Cybersecurity Weekly: MongoDB Exploit Emerges Amid Rising Threats from Wallet Breaches and Android Malware
Published on: 2025-12-29
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Weekly Recap MongoDB Attacks Wallet Breaches Android Spyware Insider Crime More
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
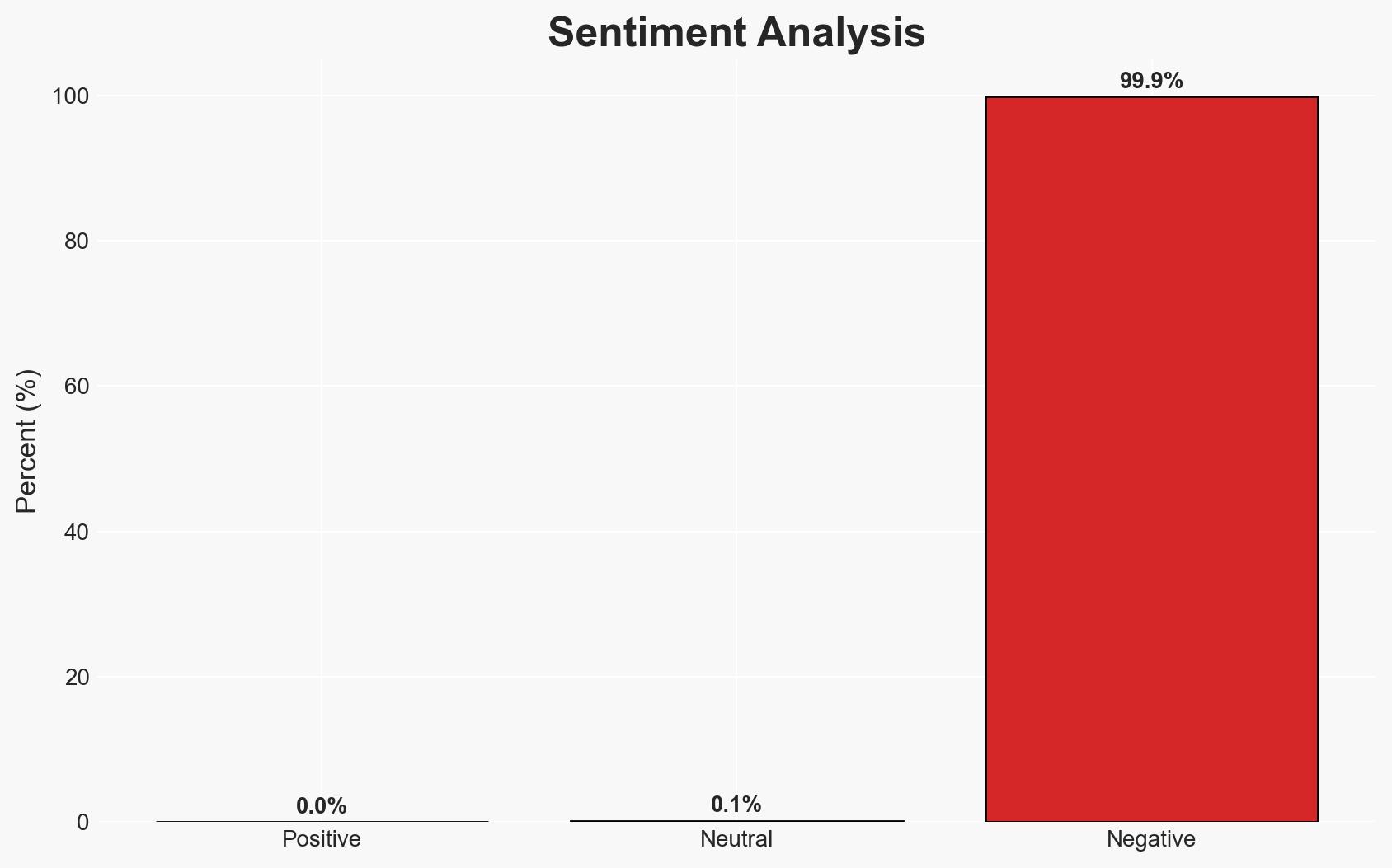
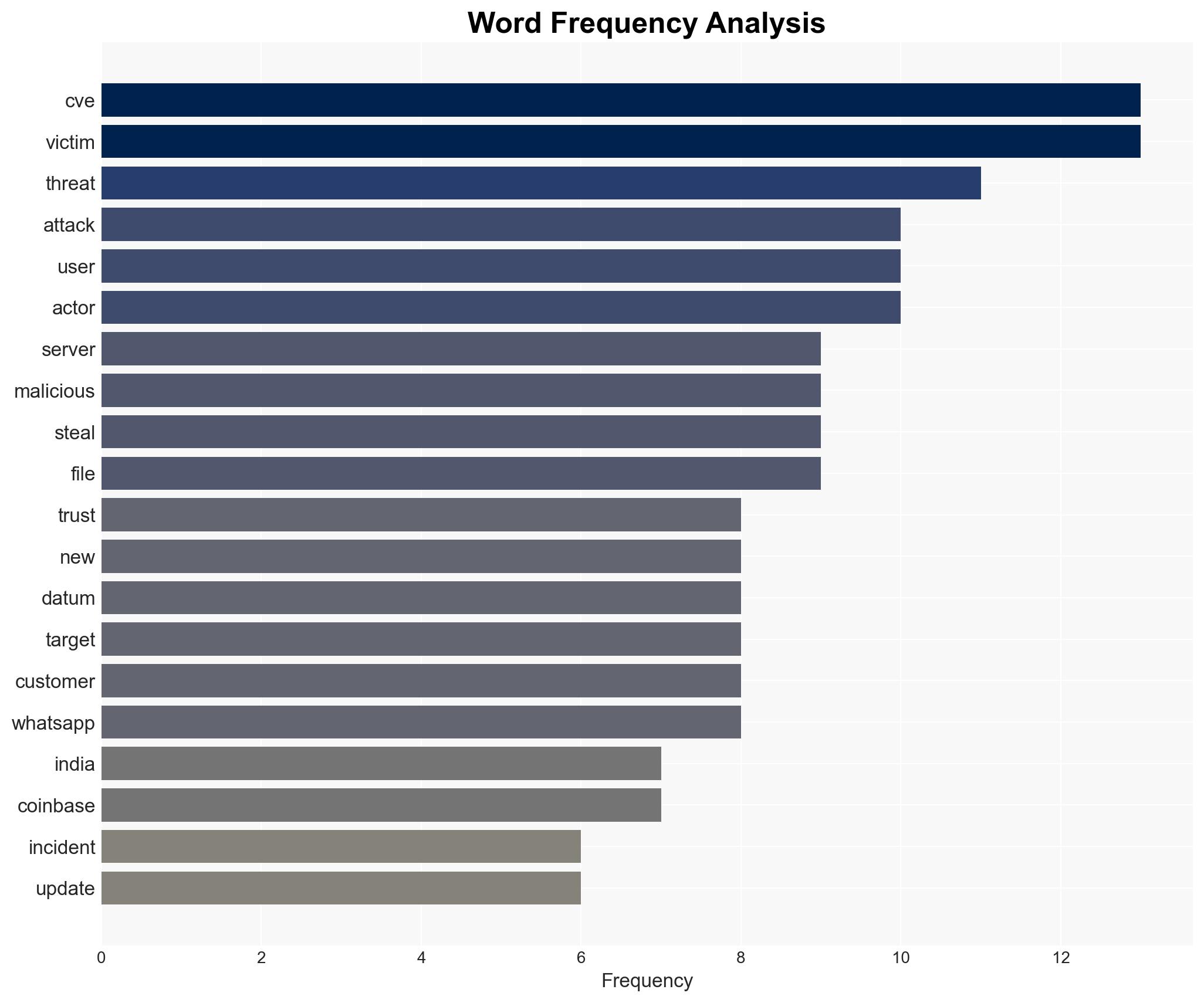
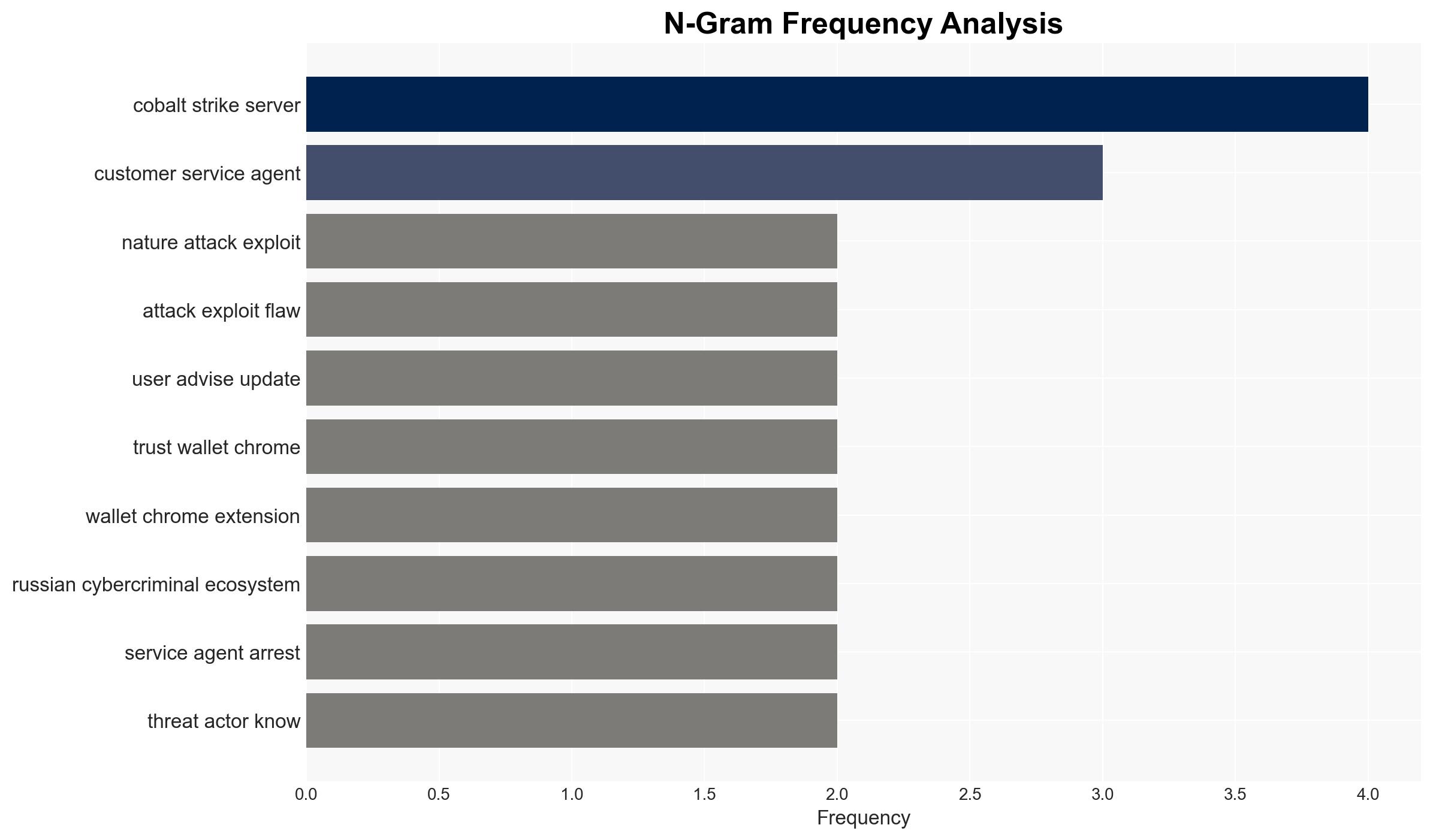
In the final stretch of 2025, multiple cyber vulnerabilities, including a significant MongoDB flaw, have been actively exploited, impacting global entities and highlighting the speed at which attackers operate relative to defense mechanisms. The most likely hypothesis is that these incidents are part of a broader trend of increasingly sophisticated cyber threats exploiting both new and resurfacing vulnerabilities. This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to incomplete details on the nature of the attacks and their perpetrators.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The recent cyber incidents, including the MongoDB vulnerability and Trust Wallet breach, are isolated events driven by opportunistic attackers exploiting known vulnerabilities. Supporting evidence includes the specific targeting of known flaws and the rapid exploitation of newly disclosed vulnerabilities. However, the lack of detailed attack methodologies creates uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: These incidents are coordinated efforts by sophisticated