LastPass breach backups still vulnerable, enabling crypto theft through 2025 due to weak passwords
Published on: 2025-12-28
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Stolen LastPass backups enable crypto theft through 2025
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
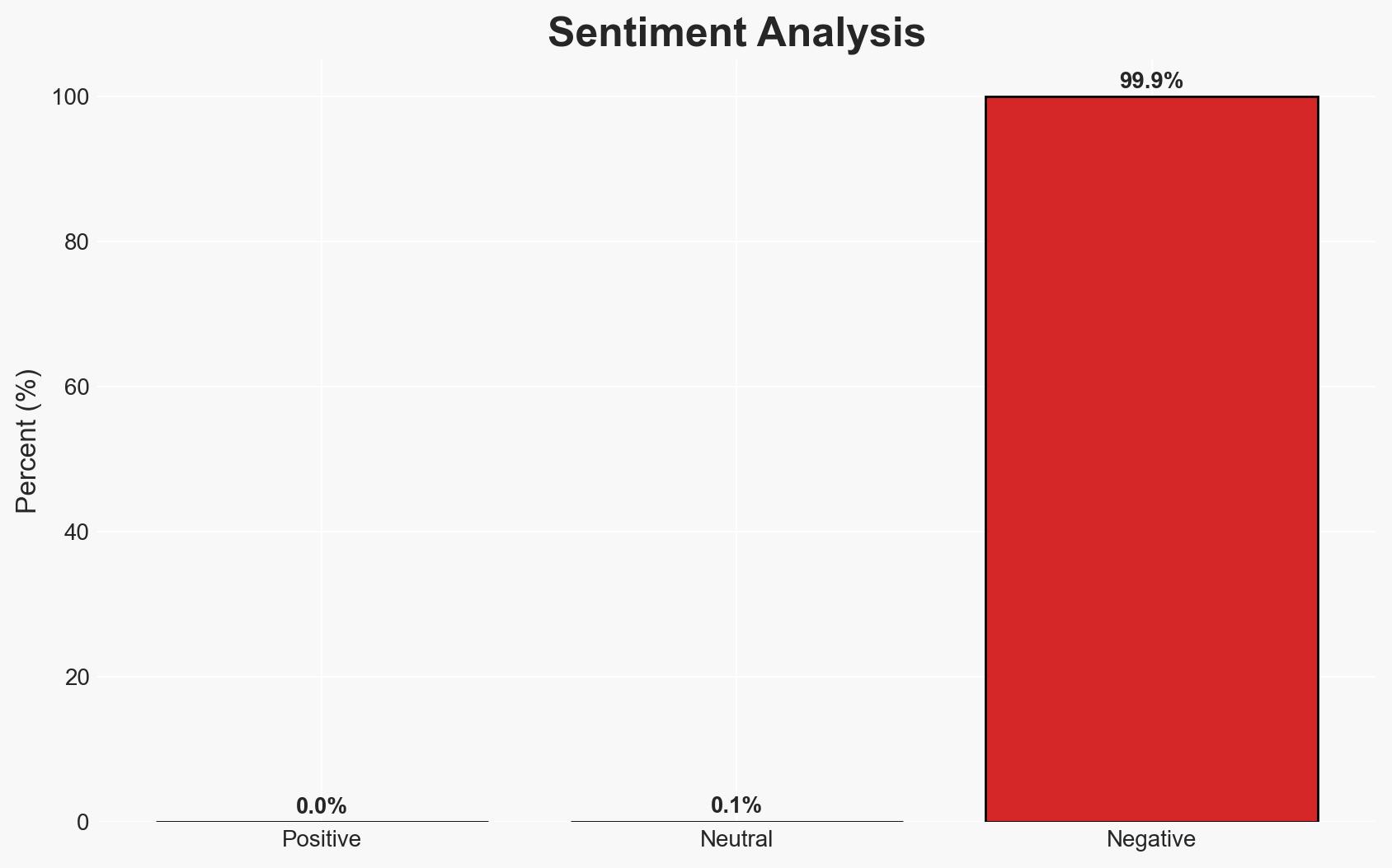
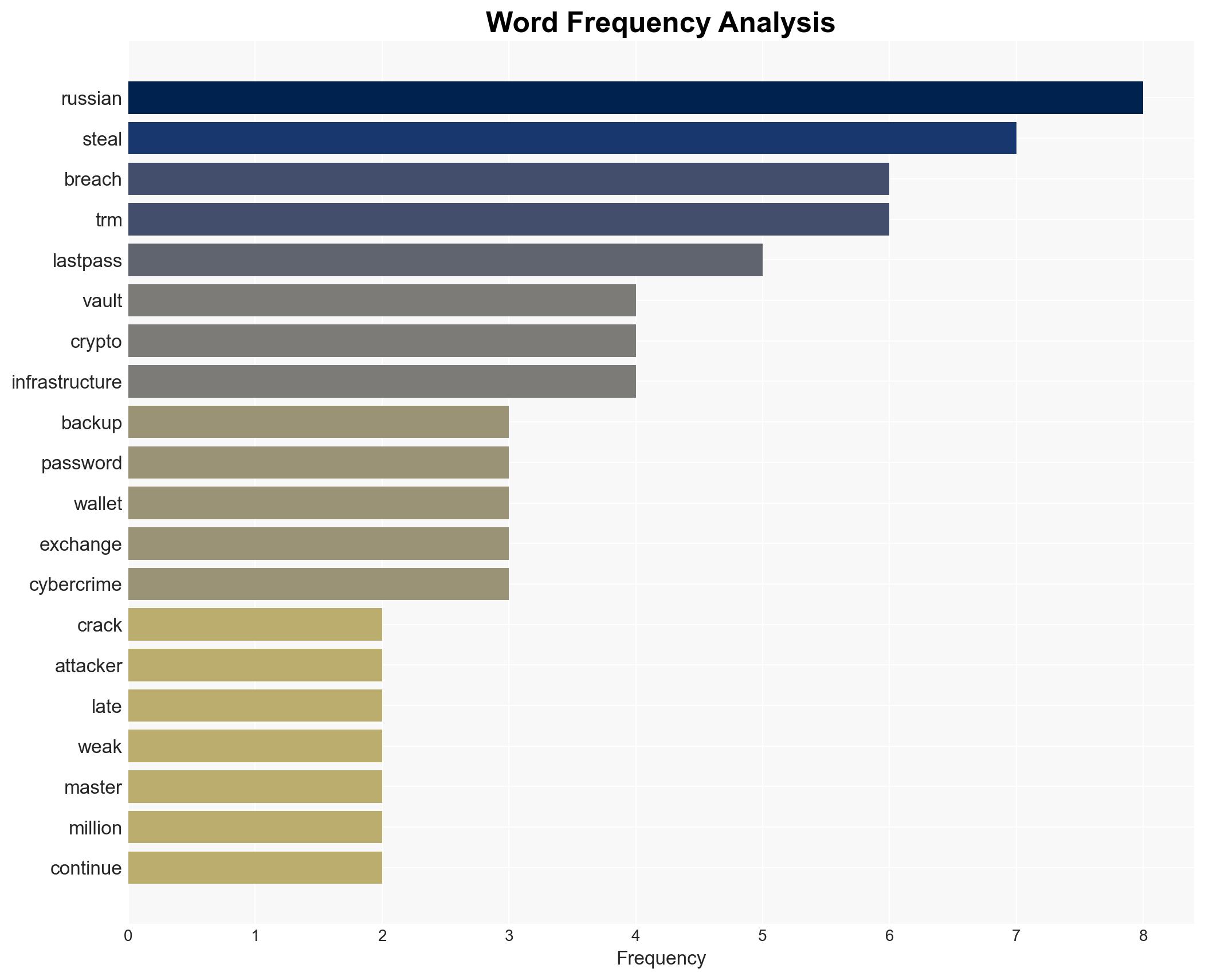
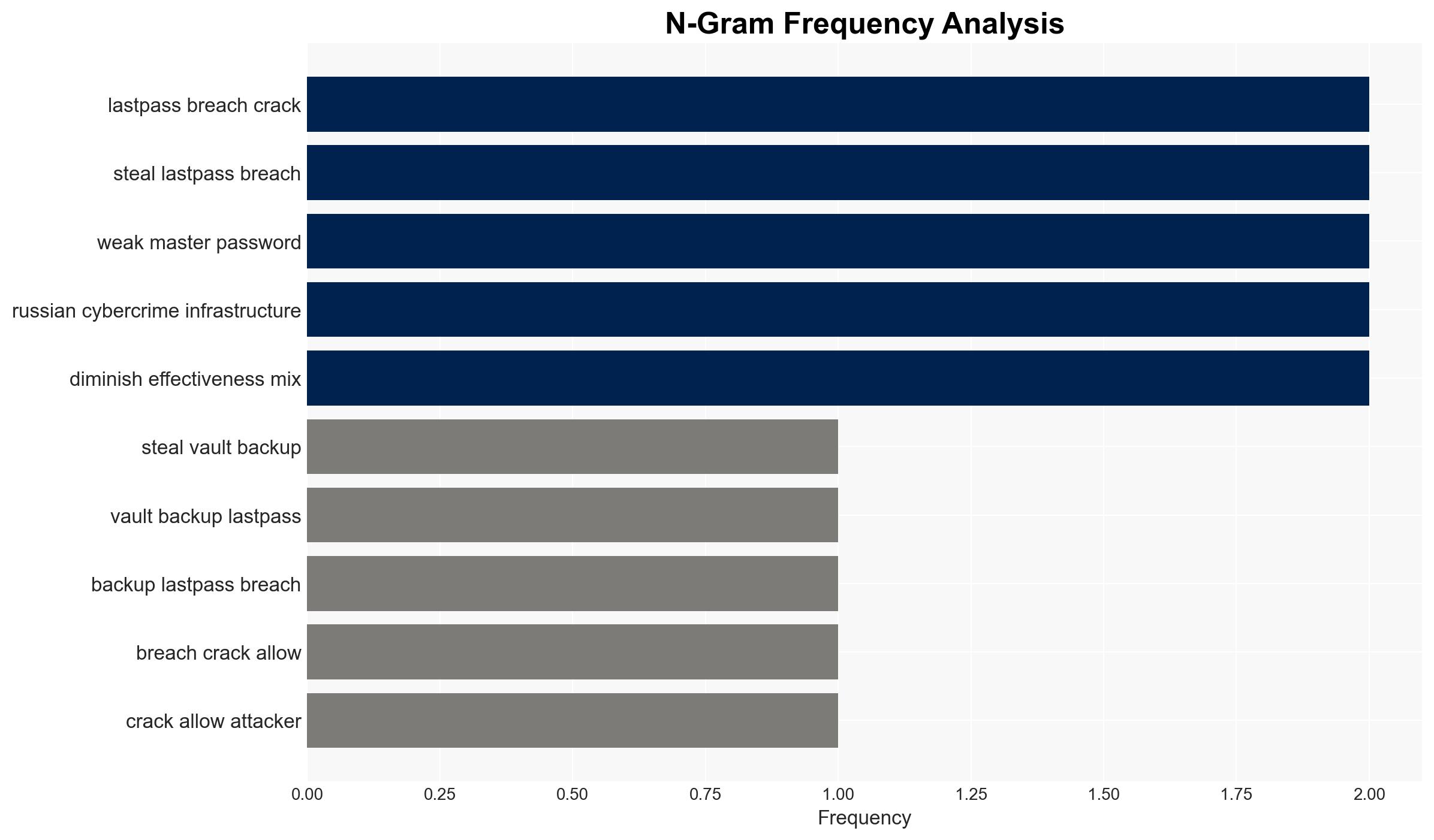
The ongoing exploitation of stolen LastPass backups from 2022 is facilitating crypto theft through 2025, with evidence suggesting Russian cybercriminal involvement. This situation poses a sustained threat to financial security and highlights vulnerabilities in digital infrastructure. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the available evidence and ongoing investigative challenges.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The crypto thefts are primarily orchestrated by Russian cybercriminals using compromised LastPass data. Supporting evidence includes the use of Russian exchanges and cybercrime infrastructure. However, definitive attribution of the original breach remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The thefts are part of a broader, decentralized cybercriminal effort not limited to Russian actors. While Russian infrastructure is used, this could be opportunistic rather than indicative of direct involvement. The lack of conclusive attribution supports this alternative.