Flow Network Vulnerability Leads to $3.9 Million Theft and 46% Price Drop Amid Rising Crypto Security Concerns
Published on: 2025-12-28
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Flow Network exploit triggers panic selling plunges price by 46
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
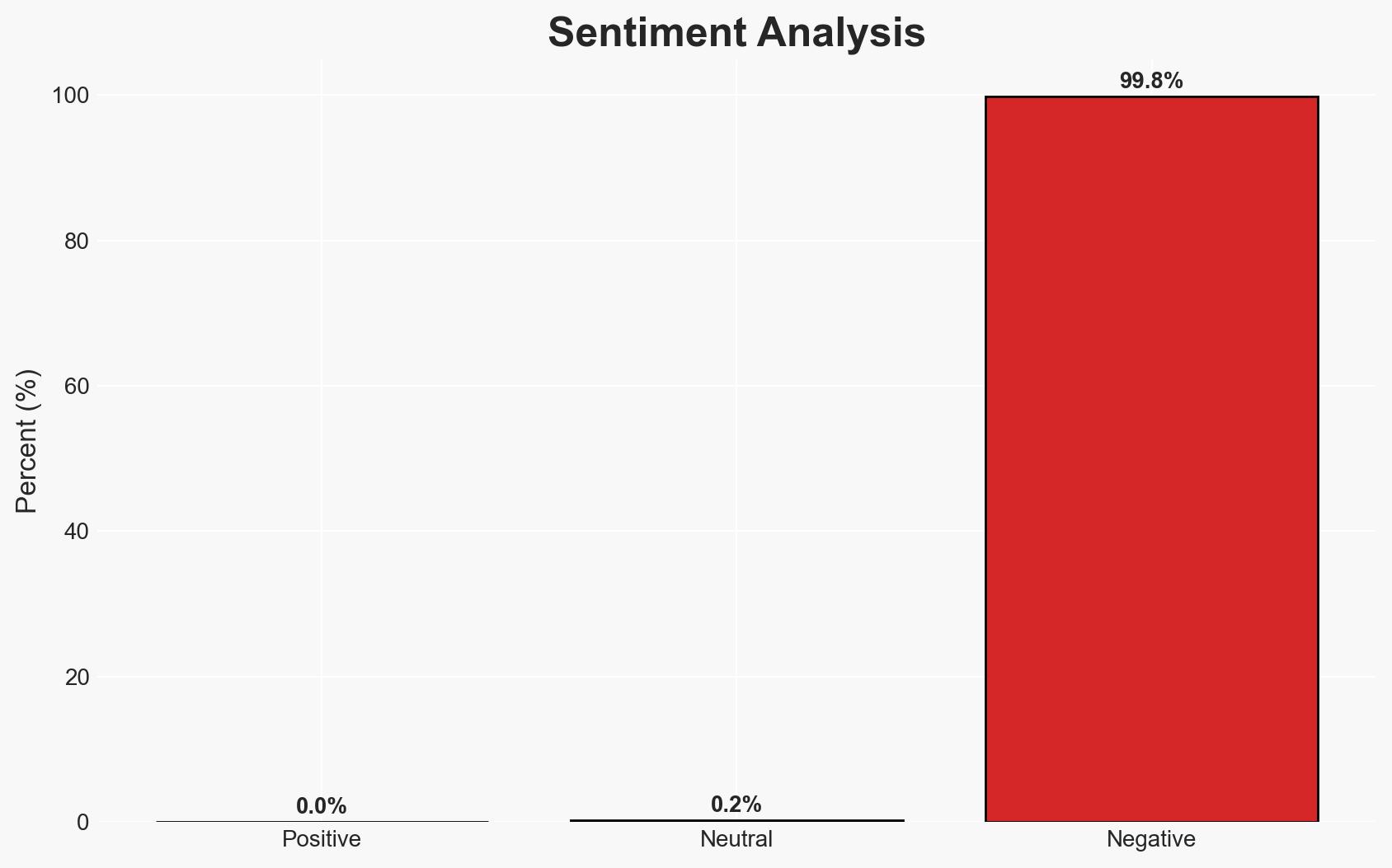
The Flow Network experienced a significant security breach resulting in a $3.9 million theft, leading to a 46% drop in its token price. The incident highlights vulnerabilities in blockchain security and the potential for market destabilization due to cyber exploits. The most likely hypothesis is that the breach was a targeted attack exploiting known vulnerabilities, with moderate confidence in this assessment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The attack was a targeted exploitation of a specific vulnerability in Flow’s execution layer. This is supported by the fact that the attack was precise and funds were quickly laundered through multiple channels. Uncertainties include the attacker’s identity and whether this was an isolated incident or part of a broader campaign.
- Hypothesis B: The breach was part of a larger, coordinated effort by a state-sponsored group, potentially from North Korea, given the increase in such activities. However, there is limited direct evidence linking this specific attack to state actors.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the specificity of the attack and the rapid laundering of funds. Indicators that could shift this judgment include new evidence of state sponsorship or similar attacks on other networks.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The vulnerability exploited was previously unknown to Flow developers; the market reaction was primarily driven by panic selling; existing security measures were insufficient to prevent the breach.
- Information Gaps: Details on the attacker’s identity and motivations; full scope of the vulnerability within Flow’s system; potential connections to other recent crypto attacks.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in attributing the attack to state actors without concrete evidence; reliance on data from potentially biased or incomplete sources.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This incident could lead to increased scrutiny and regulatory pressure on blockchain networks, affecting their operational and financial stability. It may also encourage further attacks if perceived as successful.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory actions or international cooperation on cybercrime.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened alert for similar vulnerabilities in other blockchain networks.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on cybersecurity measures and potential for misinformation campaigns exploiting the incident.
- Economic / Social: Possible loss of investor confidence in crypto markets, impacting broader financial markets and innovation in blockchain technology.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a thorough security audit of the Flow Network; enhance monitoring of blockchain networks for similar vulnerabilities; engage with exchanges to trace and recover stolen funds.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms to bolster defenses; advocate for industry-wide standards on blockchain security; invest in user education on security best practices.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Rapid recovery and improved security measures restore confidence. Worst: Continued breaches lead to regulatory crackdowns and market instability. Most-Likely: Gradual recovery with increased security focus and regulatory interest.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Flow Foundation
- Circle
- Tether
- Upbit
- Bithumb
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, blockchain security, cryptocurrency, cybercrime, market volatility, financial regulation, state-sponsored hacking, digital asset security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us