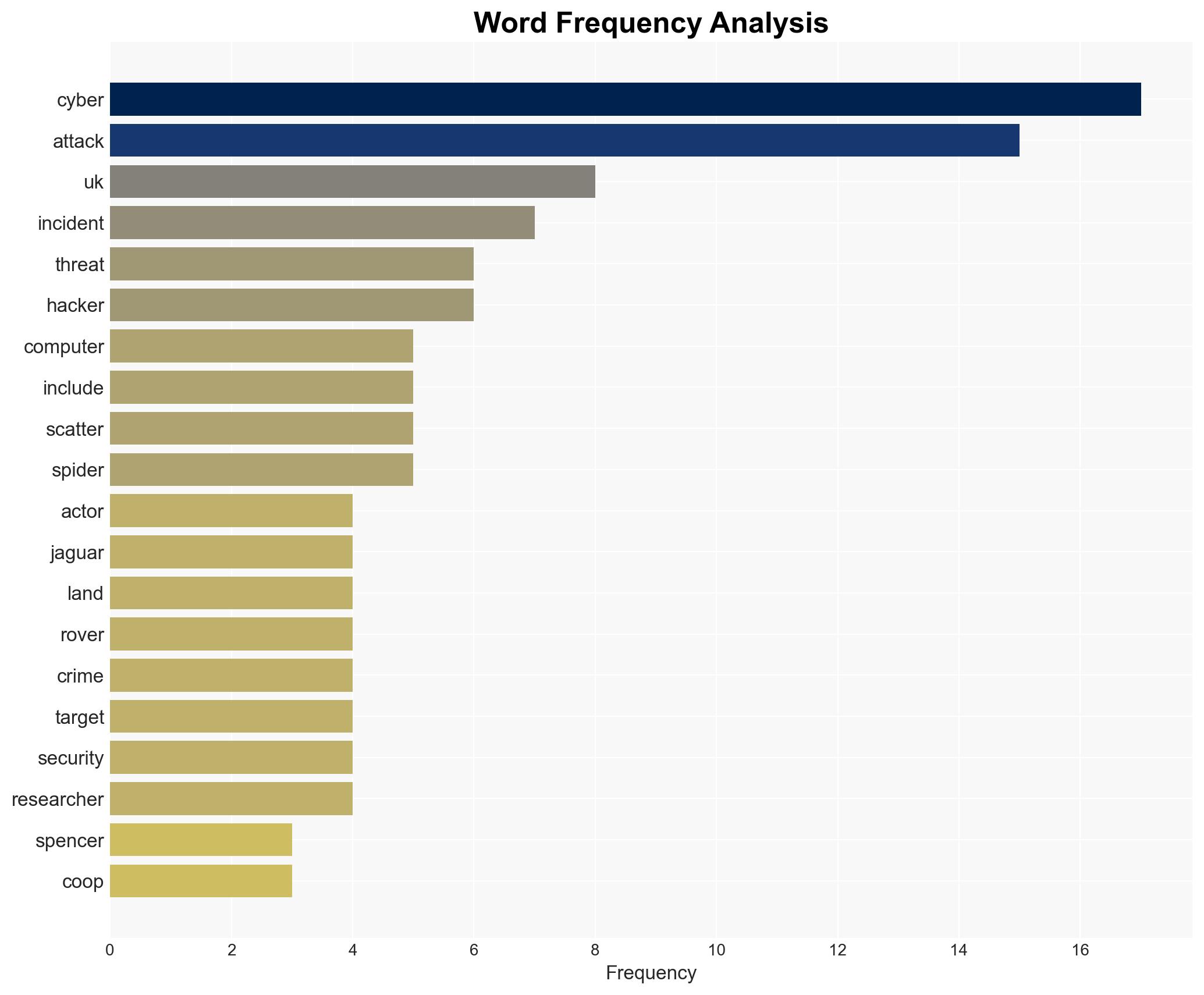
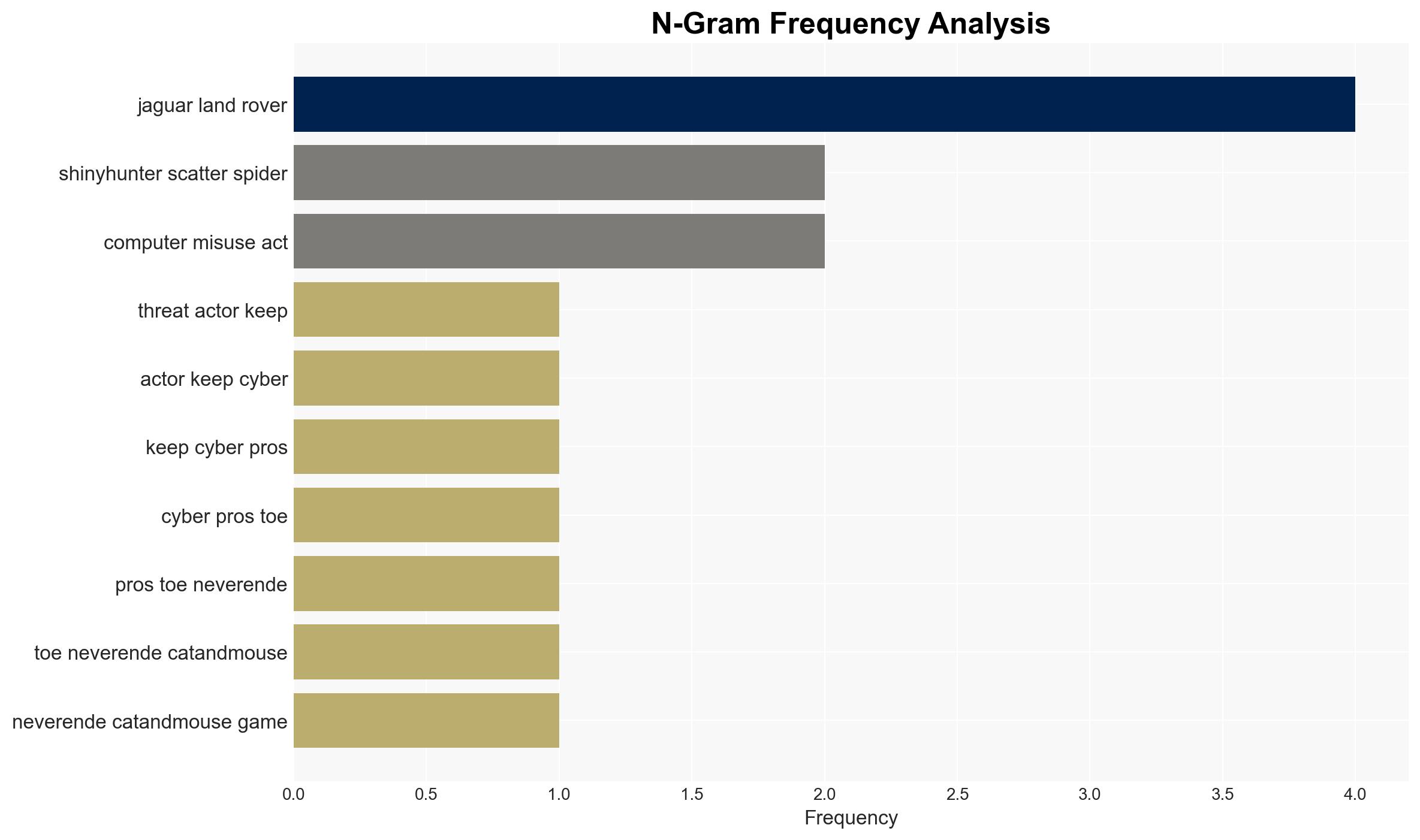
In 2025, cyber threat actors, including nation-state-backed groups, intensified their operations, exploiting AI technologies and targeting major UK companies such as Marks & Spencer and Jaguar Land Rover. The most likely hypothesis is that these activities represent a coordinated effort to destabilize critical sectors, with moderate confidence in this assessment. Key affected parties include the UK retail and aviation sectors, as well as international AI technology firms.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The cyber attacks are part of a coordinated campaign by nation-state actors to exploit AI vulnerabilities and disrupt Western economies. This is supported by the involvement of state-backed groups from China, Iran, North Korea, and Russia. However, the direct attribution to these states remains uncertain due to potential false-flag operations.
- Hypothesis B: The attacks are primarily driven by financially motivated cybercriminal groups, such as Scattered Spider, leveraging AI tools for opportunistic gains. This is supported by the targeting of high-profile commercial entities and the use of sophisticated techniques typical of organized crime.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the strategic nature of the targets and the involvement of nation-state actors. Indicators such as increased geopolitical tensions or further attribution evidence could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI technologies are vulnerable to exploitation; nation-state actors have the capability and intent to target Western economies; cybercriminal groups are increasingly sophisticated.
