Geopolitical Tensions and AI Transform Corporate Risk Management Strategies
Published on: 2025-12-28
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Why Geopolitics and AI Are Now Core to Business Strategy
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
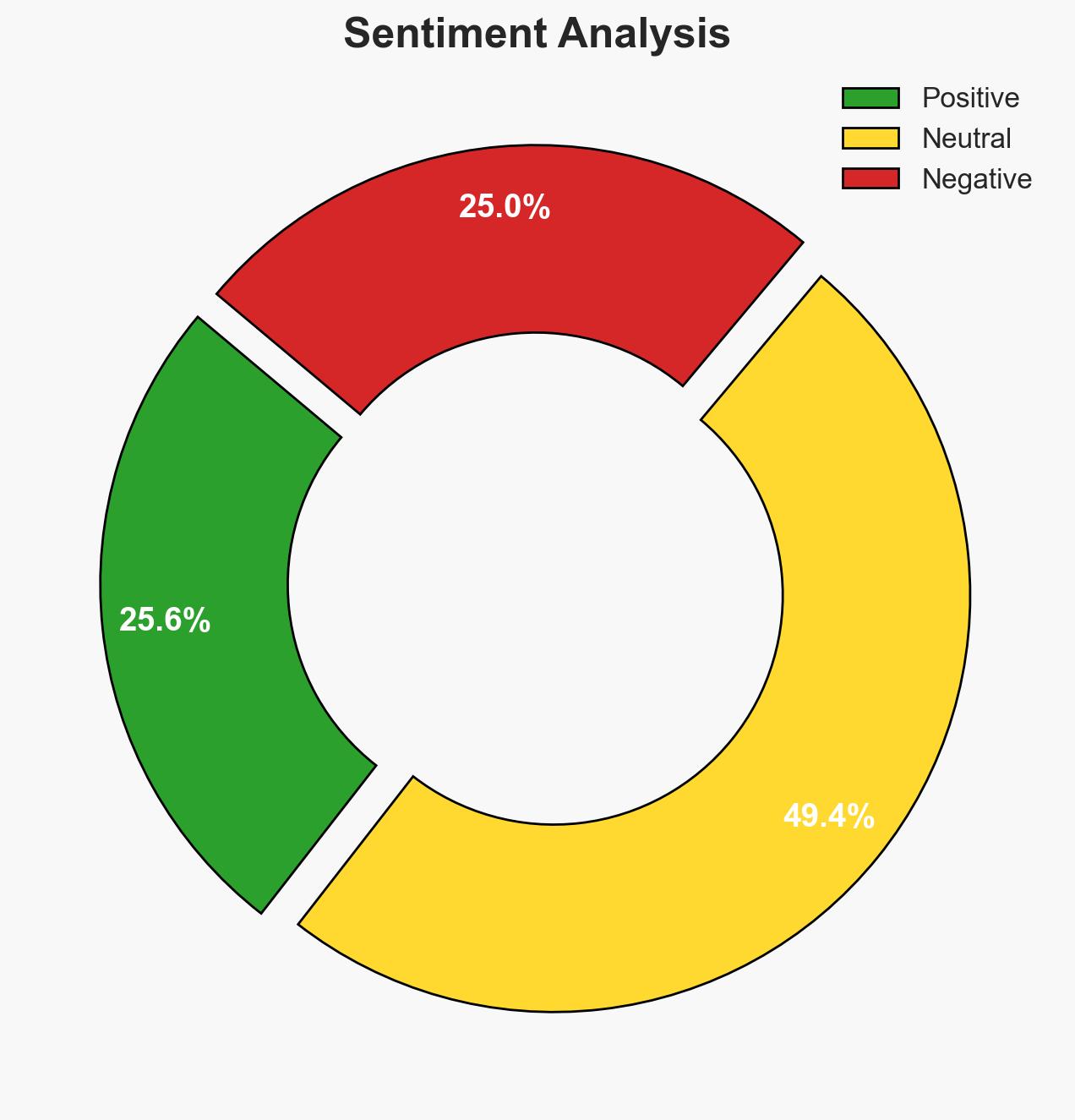
The convergence of geopolitics, AI, and cybersecurity is reshaping corporate risk landscapes, with AI significantly enhancing the capabilities of threat actors. This development affects global businesses, increasing their vulnerability to cyber espionage and economic disruption. The most likely hypothesis is that AI will continue to accelerate cyber threats, necessitating a shift to AI-native security strategies. Overall confidence in this judgment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: AI is amplifying cyber threats, making traditional security measures obsolete. Evidence includes the reduction in breach times and the increased use of AI by attackers. However, uncertainties exist regarding the full extent of AI’s impact on different sectors.
- Hypothesis B: The perceived increase in cyber threats is primarily due to heightened geopolitical tensions, with AI playing a secondary role. While geopolitical tensions are prompting strategic overhauls, evidence of AI’s direct impact on threat dynamics is more compelling.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the documented reduction in breach times and the role of AI in enhancing attack capabilities. Indicators such as further reductions in breach times or increased AI integration in attacks could reinforce this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI capabilities will continue to advance; geopolitical tensions will persist; businesses will remain primary targets for state-sponsored cyber activities.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on AI’s role in specific cyber incidents; comprehensive analysis of sector-specific vulnerabilities.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in corporate reporting due to reputational concerns; manipulation of threat data by state actors to mislead competitors.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The integration of AI into cyber threats could lead to more sophisticated and frequent attacks, challenging existing security frameworks and potentially destabilizing economic and political environments.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased cyber espionage could exacerbate international tensions and lead to retaliatory actions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat actor capabilities may complicate counter-terrorism efforts and increase the risk of critical infrastructure attacks.
- Cyber / Information Space: The digital landscape will see a shift towards AI-driven security solutions, with a focus on real-time threat detection and response.
- Economic / Social: Potential for significant financial losses and disruptions in global supply chains, affecting economic stability and social cohesion.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of AI-driven threats; initiate AI-native security training for cybersecurity teams.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with AI and cybersecurity firms; invest in adaptive security technologies and platforms.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful integration of AI-native security measures mitigates threats.
- Worst: Failure to adapt leads to widespread breaches and economic disruption.
- Most-Likely: Gradual adaptation to AI-driven threats with periodic disruptions.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, geopolitics, AI, cyber-espionage, economic risk, statecraft, digital transformation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us