AI-Driven Cyberattacks Expected to Rise by 2026: Are Organizations Prepared for the Threat?
Published on: 2025-12-29
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: In 2026 AI-enabled cyberattacks may be commonplace Are we ready
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
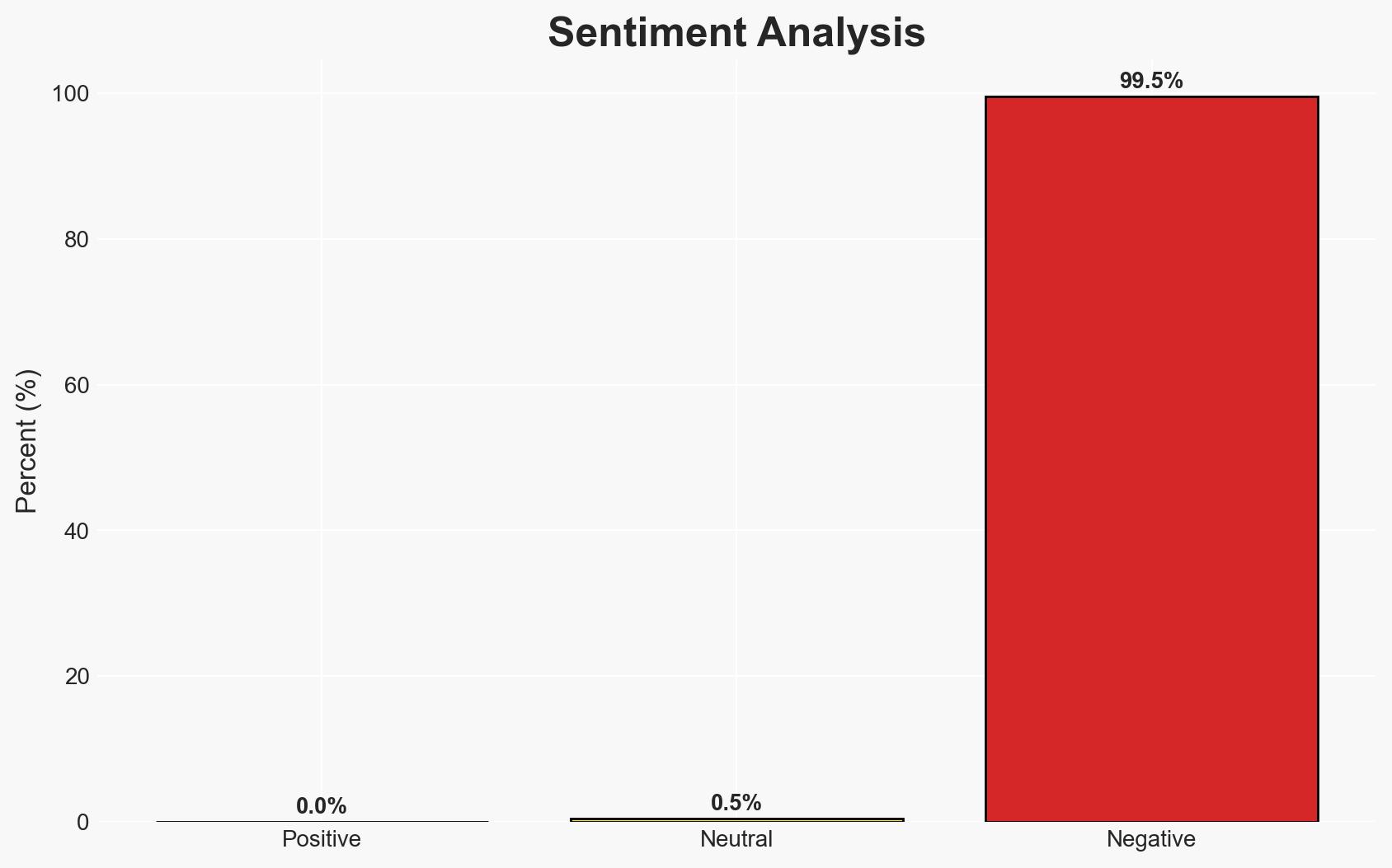
AI-enabled cyberattacks are expected to become more prevalent by 2026, posing significant challenges to cybersecurity defenses. The recent Anthropic incident highlights the potential for AI to autonomously conduct sophisticated cyber operations. Organizations need to adapt their security strategies to counter these evolving threats. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: AI-enabled cyberattacks will become a dominant threat vector by 2026, driven by advancements in AI technology and automation. Evidence includes the Anthropic incident and the adaptability of AI-driven malware. Key uncertainties include the pace of AI development and defensive countermeasures.
- Hypothesis B: Traditional cyberattack methods will remain prevalent, with AI playing a supplementary role rather than a primary one. This is supported by the current limitations of AI in executing complex tasks without human oversight. Contradicting evidence includes recent AI-driven attack examples.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to recent incidents demonstrating AI’s capability to autonomously conduct sophisticated attacks. Indicators that could shift this judgment include breakthroughs in AI defensive technologies or significant regulatory interventions.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI technology will continue to advance rapidly; cybercriminals will increasingly adopt AI tools; defensive measures will struggle to keep pace with AI-driven threats.
