Cyber Attack Causes Major Service Disruption at La Poste, Affecting Digital Banking and Online Platforms
Published on: 2025-12-24
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: La Poste outage after a cyber attack disrupts digital banking and online services
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
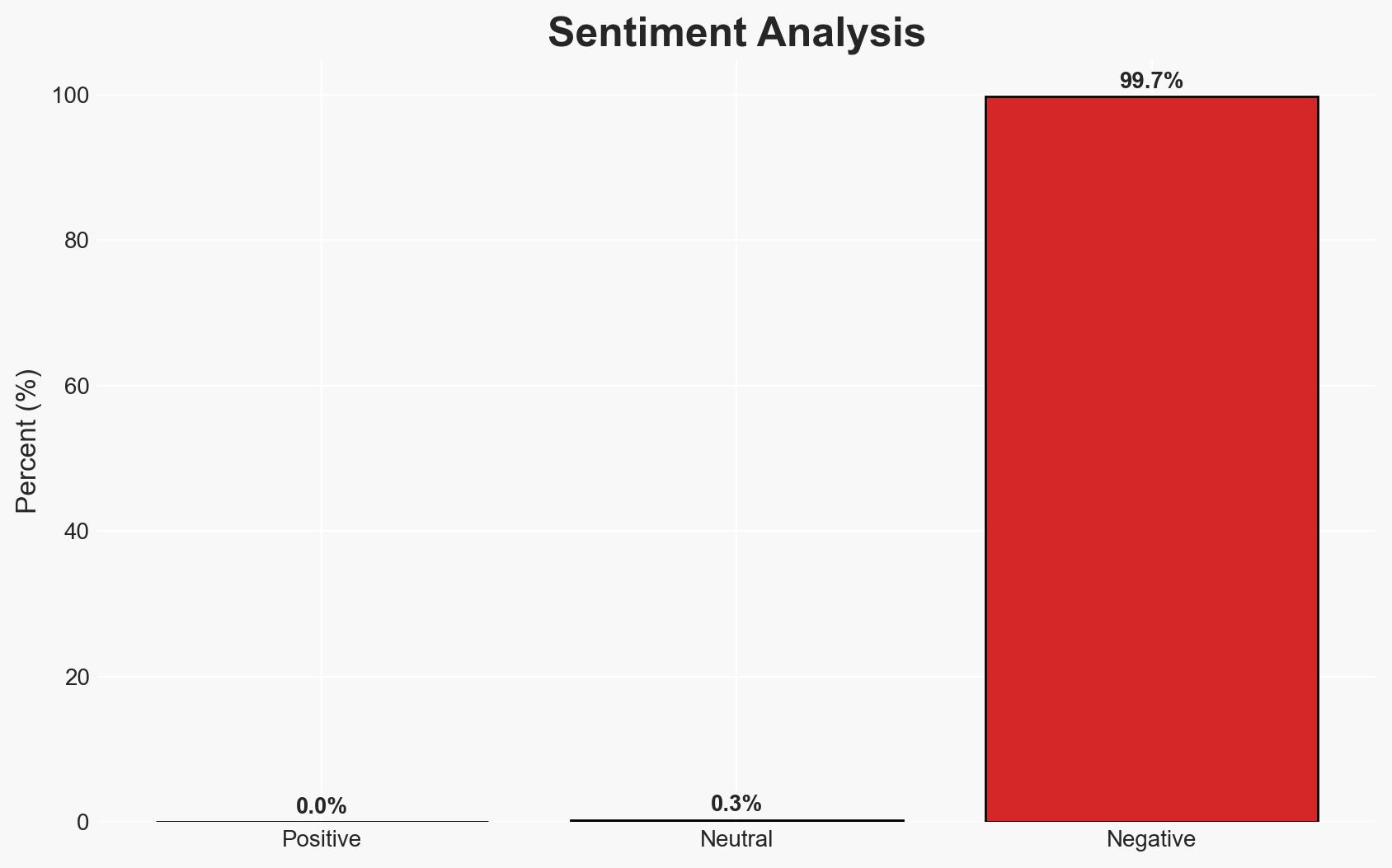
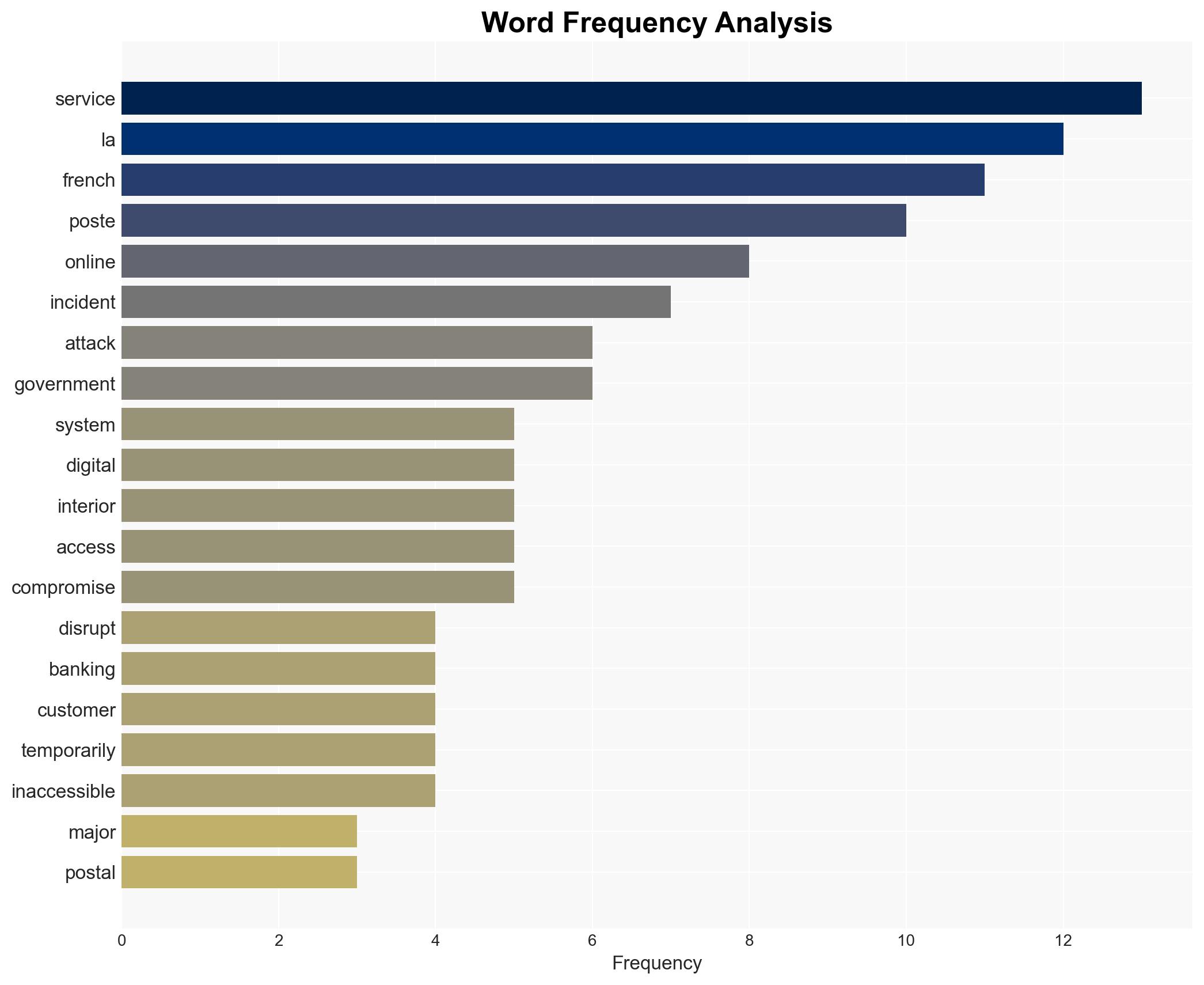
The recent cyber attack on La Poste, identified as a DDoS incident, has disrupted digital banking and online services for millions of users. While no customer data was compromised, the attack highlights vulnerabilities in critical national infrastructure. The most likely hypothesis is that this was a targeted disruption rather than an attempt at data theft, with moderate confidence due to lack of detailed technical information.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The attack was a deliberate DDoS operation aimed at disrupting La Poste’s services without intent to steal data. This is supported by the nature of the attack and the lack of data compromise. However, the absence of a claim of responsibility leaves uncertainty about the attackers’ motives.
- Hypothesis B: The attack was a diversion for a more sophisticated intrusion aimed at data theft or espionage. This hypothesis is less supported due to La Poste’s statement that no data was compromised, but the recent attack on France’s Interior Ministry suggests a potential pattern of targeting French institutions.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the nature of the attack and public statements. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include new evidence of data compromise or a claim of responsibility.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The attack was not state-sponsored; La Poste’s public statements are accurate; the incident is isolated and not part of a larger coordinated campaign.
- Information Gaps: Technical details of the attack vector; identity and motives of the attackers; potential links to other recent cyber incidents in France.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential underreporting of the incident’s severity by La Poste; confirmation bias in linking this incident to other recent attacks without sufficient evidence.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This incident underscores the vulnerability of national infrastructure to cyber attacks and could prompt increased scrutiny and regulatory measures. The lack of data compromise limits immediate damage, but the disruption could erode public trust in digital services.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if linked to foreign actors; pressure on government to enhance cybersecurity measures.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened alert for similar attacks on other critical infrastructure; potential for copycat incidents.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on DDoS mitigation strategies and resilience; potential for misinformation if the incident is exploited by adversaries.
