Surge in Cyber Attacks This Year: Key Sectors Targeted and Data Protection Strategies
Published on: 2025-12-27
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Cyber attacks that occurred this year and how you can protect your data
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
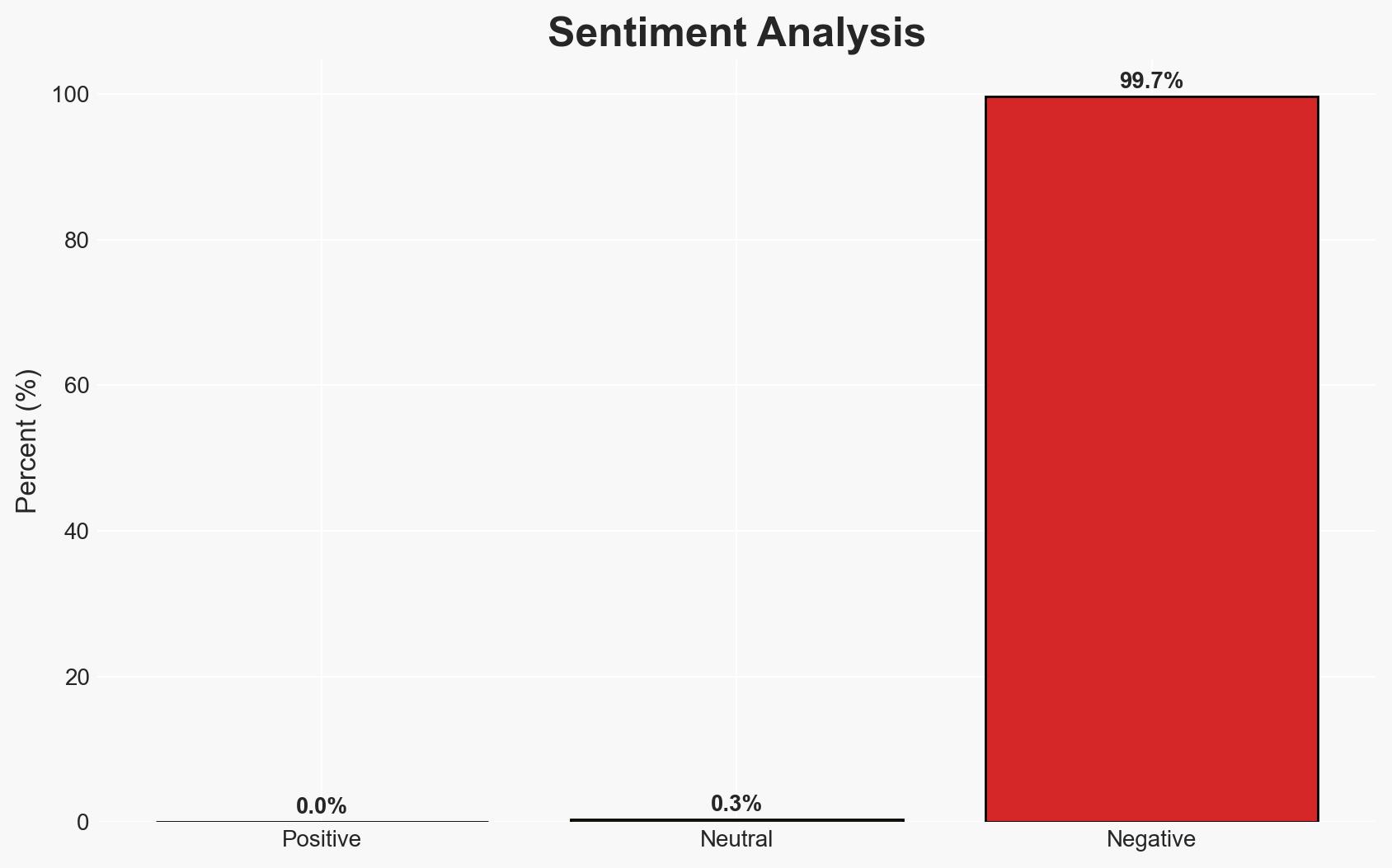
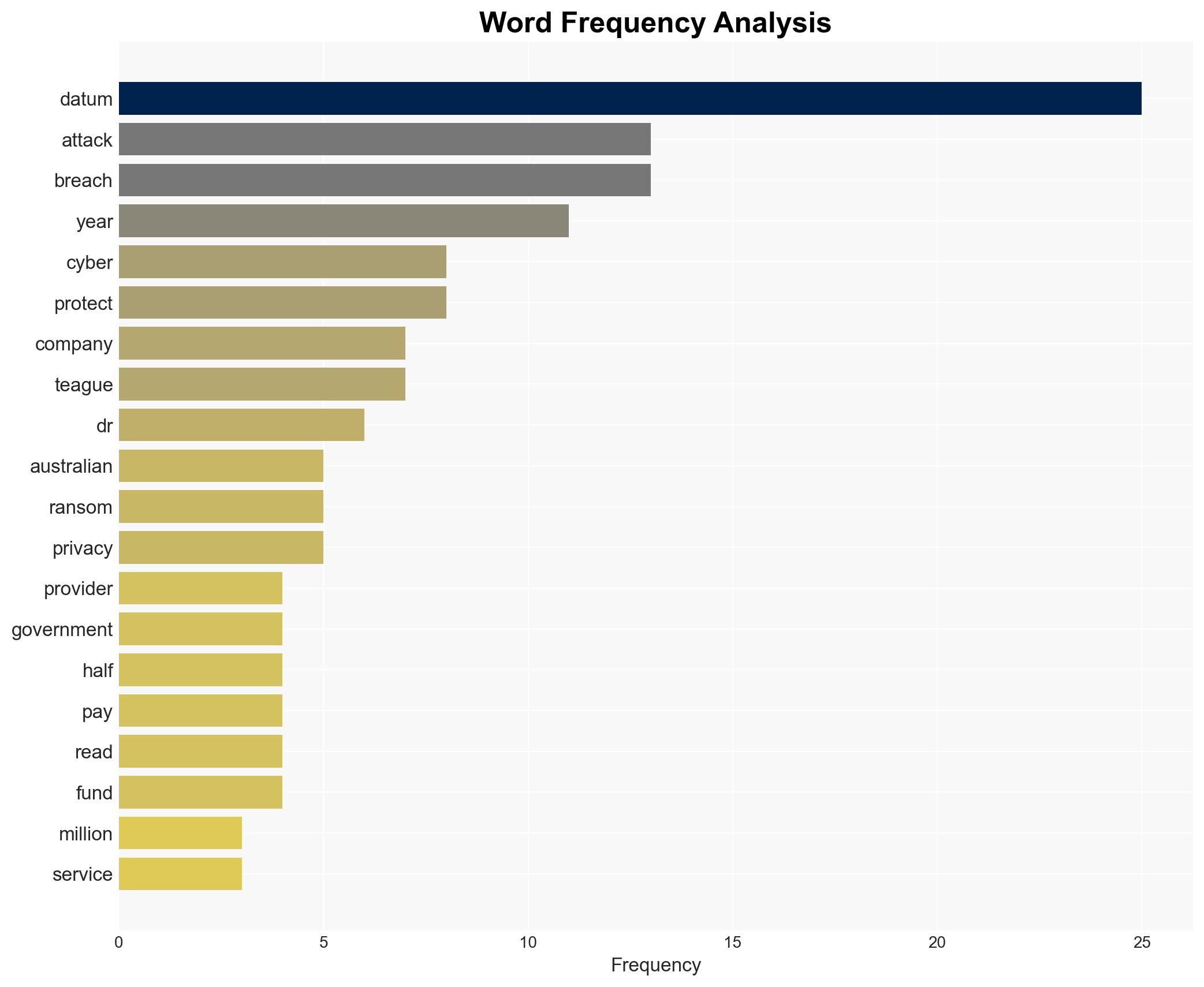
The frequency and impact of cyber attacks in Australia have increased significantly, affecting multiple sectors, notably finance, healthcare, and government. The most likely hypothesis is that these attacks will continue to rise, driven by sophisticated criminal networks. This poses substantial risks to personal data security and economic stability. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the incomplete data for the second half of the year.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The increase in cyber attacks is primarily due to enhanced capabilities and organization of cybercriminal groups. This is supported by the high number of breaches attributed to malicious attacks and the structured nature of ransomware operations. However, the lack of detailed attribution data limits full verification.
- Hypothesis B: The rise in reported cyber attacks is partly due to improved detection and reporting mechanisms, such as the OAIC’s new dashboard. While this could explain the increase in notifications, it does not account for the severity and sophistication of the attacks themselves.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the evidence of organized criminal activity and the financial impact of the breaches. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include detailed attribution of attacks and changes in reporting practices.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The data for the second half of the year will continue the trend of increasing attacks; cybercriminals are primarily motivated by financial gain; the OAIC’s reporting is comprehensive and accurate.