threat actors aiming to destabilize critical infrastructure and financial systems. This is supported by the simultaneous targeting of diverse systems and the involvement of an APT group in the DNS poisoning attack. Contradicting evidence includes the absence of direct links between the incidents.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the opportunistic nature of the attacks and the exploitation of readily available vulnerabilities. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of coordination between the attacks or attribution to a single actor or group.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Attackers have access to advanced tools and techniques; vulnerabilities will continue to be exploited faster than they can be patched; affected entities will not immediately disclose full details of breaches.
- Information Gaps: Specific attack vectors and methodologies for the MongoDB and Trust Wallet incidents; identity and motivations of the attackers; extent of the impact on affected systems.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in attributing attacks to specific actors without concrete evidence; risk of underestimating the coordination level of these incidents.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ongoing exploitation of cyber vulnerabilities could lead to increased instability in digital and financial systems, potentially affecting geopolitical relations and economic stability.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased tensions between nations due to perceived state-sponsored cyber activities.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment as attackers exploit vulnerabilities in critical infrastructure.
- Cyber / Information Space: Escalation in cyber operations and information warfare tactics, with potential for increased disinformation campaigns.
- Economic / Social: Potential loss of consumer trust in digital financial services and increased regulatory scrutiny on cybersecurity practices.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Urgently patch affected systems, particularly MongoDB instances; enhance monitoring for signs of exploitation; engage with cybersecurity firms for threat intelligence sharing.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures, including regular security audits and employee training; strengthen partnerships with international cybersecurity agencies.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid patching and improved defenses reduce vulnerability exploitation.
- Worst: Continued exploitation leads to significant disruptions in critical sectors.
- Most-Likely: Ongoing incidents with sporadic impacts as defenses catch up with threats.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- MongoDB
- Trust Wallet
- Evasive Panda (APT group)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, vulnerability exploitation, financial technology, APT groups, cyber resilience, information warfare, digital trust
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us