UN Calls for Immediate Ceasefire and Compromise Amid Escalating Violence in Sudan
Published on: 2025-12-27
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: UN renews ceasefire push in Sudan
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
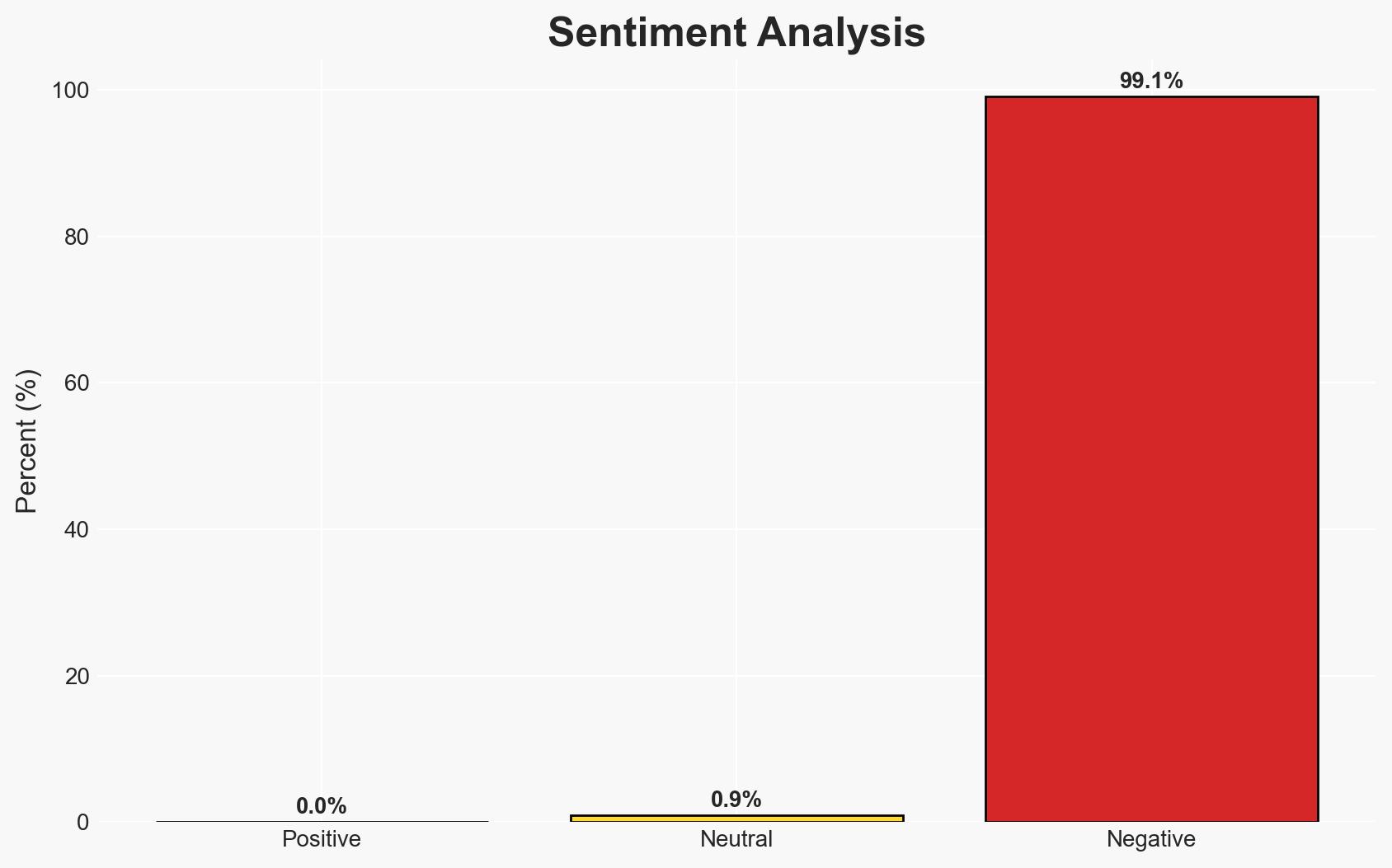
The UN’s renewed push for a ceasefire in Sudan faces significant challenges due to ongoing violence and humanitarian crises. The most likely hypothesis is that without substantial international pressure and compromise from Sudanese factions, the conflict will persist, exacerbating regional instability. The situation affects civilians, peacekeepers, and regional security, with moderate confidence in this assessment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The UN’s ceasefire initiative will lead to a temporary reduction in hostilities. This is supported by the involvement of the UN Secretary-General and regional partners, but contradicted by ongoing violence and past failures to secure lasting peace. Key uncertainties include the willingness of Sudanese factions to compromise.
- Hypothesis B: The ceasefire initiative will fail to significantly alter the conflict dynamics, leading to continued violence and humanitarian crises. This is supported by the recent escalation in violence and the withdrawal of peacekeepers, indicating entrenched hostilities. However, the international community’s engagement could provide leverage.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the persistent violence and lack of concrete progress in peace negotiations. Indicators that could shift this judgment include a formal agreement between the Sudanese Armed Forces and the Rapid Support Forces or increased international intervention.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The Sudanese factions are primarily motivated by territorial and political control; international actors have limited influence; humanitarian conditions will continue to deteriorate without intervention.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on the peace initiative’s terms and the internal dynamics within Sudanese factions are lacking.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in UN reporting due to reliance on official sources; risk of manipulation by Sudanese factions to gain international sympathy or support.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ongoing conflict in Sudan could further destabilize the region, impacting neighboring countries and international interests. The humanitarian crisis may worsen, increasing refugee flows and regional tensions.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for regional spillover effects, affecting South Sudan and other neighboring states.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of radicalization and recruitment by extremist groups exploiting the instability.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for disinformation campaigns by involved parties to influence international perception.
