The Rising Costs of Neglecting AI-Driven Cyber Threats Ahead of 2026
Published on: 2025-12-31
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: The Cost of Ignoring AI-Based Threats Going Into 2026
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
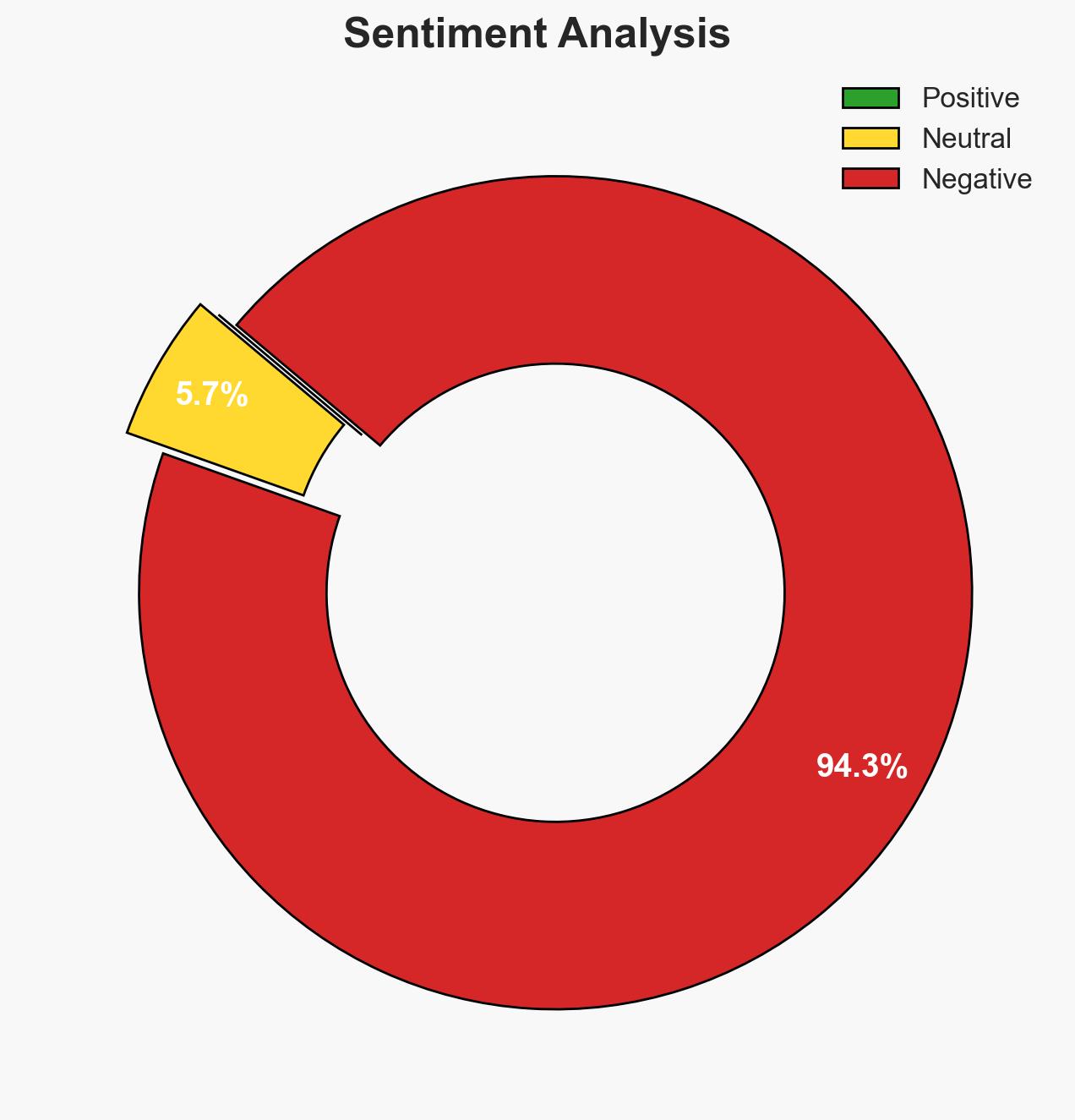
The increasing sophistication of AI-driven cyber threats poses a significant risk to businesses, with outdated security models proving inadequate. The most likely hypothesis is that AI will continue to enhance cybercriminal capabilities, leading to severe financial, operational, and reputational impacts for unprepared organizations. This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to existing evidence of AI’s transformative role in cybercrime.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: AI will significantly enhance cybercriminal capabilities, leading to more frequent and damaging cyberattacks. This is supported by the current trend of AI being used to craft sophisticated phishing attacks and deepfakes, and the development of automated hacking tools. However, the extent of AI’s impact on future cybercrime remains uncertain due to potential advancements in defensive technologies.
- Hypothesis B: The impact of AI on cybercrime will be mitigated by advancements in cybersecurity defenses and increased collaboration with managed IT services. While partnerships with IT services are becoming critical, there is less evidence to suggest that defensive measures will outpace the rapid evolution of AI-driven threats.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the observed increase in AI-driven cyber threats and the inadequacy of traditional defenses. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include significant breakthroughs in AI-based defensive technologies or regulatory changes enhancing cybersecurity standards.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI technology will continue to advance rapidly; cybercriminals will have access to sophisticated AI tools; businesses will remain slow to adopt new security measures.