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to consistent patterns linking activities to Russian entities and infrastructure. Future intelligence confirming the origin of the breach or identifying other actors could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The encryption on stolen backups is weak enough to be cracked; Russian exchanges are knowingly facilitating laundering; TRM Labs’ analysis is accurate and unbiased.
- Information Gaps: The exact identity of the original intruders; the full extent of compromised vaults; the role of non-Russian actors in the laundering process.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in attributing activities to Russian actors due to historical patterns; deception by cybercriminals using Russian infrastructure to mislead attribution efforts.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could exacerbate tensions between countries over cybercrime attribution and response, potentially leading to increased sanctions or cyber retaliations. The persistence of vulnerabilities in password management systems underscores the need for improved cybersecurity practices.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for diplomatic friction over perceived state sponsorship or harboring of cybercriminals.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of financial destabilization through cyber-enabled thefts, potentially funding other illicit activities.
- Cyber / Information Space: Highlighting the need for stronger encryption and security measures in digital vaults; potential for misinformation campaigns around attribution.
- Economic / Social: Erosion of trust in digital financial systems; potential economic impacts from large-scale financial thefts.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of Russian exchanges and cybercrime forums; enhance cooperation with blockchain analysis firms; issue alerts to potentially affected users.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for password management systems; strengthen international partnerships to combat cybercrime; invest in advanced encryption technologies.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Enhanced international cooperation leads to arrests and dismantling of the criminal network.
- Worst: Continued exploitation leads to significant financial losses and geopolitical tensions.
- Most-Likely: Ongoing thefts with gradual improvements in security and attribution capabilities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- TRM Labs
- LastPass
- Russian exchanges (e.g., Cryptex, Audi6)
- Wasabi Wallet
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, cybercrime, cryptocurrency theft, Russian cyber operations, digital security, blockchain analysis, financial infrastructure, international cooperation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us