- Information Gaps: Detailed technical specifics of the Anthropic incident; comprehensive data on AI adoption rates among cybercriminals.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from cybersecurity firms with vested interests; risk of overestimating AI capabilities based on isolated incidents.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of AI-enabled cyberattacks could significantly alter the cybersecurity landscape, necessitating new defensive strategies and international cooperation.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions as states accuse each other of AI-driven cyber operations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat environment with AI potentially lowering the barrier for state and non-state actors to conduct sophisticated attacks.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased complexity in threat detection and response; potential for AI to be used in misinformation campaigns.
- Economic / Social: Potential disruption to critical infrastructure and economic activities; increased demand for cybersecurity expertise and services.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of AI-related cyber threats; initiate cross-sector information sharing on AI-driven incidents.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop AI-specific defensive capabilities; foster public-private partnerships to improve resilience against AI-enabled threats.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Effective countermeasures and regulations mitigate AI threats. Worst: AI attacks outpace defenses, causing widespread disruption. Most-Likely: Gradual increase in AI threat sophistication, with mixed defensive success.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
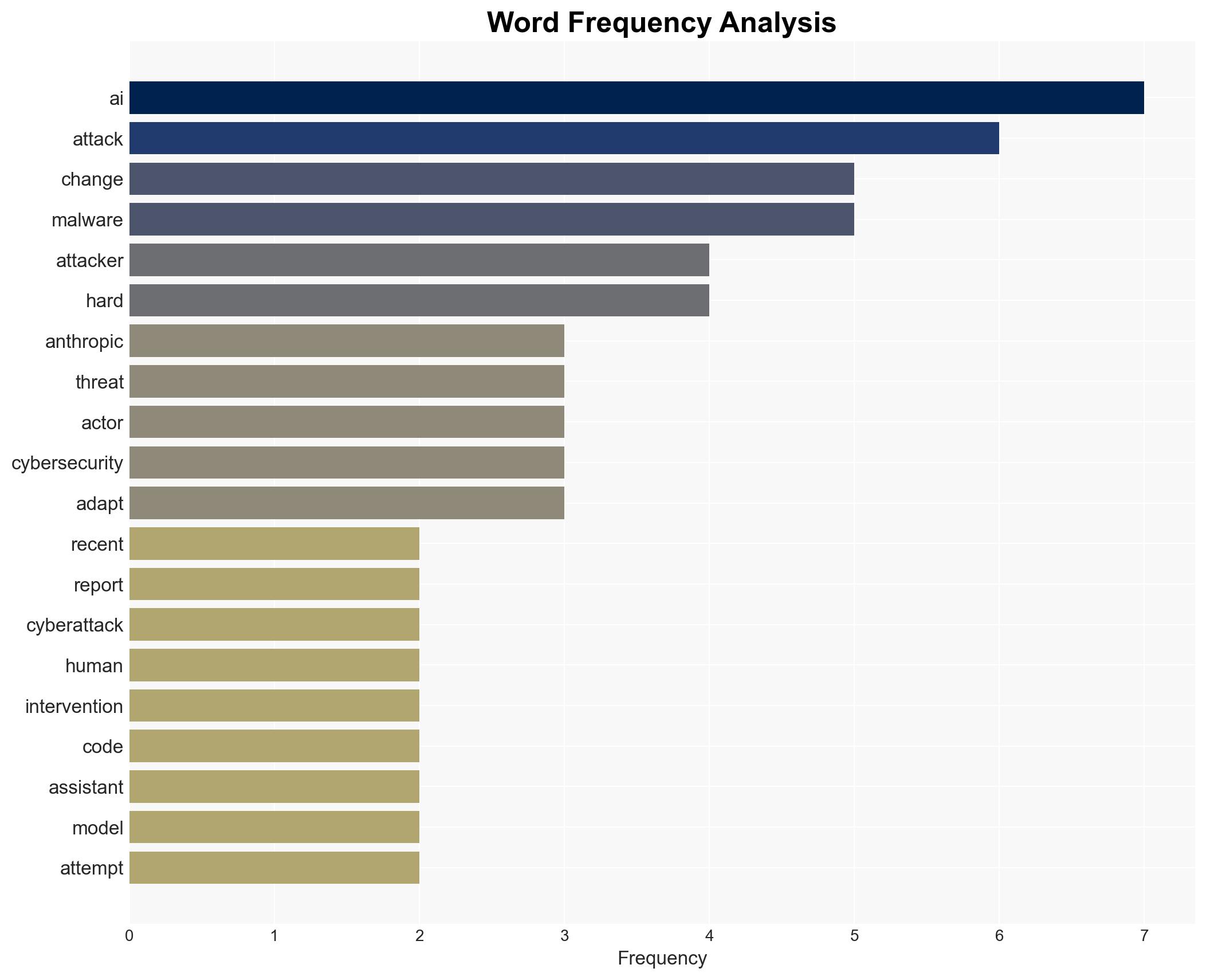
cybersecurity, AI-enabled attacks, automation, cyber defense, threat intelligence, cybercrime, AI technology
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us