- Information Gaps: Detailed attribution of specific attacks to nation-state actors; comprehensive understanding of AI vulnerabilities exploited.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential for confirmation bias in attributing attacks to state actors; risk of deception through false-flag operations.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The exploitation of AI and cyber attacks on critical sectors could lead to increased geopolitical tensions and economic instability. Over time, these developments may drive regulatory changes and increased investment in cybersecurity.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential escalation in cyber warfare tactics between nation-states, impacting diplomatic relations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment requiring enhanced defensive measures and international cooperation.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on securing AI technologies and infrastructure from cyber threats.
- Economic / Social: Disruption to major industries could affect economic stability and consumer confidence.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of AI systems for vulnerabilities; increase collaboration with international partners for threat intelligence sharing.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for critical sectors; invest in AI security research and development; strengthen public-private partnerships.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Improved AI security reduces attack success; Worst: Escalation of cyber attacks leads to significant economic damage; Most-Likely: Continued cyber threats with incremental improvements in defenses.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG)
- Marks & Spencer
- Co-op Group
- Scattered Spider
- UK National Crime Agency (NCA)
- OneAdvanced (formerly Advanced Computer Software Group)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, AI exploitation, nation-state actors, economic disruption, cybercrime, geopolitical tensions, public-private partnerships
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us