- Information Gaps: Detailed attribution of specific attacks and comprehensive data for the second half of the year are missing.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting due to reliance on public notifications; risk of underreporting by companies to avoid reputational damage.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ongoing trend of cyber attacks could lead to increased regulatory scrutiny and demand for enhanced cybersecurity measures. This may strain resources and require significant investment in cybersecurity infrastructure.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased international cooperation on cybersecurity and pressure on governments to enhance regulatory frameworks.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment as cyber capabilities could be leveraged by non-state actors for disruptive purposes.
- Cyber / Information Space: Escalation in cyber arms race as entities bolster defenses, potentially leading to more advanced attack techniques.
- Economic / Social: Economic strain on businesses due to breach costs; erosion of public trust in digital services and institutions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of cyber threat activity, encourage reporting of breaches, and provide guidance on ransomware response strategies.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures, foster public-private partnerships, and invest in cybersecurity training and technology.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Reduction in attack frequency due to improved defenses and international cooperation.
- Worst Case: Continued escalation of attacks leading to significant economic and social disruption.
- Most Likely: Persistent threat environment with gradual improvements in defense capabilities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Office of the Australian Information Commissioner (OAIC)
- Vanessa Teague, Associate Professor at ANU College of Engineering, Computing and Cybernetics
- Qantas
- Genea Fertility
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, data breaches, ransomware, cybercrime, information security, regulatory response, public-private partnership
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us