Rising Tensions: UAE Withdraws Forces from Yemen Amid Saudi Bombing of Alleged Separatist Supplies
Published on: 2025-12-30
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: ‘Teetering on the brink’ Fears of Middle East conflict after Saudi strikes in Yemen
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
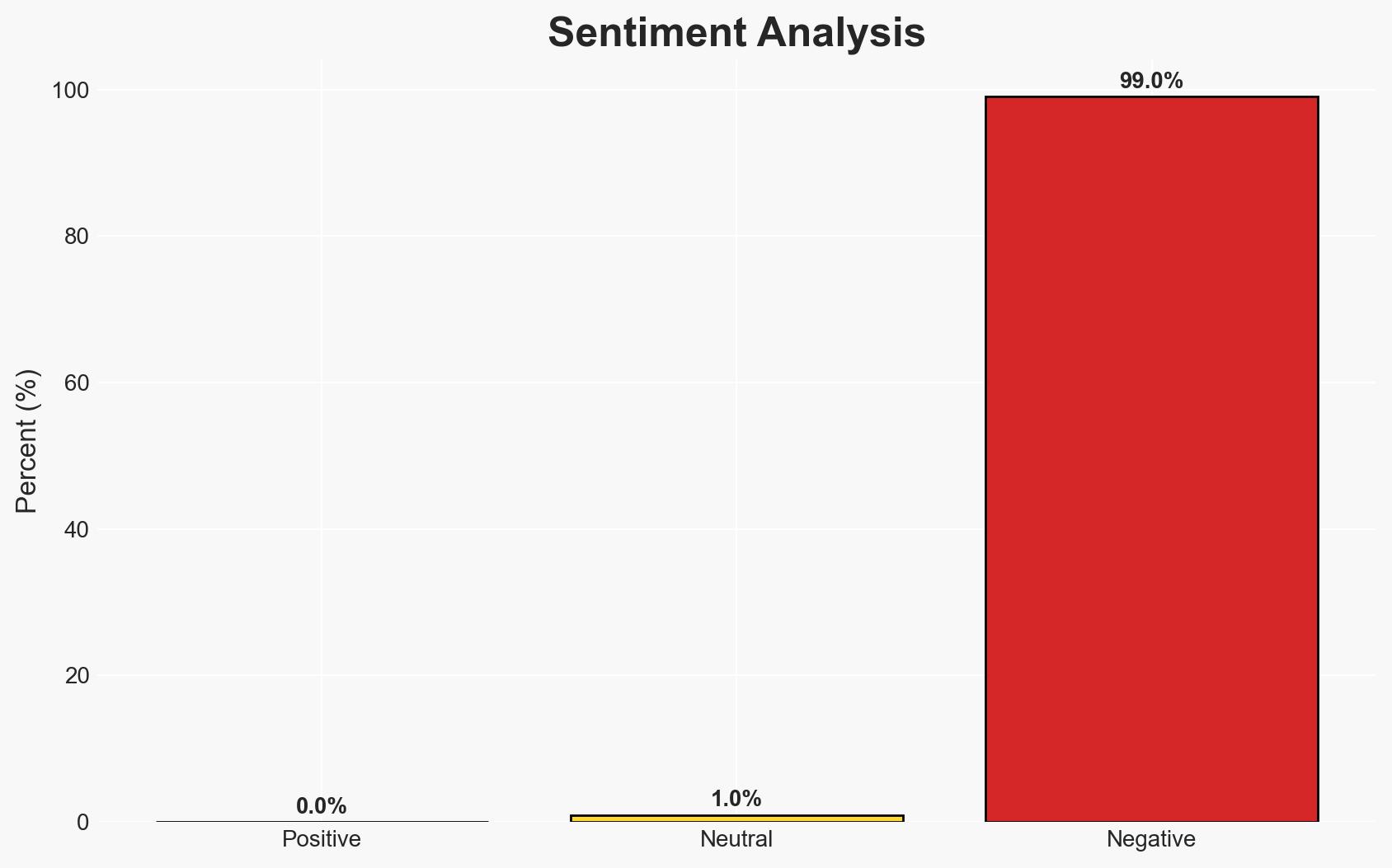
The recent Saudi strikes on alleged UAE-backed separatist shipments in Yemen have escalated tensions between Saudi Arabia and the UAE, raising the risk of broader regional conflict. The situation threatens to destabilize southeastern Yemen, previously a relatively safe area. This assessment is made with moderate confidence, given the complexities of regional alliances and the lack of complete information.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The UAE is deliberately supporting the Southern Transitional Council (STC) to establish an independent southern Yemen, challenging Saudi Arabia’s preference for a unified Yemen. Evidence includes UAE’s military presence and the alleged shipment of weapons. However, uncertainties remain regarding the UAE’s long-term strategic goals.
- Hypothesis B: The UAE’s actions are misinterpreted, and it is not seeking to destabilize the region but rather securing its interests against Houthi threats. The UAE’s withdrawal of personnel suggests a de-escalation intent, but this is contradicted by the alleged support to the STC.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the UAE’s historical support for the STC and the recent military activities. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include further diplomatic engagements or military withdrawals by the UAE.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions:
- The UAE intends to maintain influence in southern Yemen.
- Saudi Arabia is committed to a unified Yemen.
- The STC seeks independence with UAE backing.
- Saudi military actions are primarily defensive.
