Two former cybersecurity professionals admit guilt in BlackCat ransomware scheme targeting U.S. firms
Published on: 2025-12-30
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: US cybersecurity experts plead guilty to BlackCat ransomware attacks
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
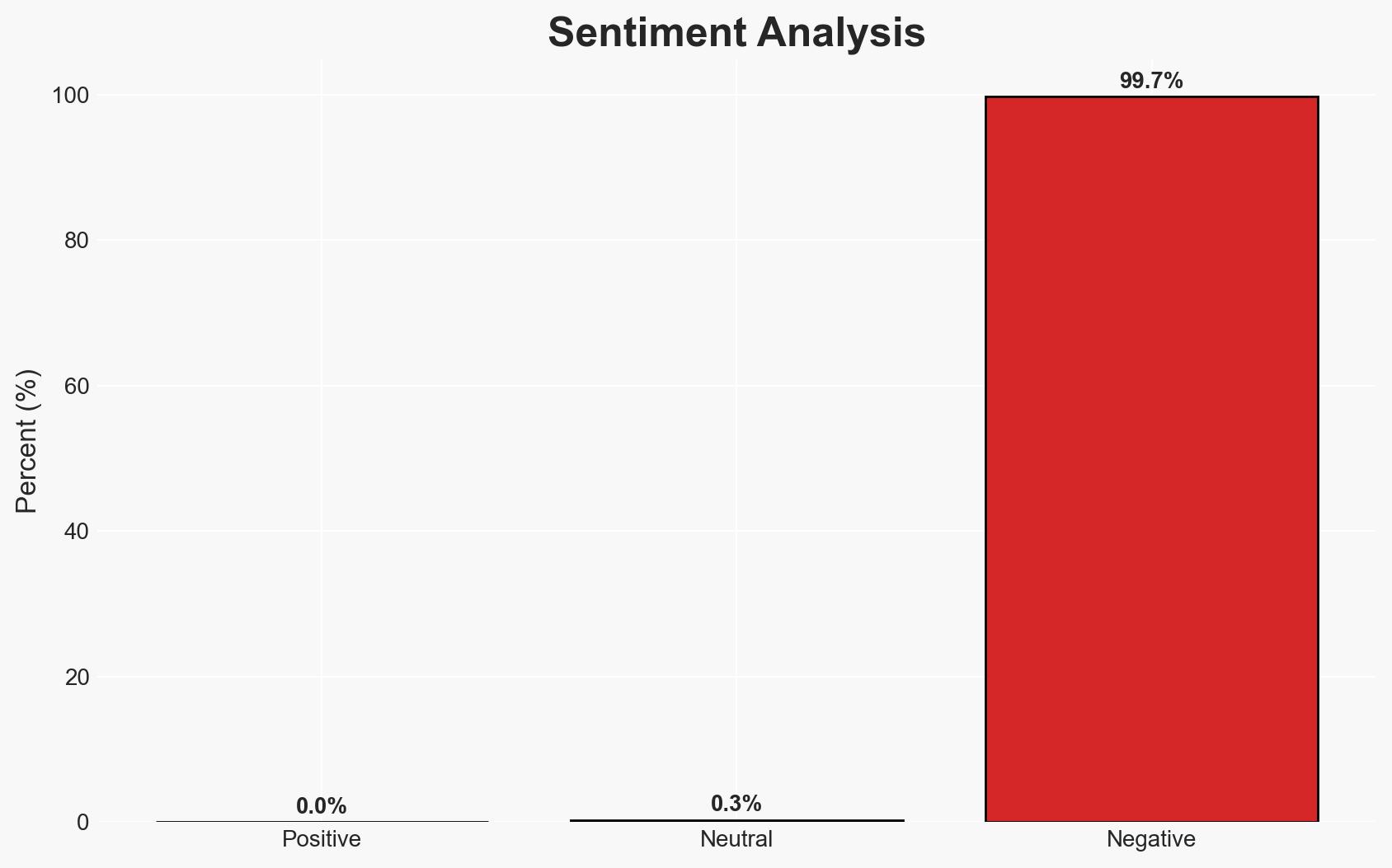
Two former cybersecurity professionals have pleaded guilty to participating in BlackCat ransomware attacks, highlighting a significant insider threat within cybersecurity firms. This development underscores vulnerabilities in cybersecurity defenses and the potential for misuse of technical expertise. The most likely hypothesis is that these individuals acted primarily for financial gain. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The individuals engaged in ransomware activities primarily for financial gain, leveraging their insider knowledge and technical expertise. This is supported by their guilty pleas and the financial transactions involving ransom payments.
- Hypothesis B: The individuals were coerced or manipulated into participating in these activities by external actors, possibly under duress. There is no direct evidence supporting this, and their professional backgrounds suggest a voluntary engagement.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the direct financial incentives and lack of evidence for coercion. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include new evidence of external pressure or manipulation.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The individuals acted independently without coercion; BlackCat’s operational structure allowed for such insider participation; financial gain was the primary motivator.
- Information Gaps: Details on the involvement of the unnamed third accomplice; full extent of the financial transactions and any potential coercion.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in interpreting financial motivations; risk of deception by defendants to minimize sentences or shift blame.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This case could lead to increased scrutiny of cybersecurity professionals and highlight the need for stronger internal controls within cybersecurity firms. The involvement of insiders in cybercrime poses a significant threat to organizational security.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory measures and international cooperation against cybercrime.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of insider threats within critical infrastructure sectors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible increase in cyber defense measures and monitoring of cybersecurity personnel.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact on affected companies and loss of trust in cybersecurity services.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of cybersecurity personnel; conduct internal audits of cybersecurity firms.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for sharing threat intelligence; invest in training and awareness programs for cybersecurity professionals.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Strengthened cybersecurity measures prevent further insider threats.
- Worst: Increased insider threats lead to significant breaches and financial losses.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in internal controls and monitoring reduces insider threat risks.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Ryan Clifford Goldberg, former Sygnia incident response manager
- Kevin Tyler Martin, former DigitalMint ransomware threat negotiator
- BlackCat (ALPHV) ransomware group
- Unnamed third accomplice
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, insider threat, ransomware, cybercrime, financial gain, law enforcement, digital extortion
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us