- Information Gaps: Specific data on the rate of AI adoption among cybercriminals and the effectiveness of AI-driven defenses is lacking.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in underestimating the capability of defensive measures; risk of deception from sources overstating AI threat levels for commercial gain.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of AI-driven cyber threats could lead to increased regulatory scrutiny and demand for cybersecurity innovations. This development may exacerbate geopolitical tensions as states respond to cyber threats with varying levels of capability and intent.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased international cooperation or conflict over cybersecurity norms and AI regulation.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat environment with AI tools potentially being used by state and non-state actors for espionage or sabotage.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased complexity in defending against AI-driven misinformation and cyberattacks.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic destabilization from successful cyberattacks; erosion of public trust in digital systems.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive review of current cybersecurity measures; engage with managed IT services to assess AI threat readiness.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Invest in AI-based defensive technologies; foster partnerships for information sharing on AI threats.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Rapid development of AI defenses reduces threat impact. Worst: AI-driven attacks cause widespread disruption. Most-Likely: Continued evolution of AI threats with incremental improvements in defenses.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
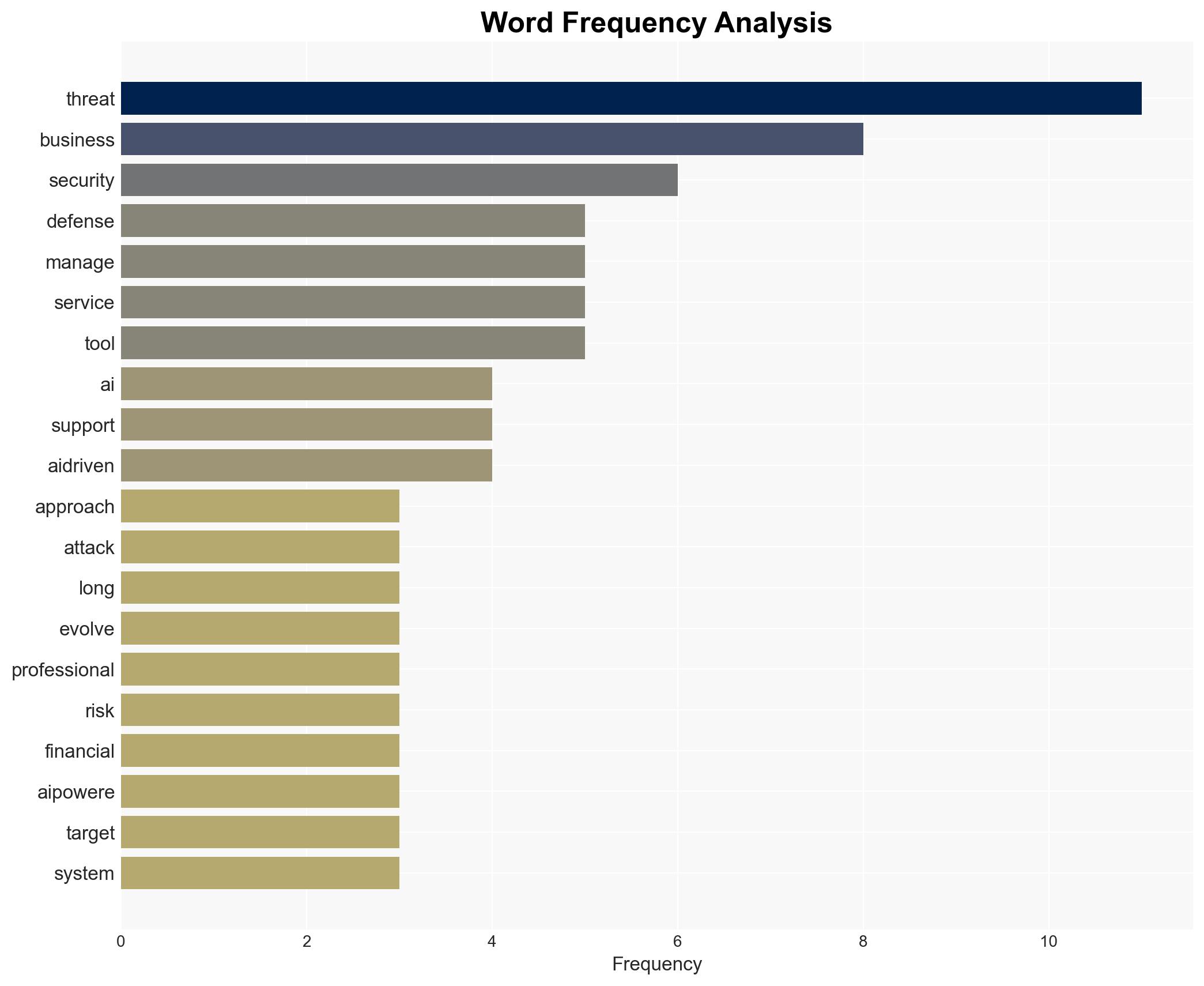
cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, cybercrime, managed IT services, deepfake technology, phishing, ransomware
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us