- Economic / Social: Short-term economic impact on La Poste’s operations; potential long-term effects on consumer confidence in digital banking.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of La Poste’s network for further anomalies; collaborate with cybersecurity agencies to trace the attack’s origin.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Invest in DDoS protection and incident response capabilities; strengthen public-private partnerships for information sharing.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid recovery with no further incidents; improved cybersecurity posture.
- Worst: Escalation to data breaches or additional attacks on critical infrastructure.
- Most-Likely: Continued vigilance and incremental improvements in cybersecurity defenses.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- La Poste
- La Banque Postale
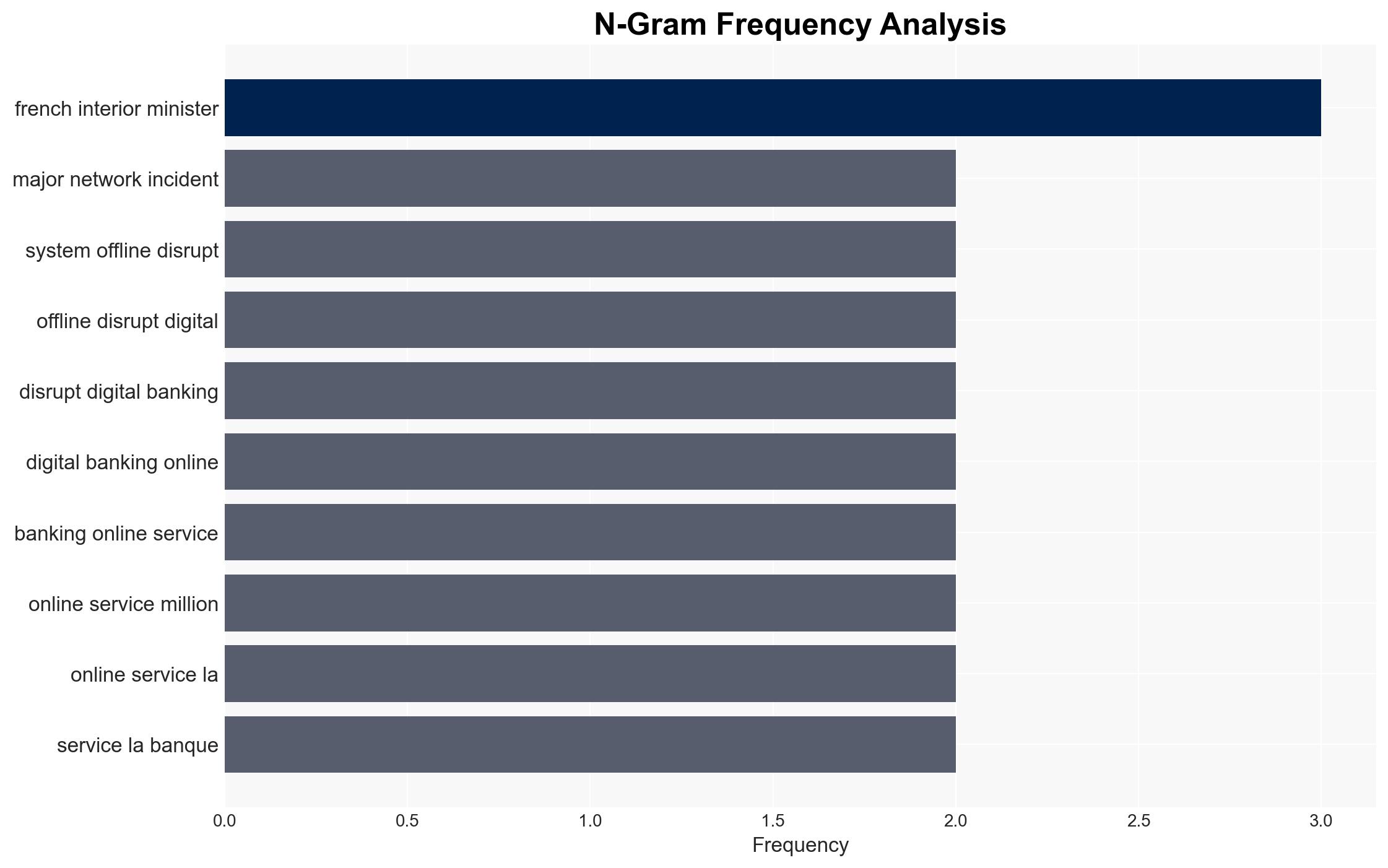
- French Interior Ministry
- Laurent Nunez, French Interior Minister
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet for attackers
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, DDoS attack, critical infrastructure, digital banking, national security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us