- Information Gaps: The full extent of UAE’s strategic objectives in Yemen and the internal dynamics of the STC.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in Saudi-released intelligence and UAE’s public statements; risk of both parties engaging in information manipulation to justify actions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased regional instability, affecting global energy markets and security dynamics in the Middle East.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for diplomatic fallout between Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) members, affecting regional alliances.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of terrorist exploitation of instability in Yemen, potentially affecting global counter-terrorism efforts.
- Cyber / Information Space: Likely increase in cyber operations and propaganda campaigns by involved states to sway international opinion.
- Economic / Social: Disruption in Yemen could impact Red Sea shipping routes, affecting global trade and oil prices.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase intelligence collection on UAE-STC interactions; engage in diplomatic dialogue to de-escalate tensions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen regional partnerships and support UN-led peace initiatives in Yemen; enhance monitoring of Gulf maritime routes.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Diplomatic resolution leads to stabilization in Yemen.
- Worst: Open conflict between Saudi Arabia and UAE destabilizes the region.
- Most-Likely: Continued proxy conflict in Yemen with intermittent diplomatic tensions.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Saudi Arabia
- United Arab Emirates
- Southern Transitional Council (STC)
- Major General Turki Al-Malki
- Elisabeth Kendall
7. Thematic Tags
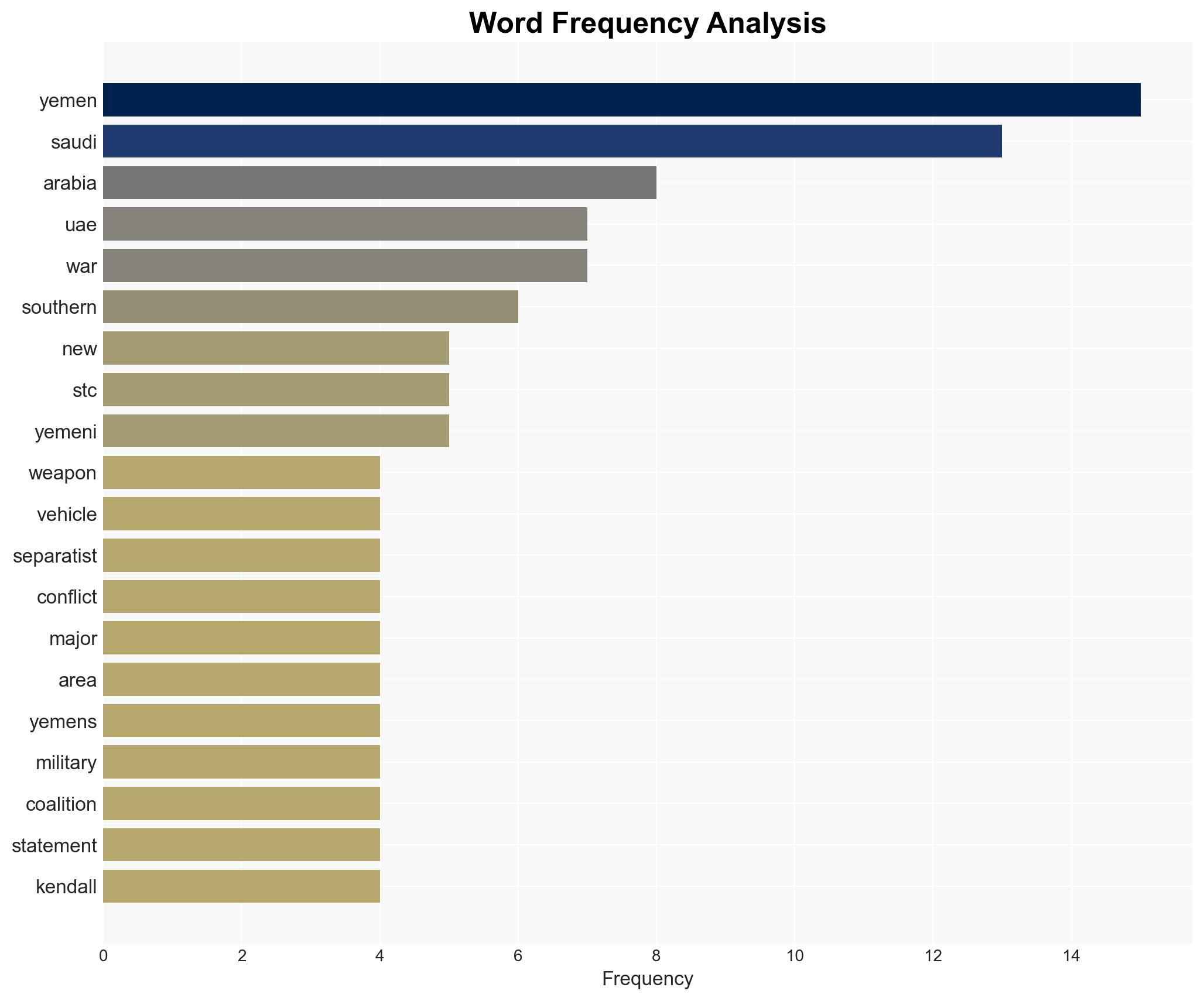
regional conflicts, Middle East conflict, regional stability, Yemen civil war, Saudi-UAE relations, separatist movements, Gulf geopolitics, military escalation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us