- Economic / Social: Continued conflict could lead to economic collapse and further social fragmentation within Sudan.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase diplomatic engagement with Sudanese factions; enhance monitoring of ceasefire violations; provide immediate humanitarian aid to affected regions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop regional partnerships to support peace efforts; strengthen UNISFA’s mandate and capabilities; prepare contingency plans for refugee influx.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful ceasefire leading to peace talks, triggered by international pressure and compromise.
- Worst: Escalation of conflict and regional destabilization, triggered by breakdown of negotiations.
- Most-Likely: Prolonged conflict with intermittent ceasefires, triggered by lack of sustained international engagement.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- António Guterres – UN Secretary-General
- Ramtane Lamamra – UN Secretary-General’s Personal Envoy for Sudan
- Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF)
- Rapid Support Forces (RSF)
- UNISFA – United Nations Interim Security Force for Abyei
7. Thematic Tags
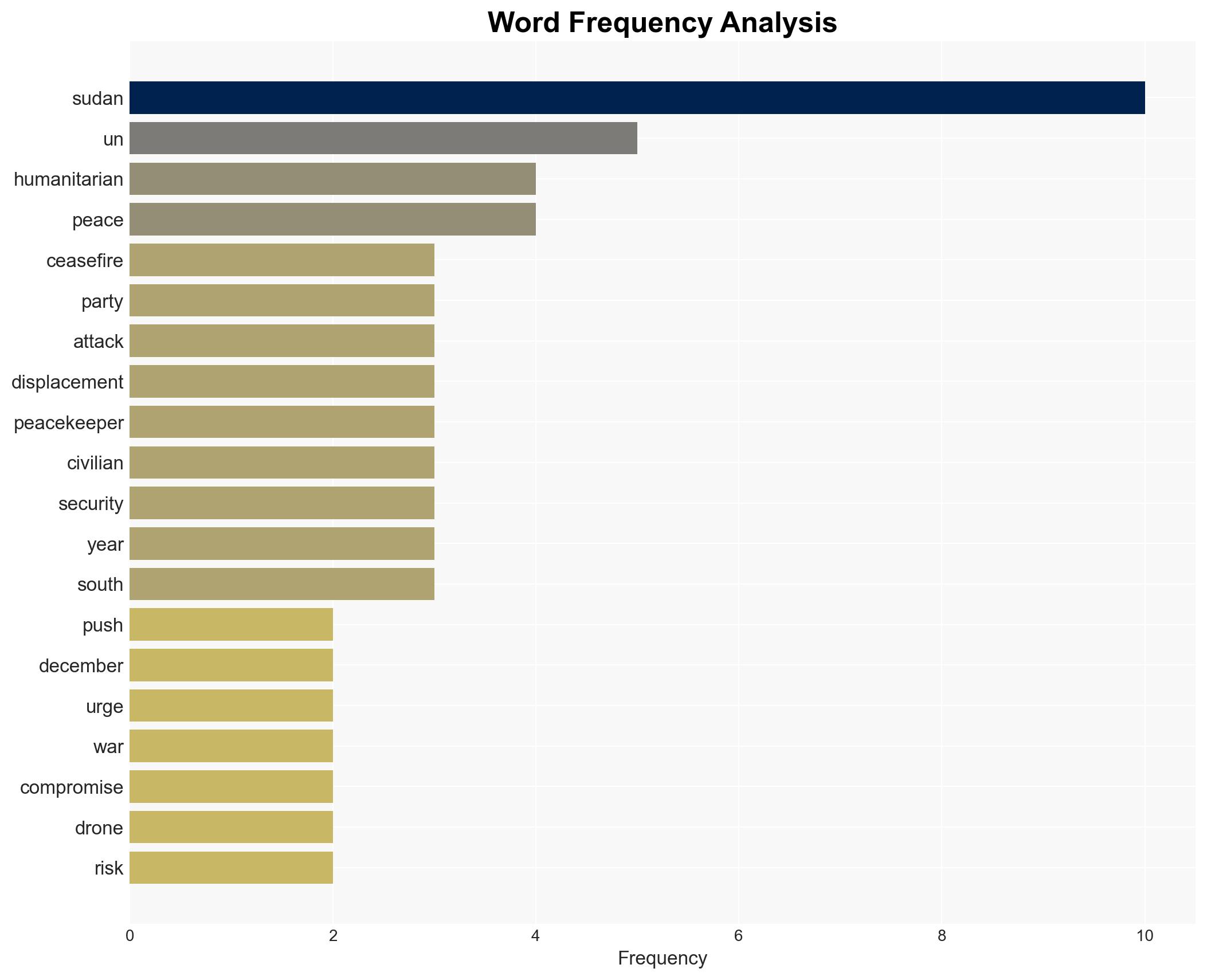
regional conflicts, ceasefire, humanitarian crisis, regional stability, peace negotiations, Sudan conflict, UN intervention, geopolitical risk
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us